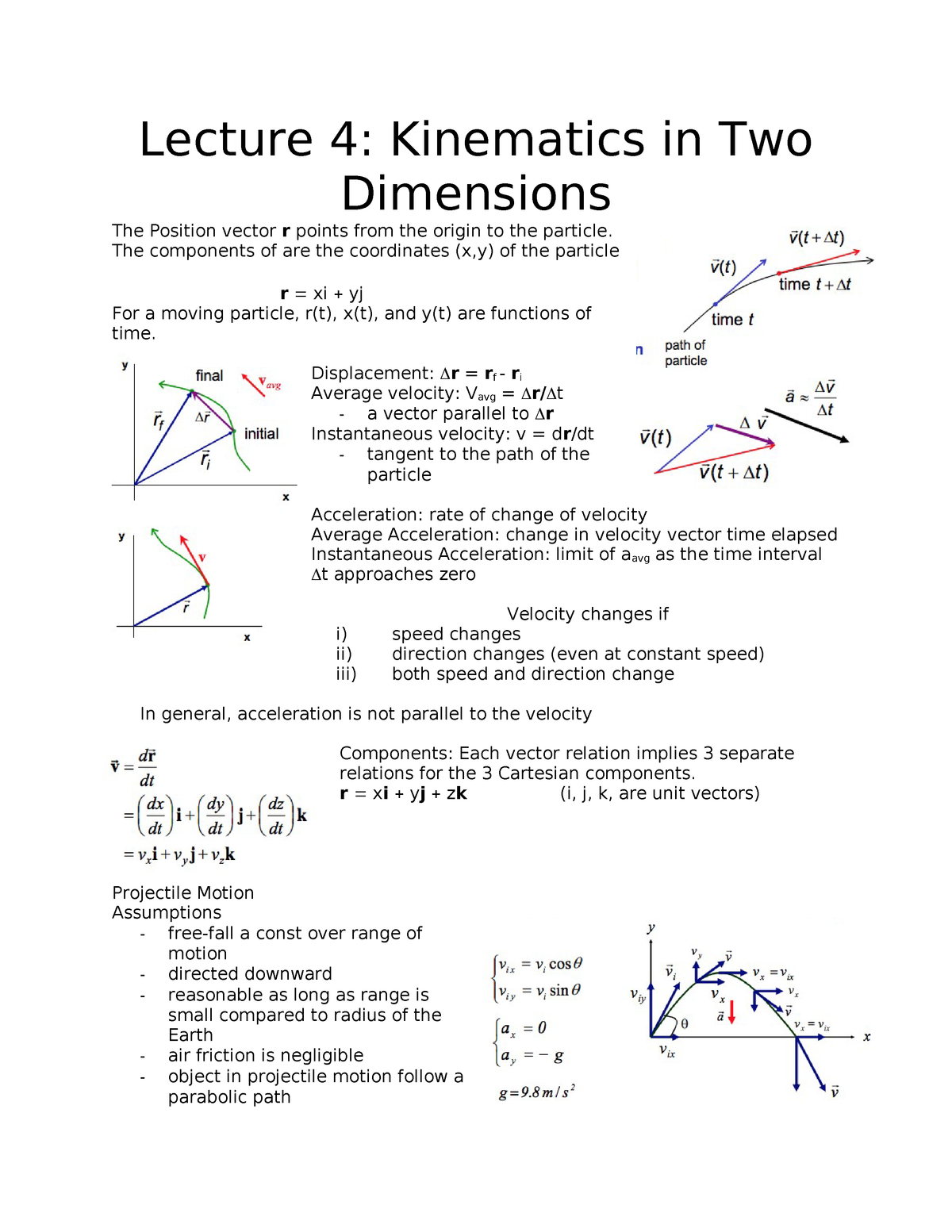
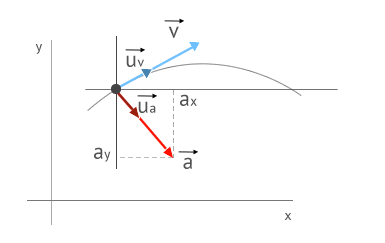
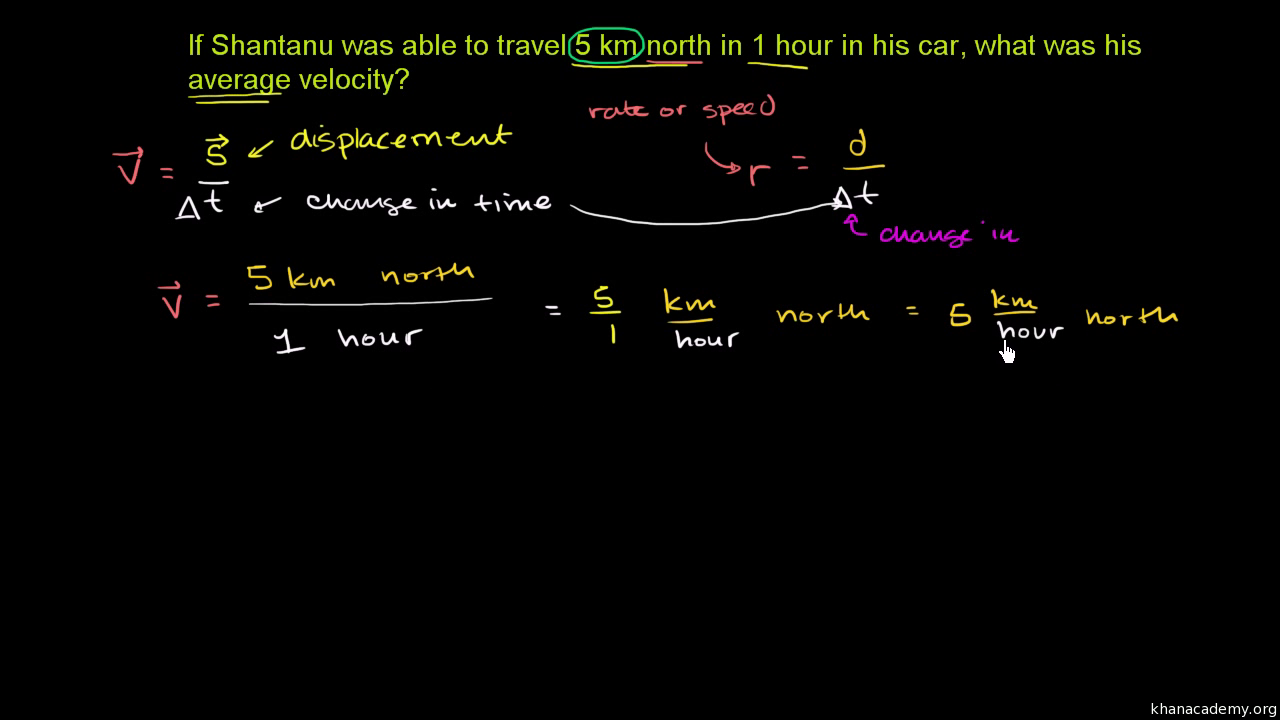
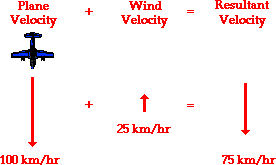
Average Velocity Vector
For our example the bikes initial velocity v i is 5 ms.

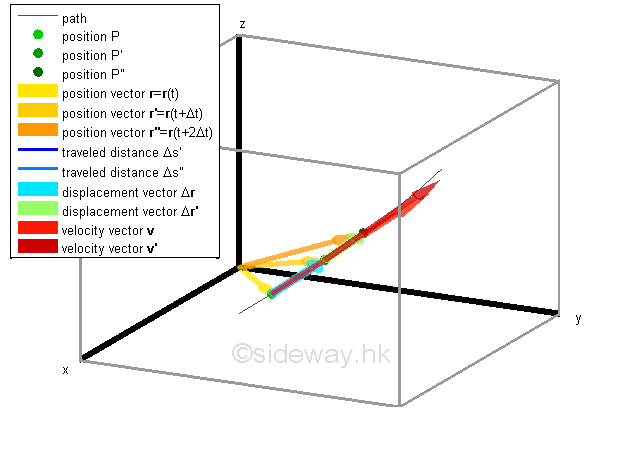
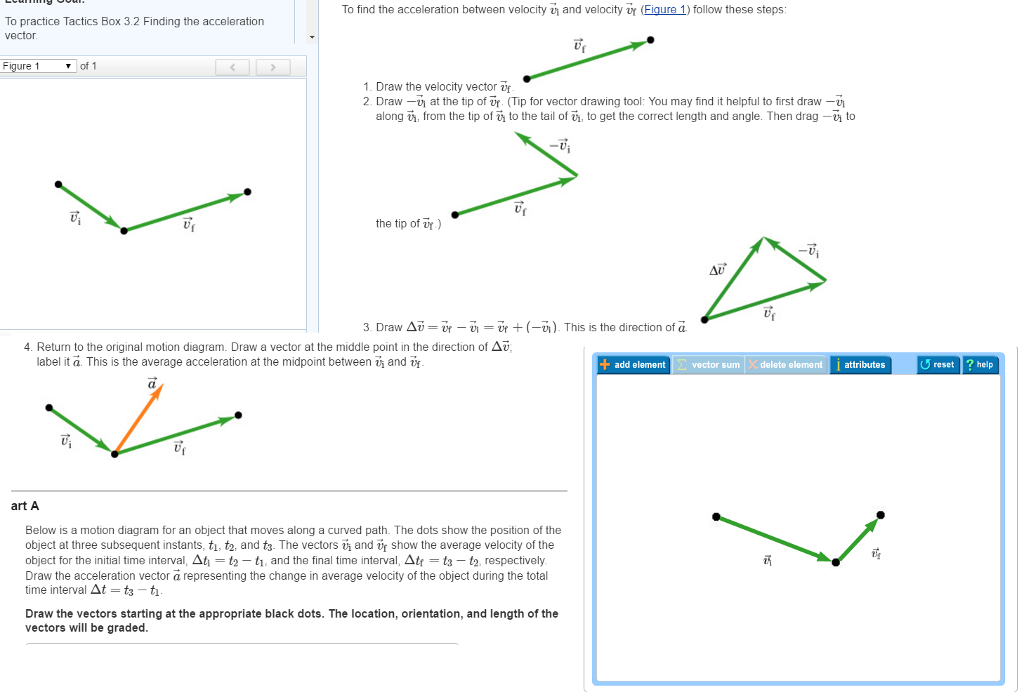
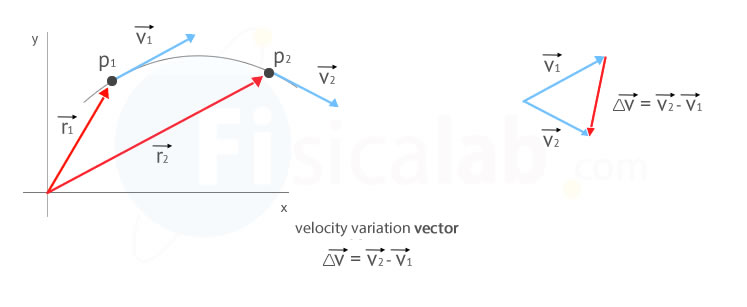
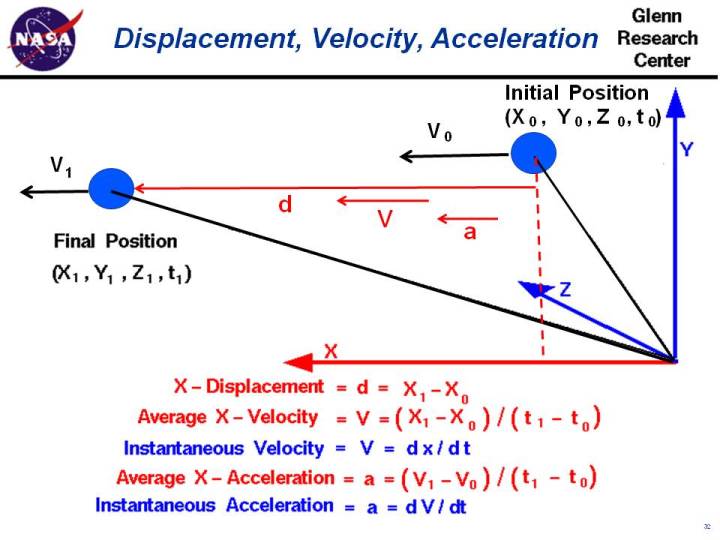
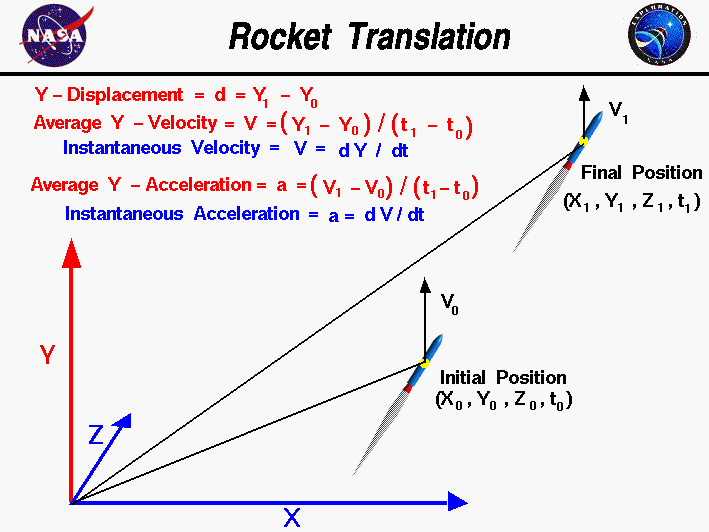
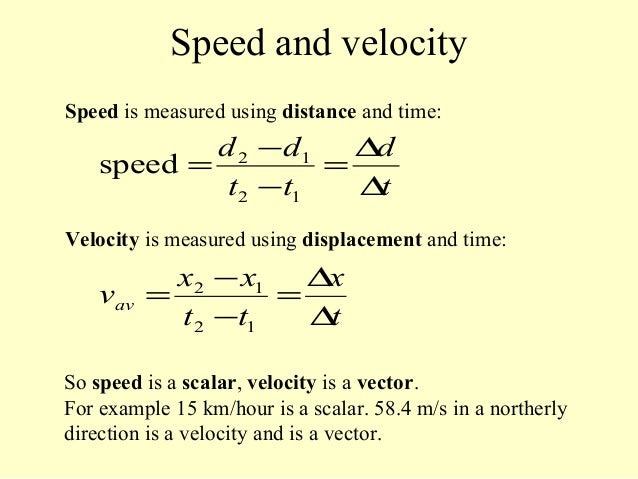
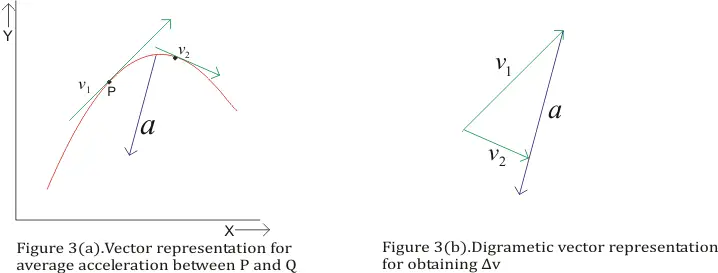
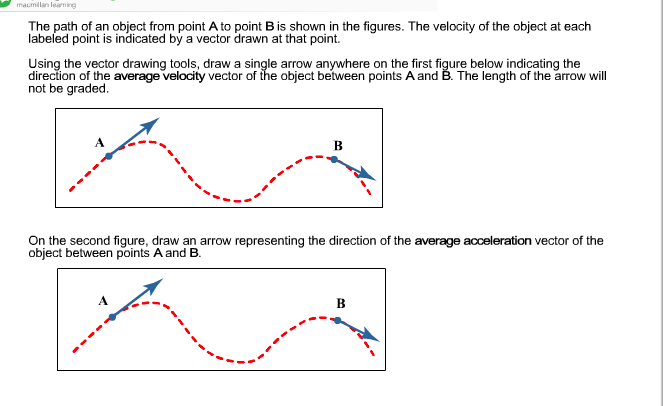
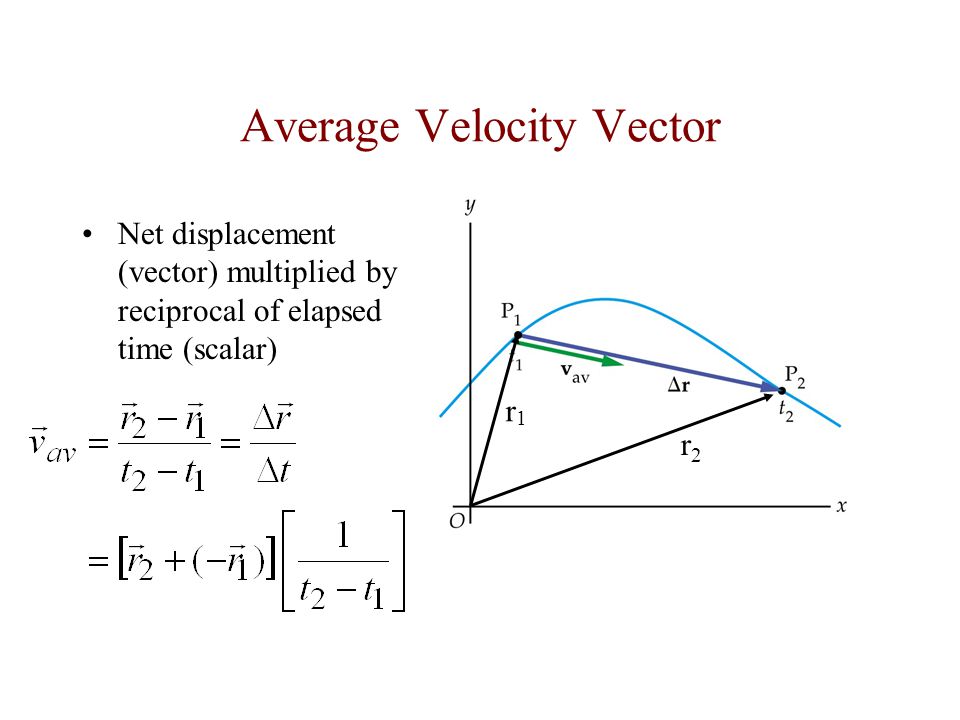
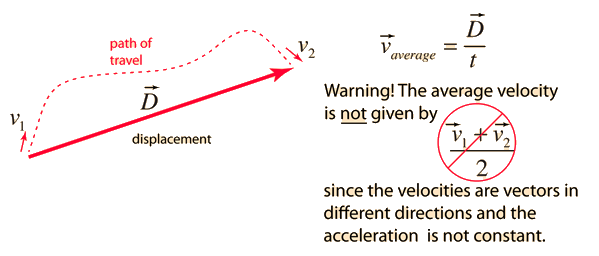
Average velocity vector. Velocity is a vector that indicates the rate at which an object changes its position in other words speed is just a number eg. Velocity is a vectorquantity and average velocity can be defined as the displacementdivided by the time. It has a direction and an associated value. If and only if the acceleration is constant the average velocity is the same as the average of the final velocity and the initial velocity.
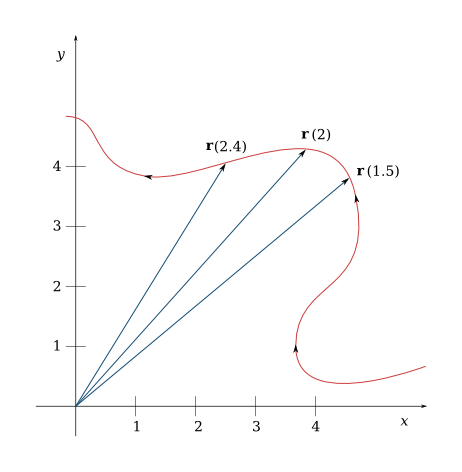
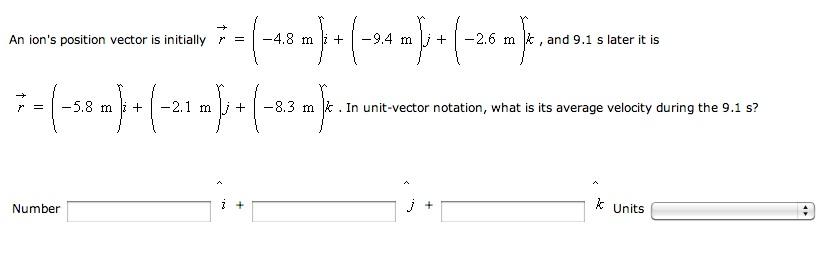
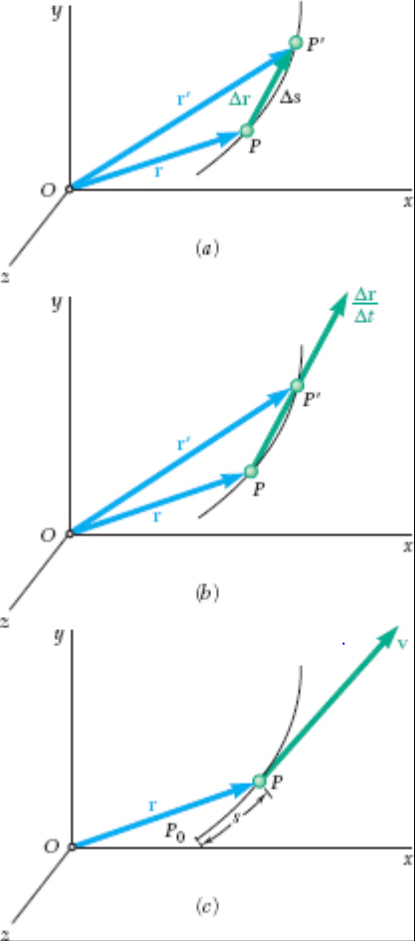
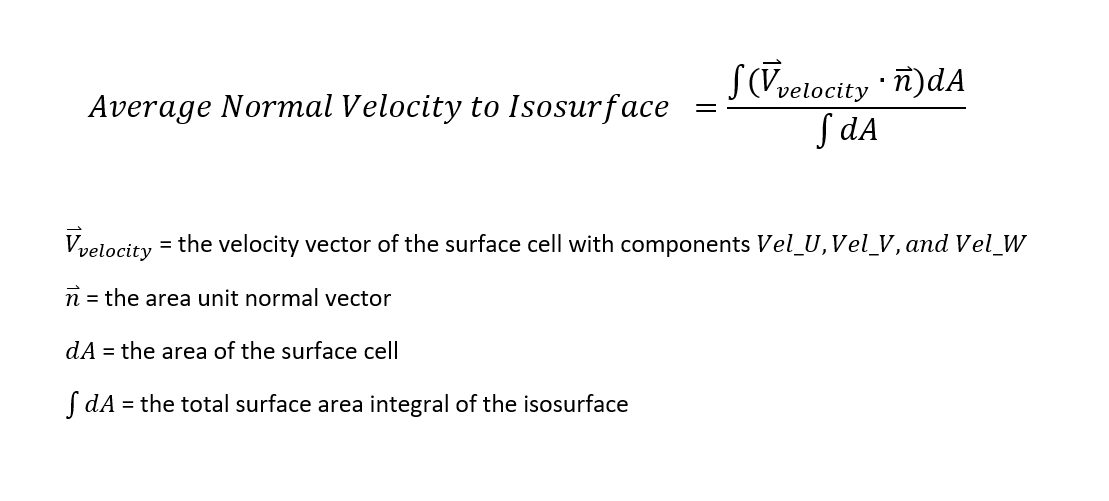
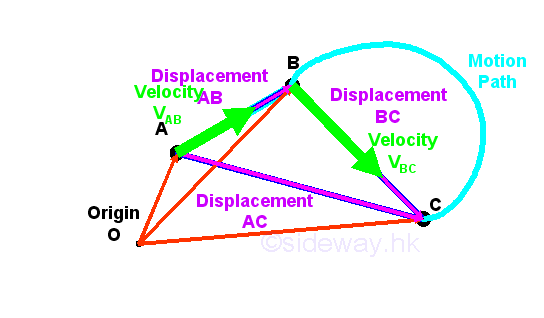
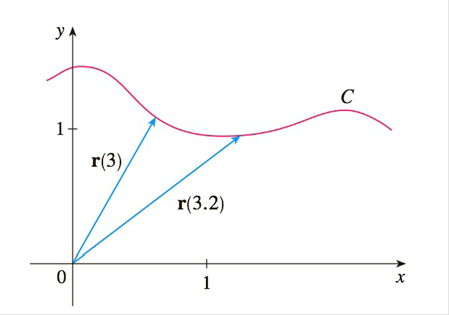
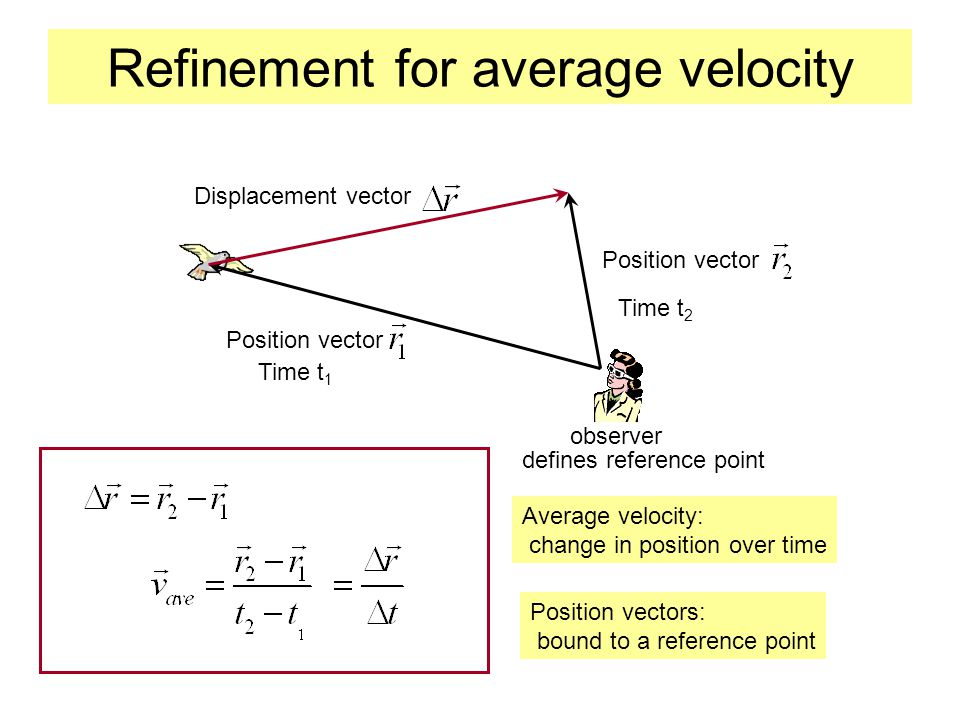
Calculate the velocity vector given the position vector as a function of time. So if a particle covers a certain displacement overrightarrowab in a time t1 to t2 then the average velocity of the particle is. The length of the resultant is called it magnitude the angle that the resultant makes with the original x axis is called its direction. The unitsfor velocity can be implied from the definition to be meterssecond or in general any distance unit over any time unit.
In other words it is the rate at which an object changes its position from one place to another. The average velocity is the same as the velocity averaged over time that is to say its time weighted average which may be calculated as the time integral of the velocity. Average velocity is defined as displacement divided by the time during which that displacement occurred. Si per modesymbol 3 meterpersecond 3 ms while velocity is a vector ie.
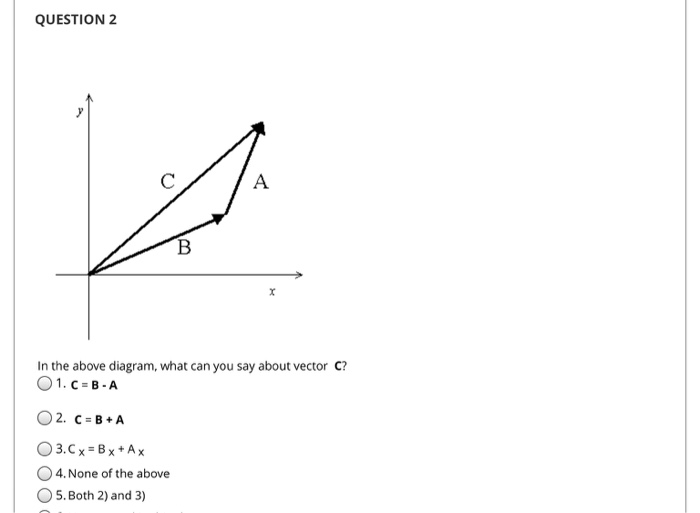
It begins at the origin of the original co ordinate both ends and points towards the head of the last vector being added. Average velocity is a vector quantity. However any distance unit per any time unit can be used when necessary such as miles per hour mph or kilometer per hour kmph. Calculate the average velocity in multiple dimensions.
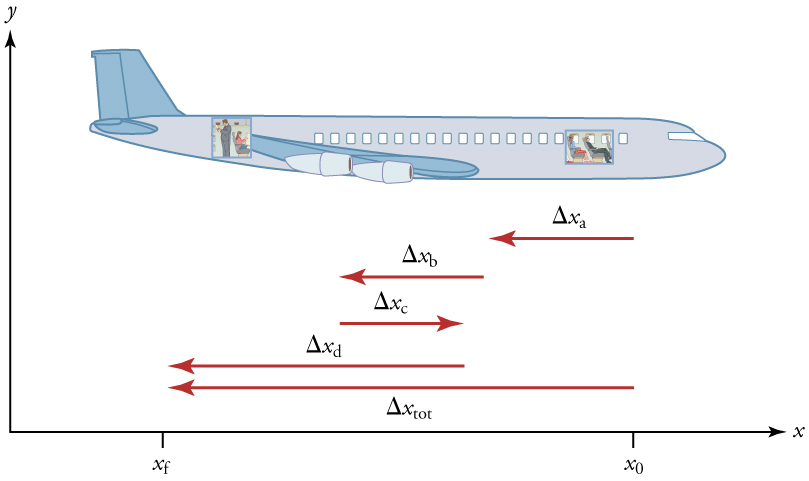
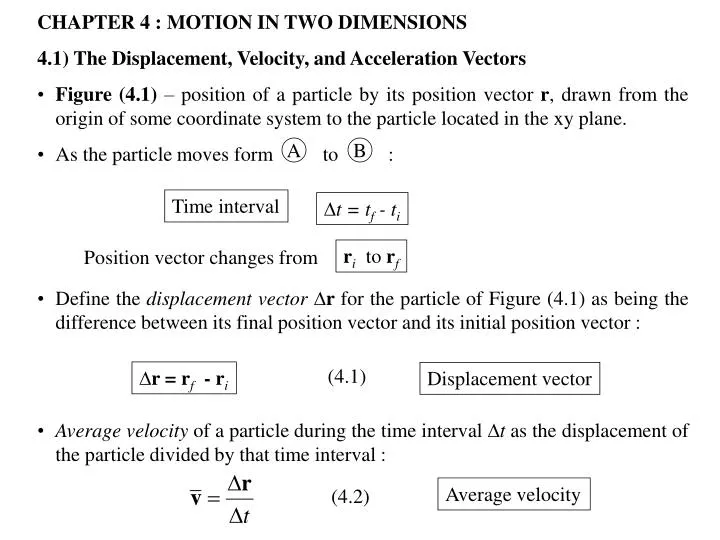
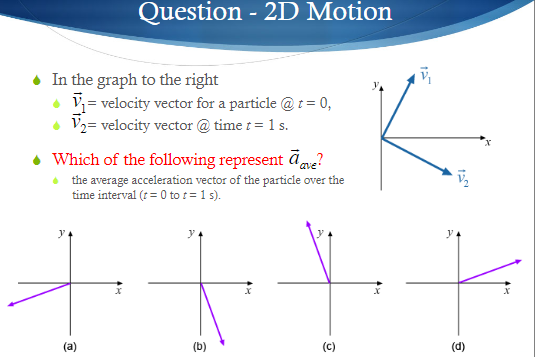
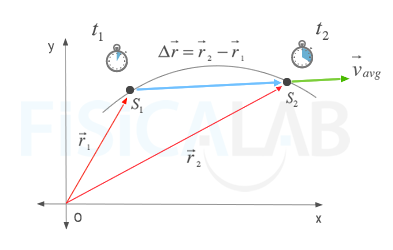
The average velocity of an object is its total displacement divided by the total time taken. Displacement and velocity in two or three dimensions are straightforward extensions of the one dimensional definitions. What does average velocity mean. V 1 t 1 t 0 t 0 t 1 v t d t displaystyle boldsymbol bar v1 over t1 t0int t0t1boldsymbol vt dt.
For the special case of straight line motion in the x direction the average velocity takes the form. The average velocity of a body in a certain time interval is given as the displacement of the body in that time interval divided by time. The si unit is meters per second. The green vector represents the sum of the two vectors or the resultant.
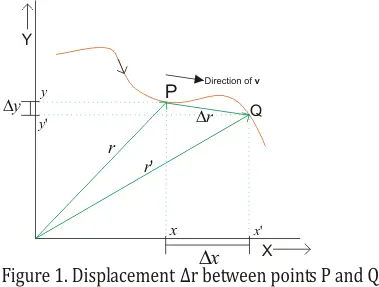
In other words displacement is a straight line distance in the direction from start to finish. Displacement is a vector an arrow from start to finish.