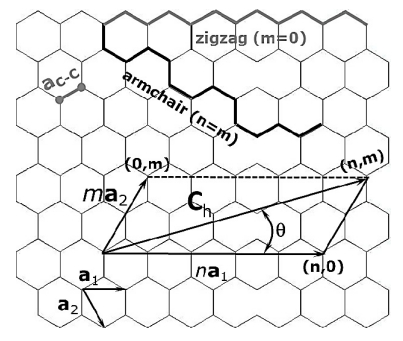
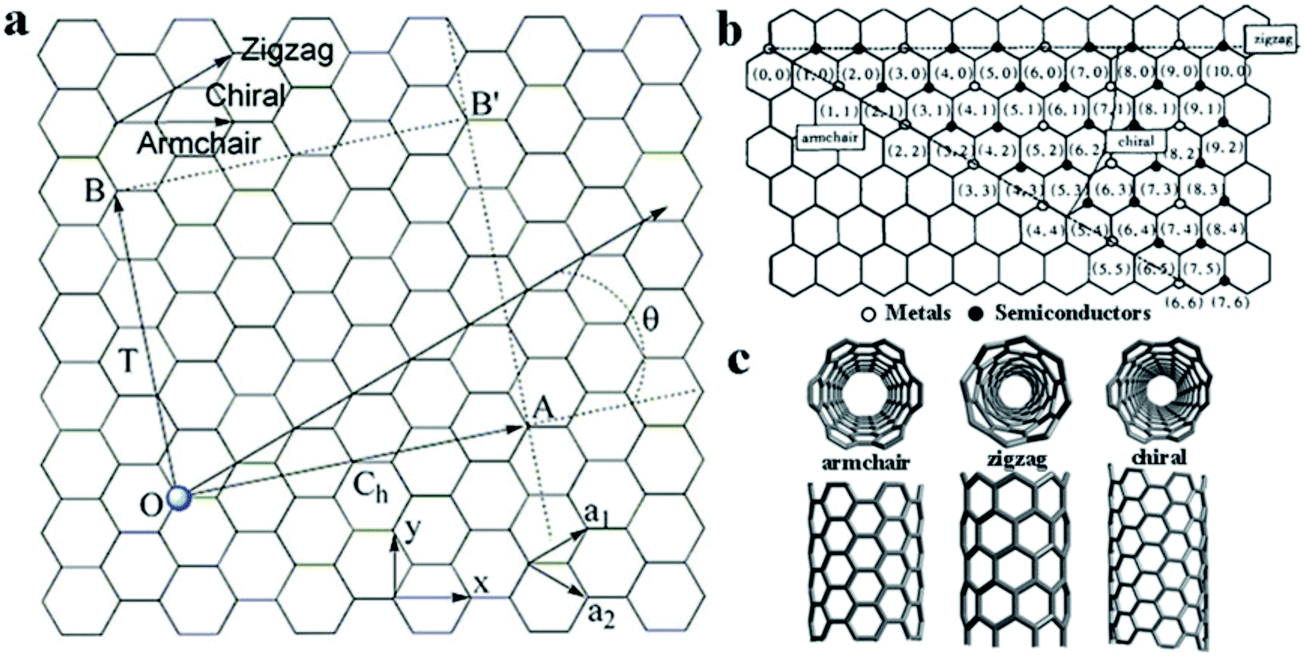
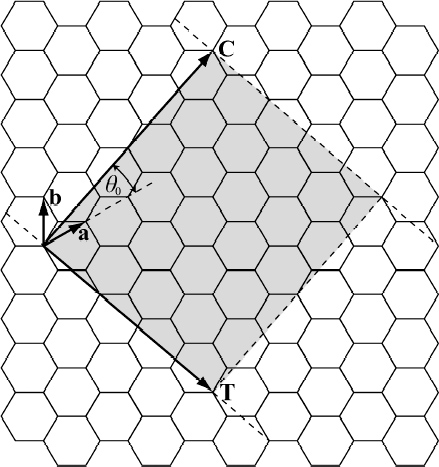
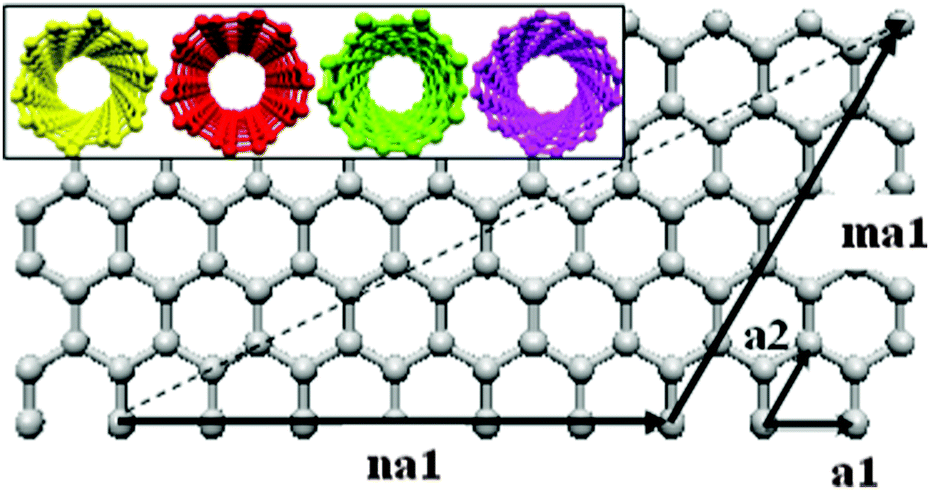
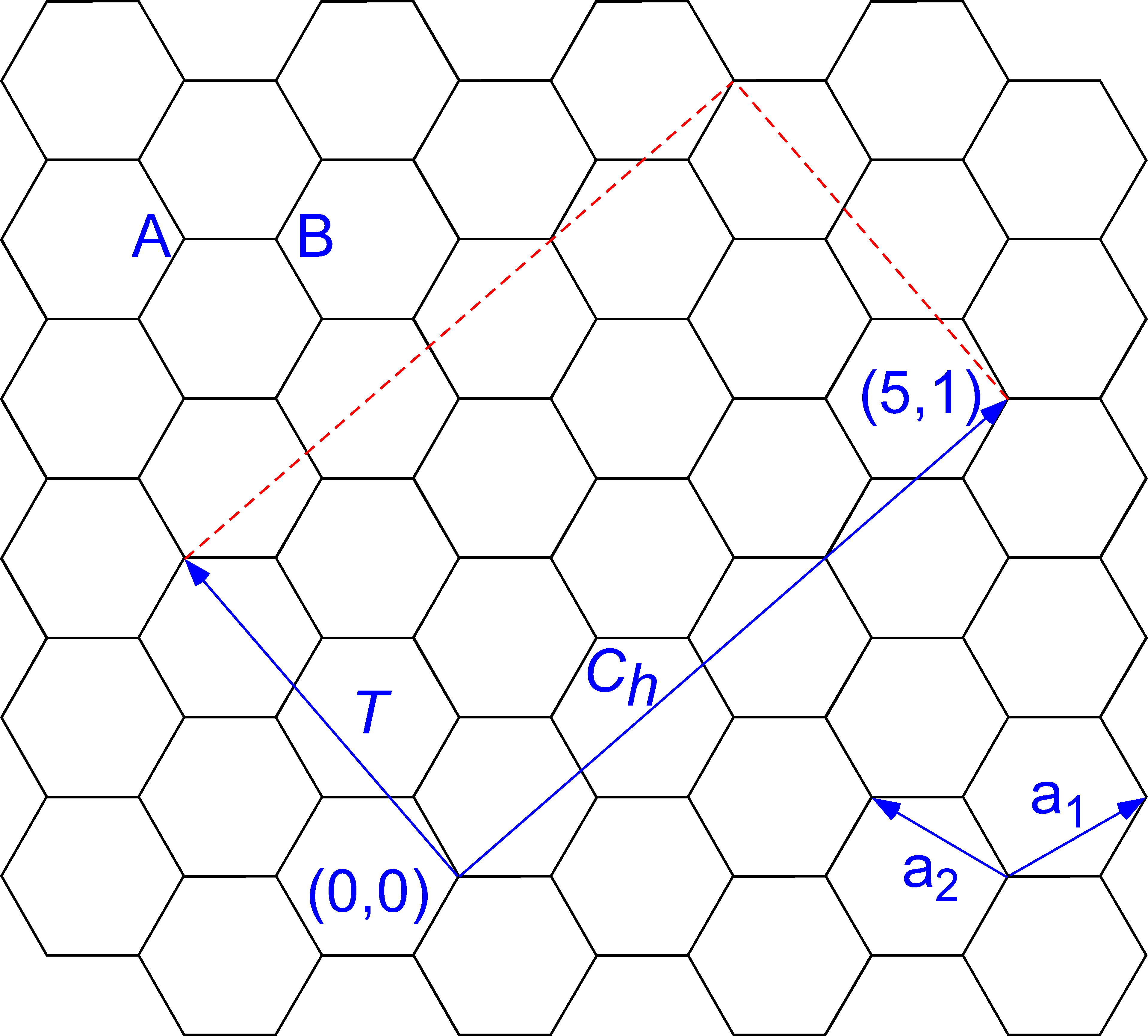
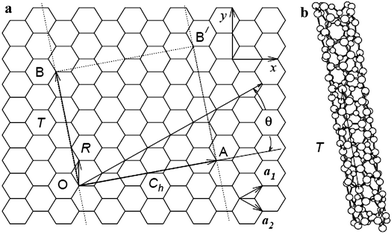
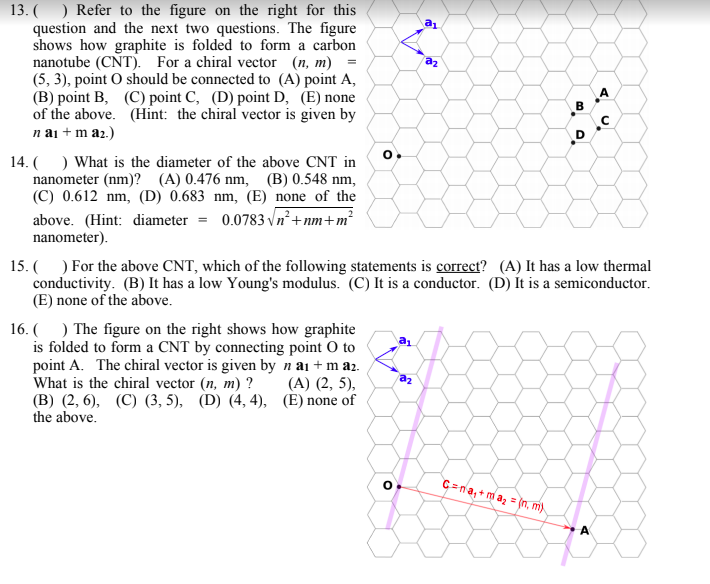
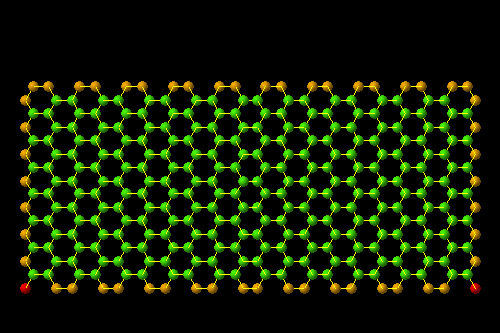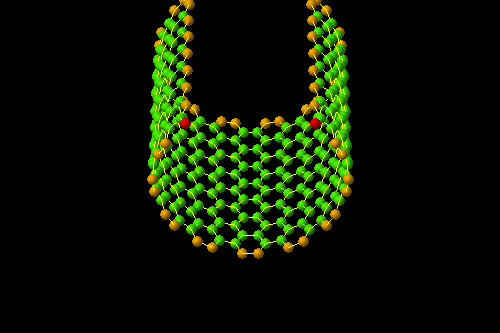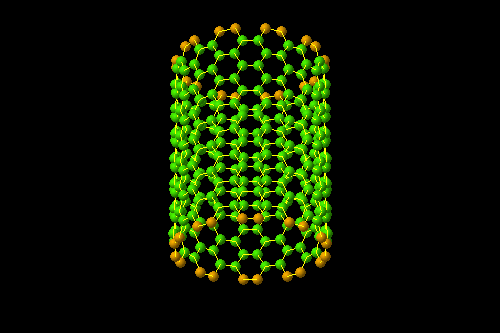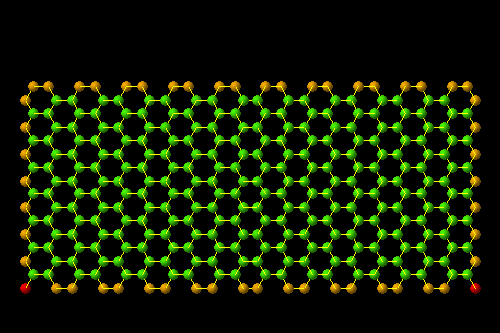
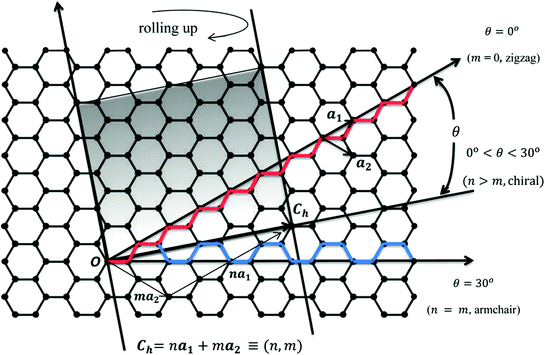
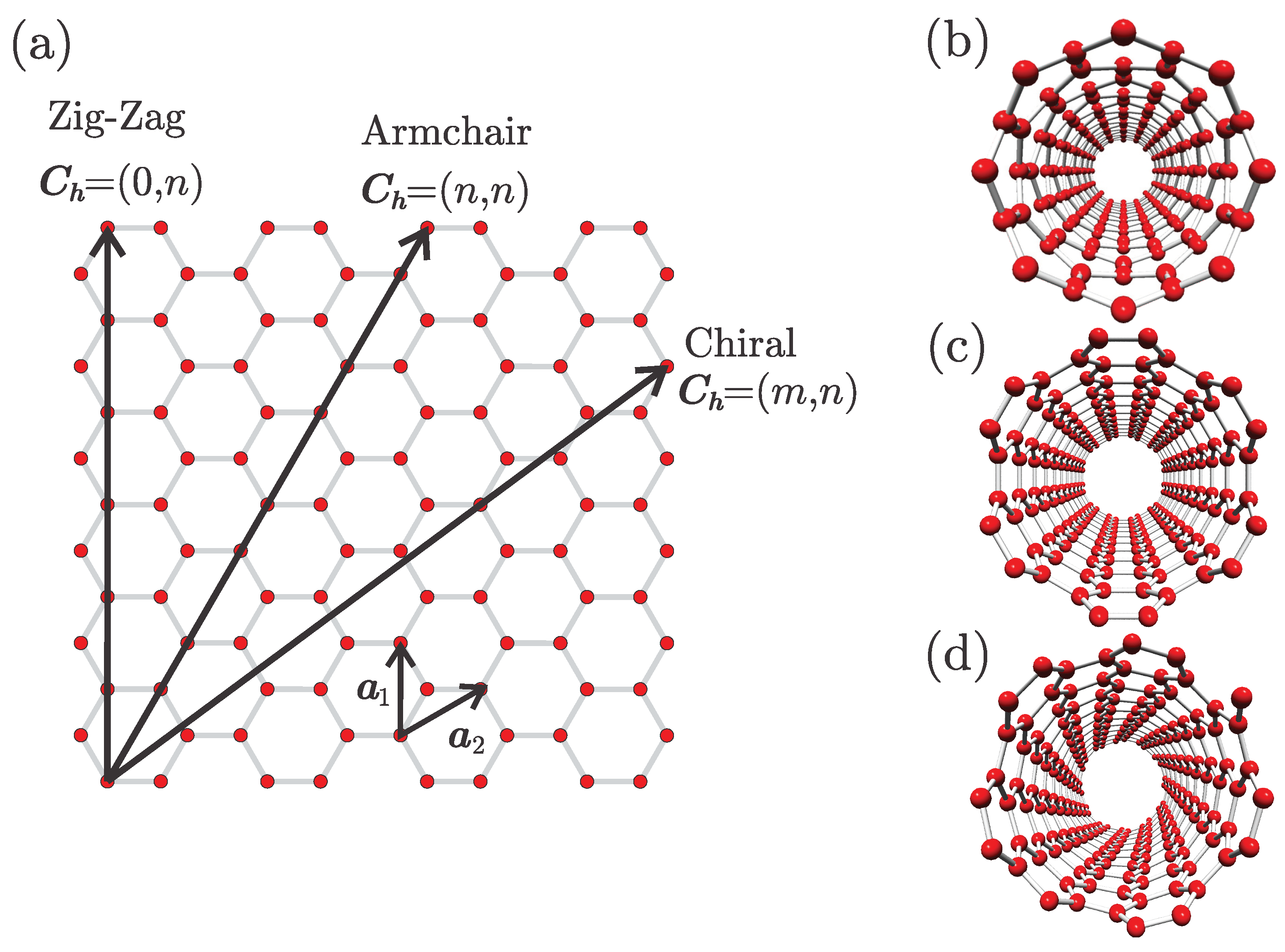
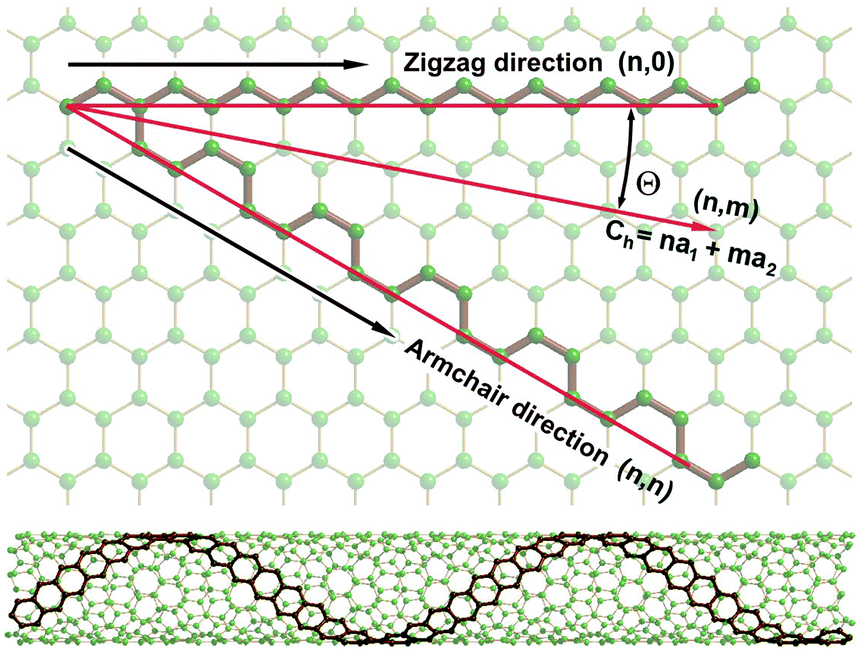
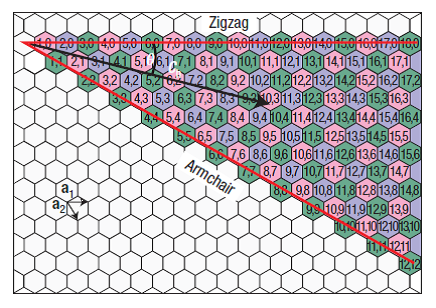
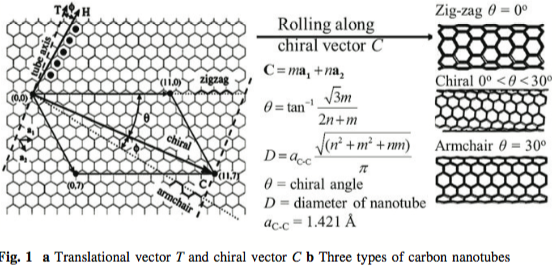
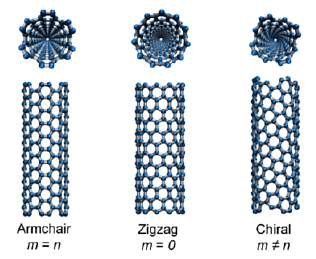
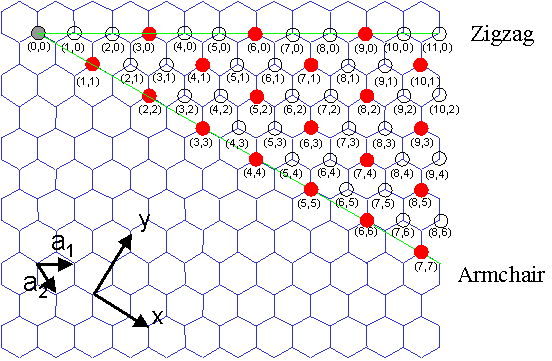
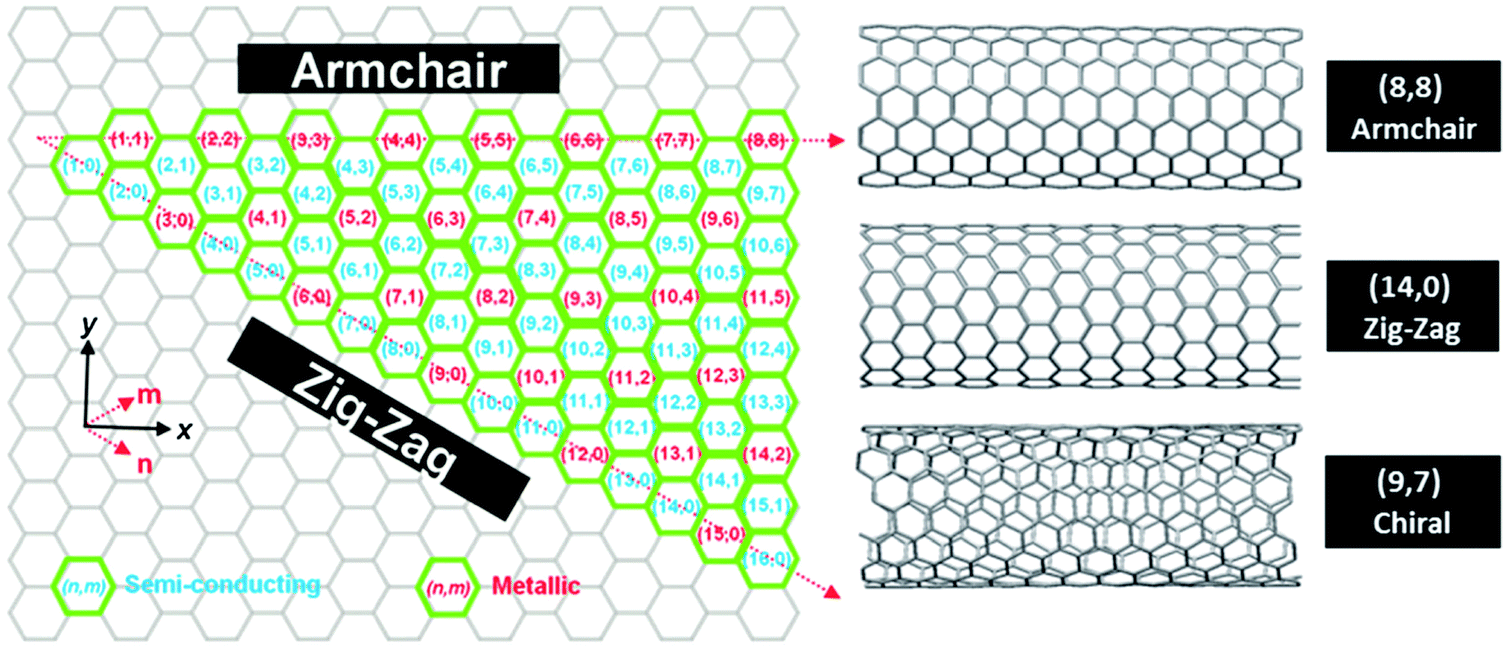
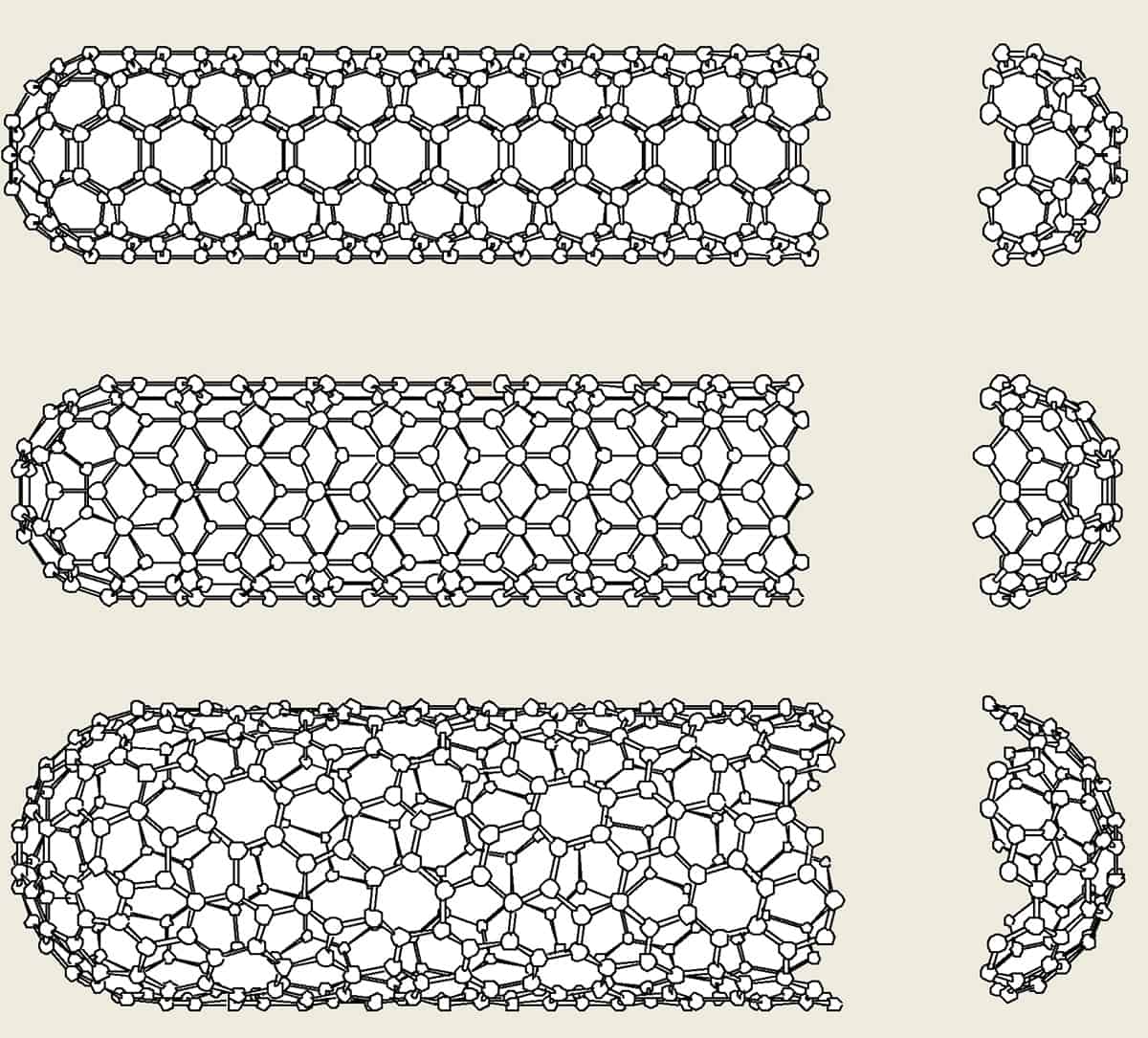
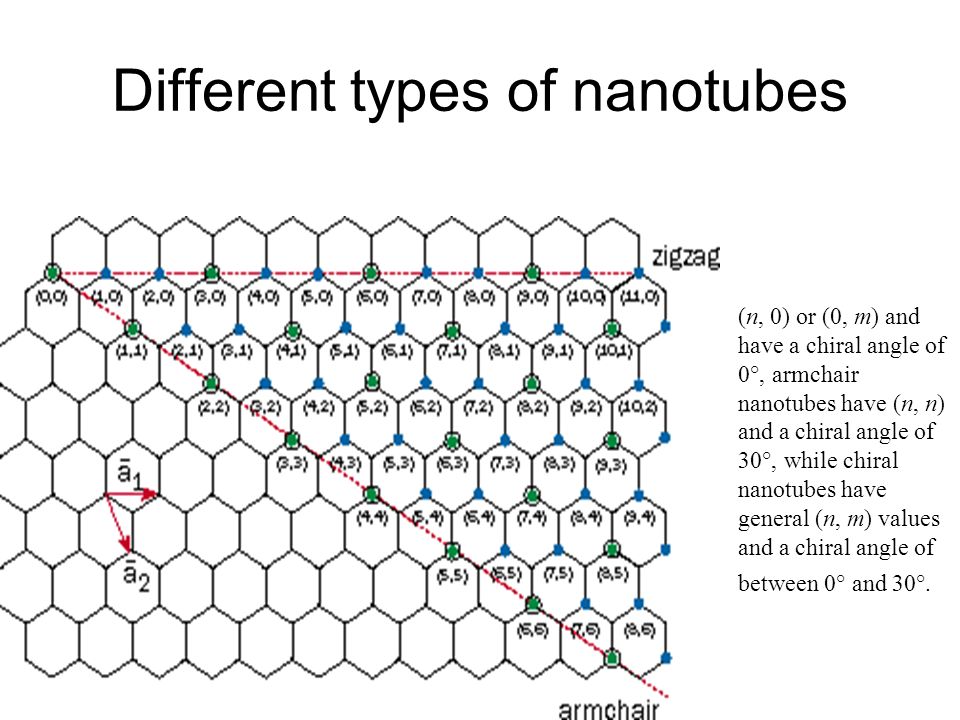
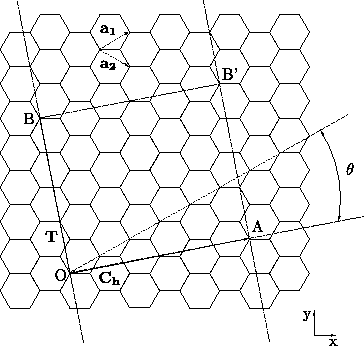
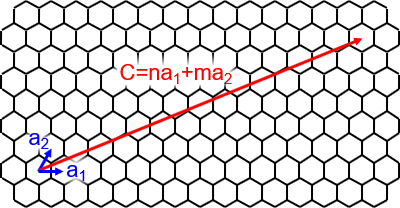Chiral Vector Of Carbon Nanotubes
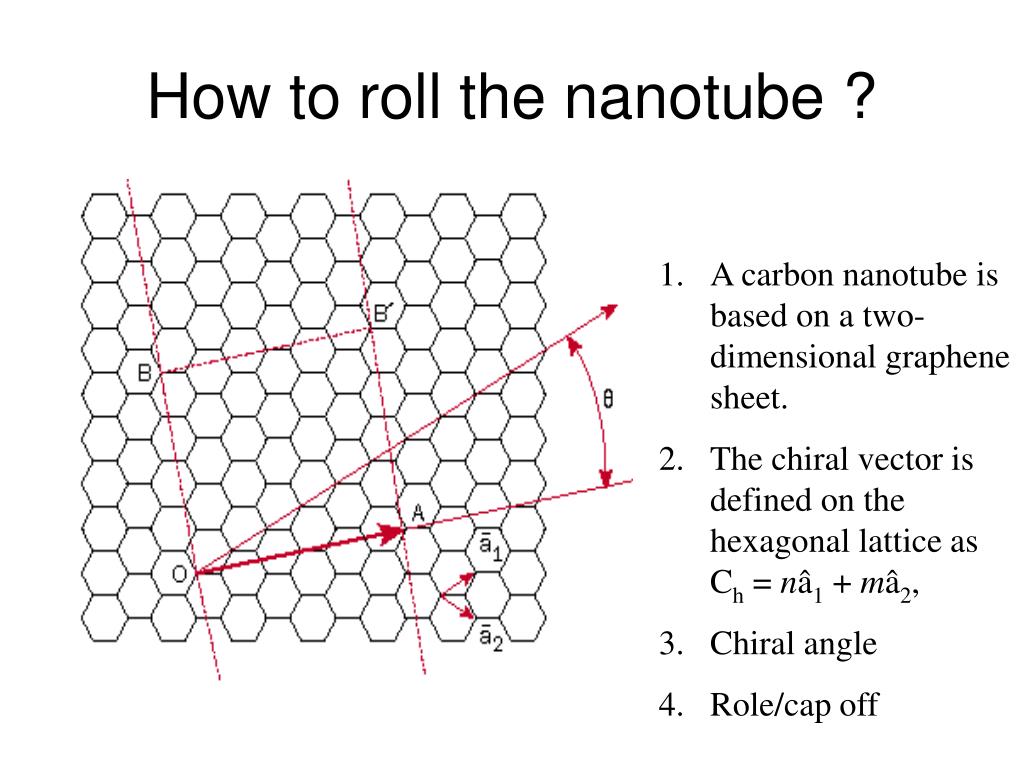
Thus the tuple nm uniquely defines the structure of a particular tube.

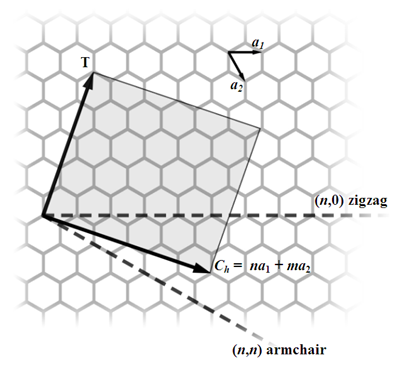
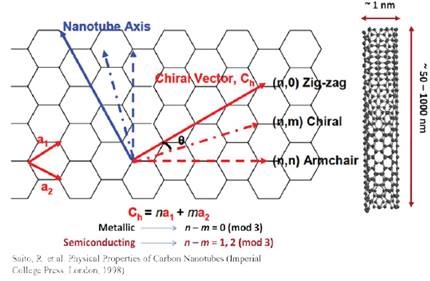
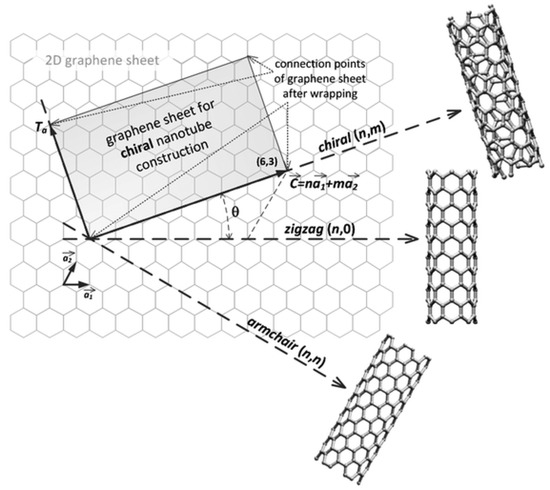
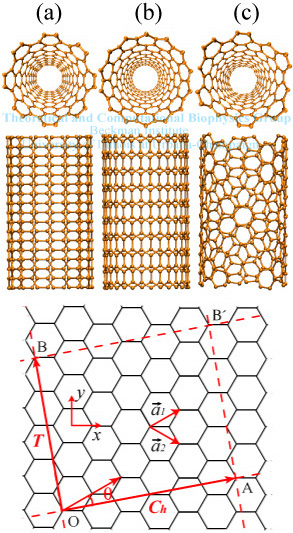
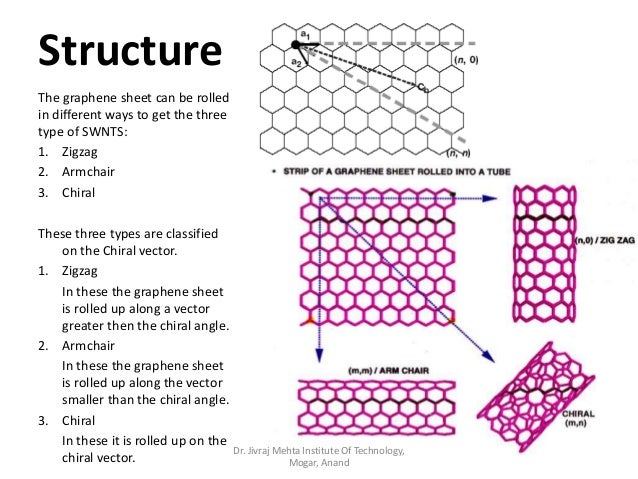
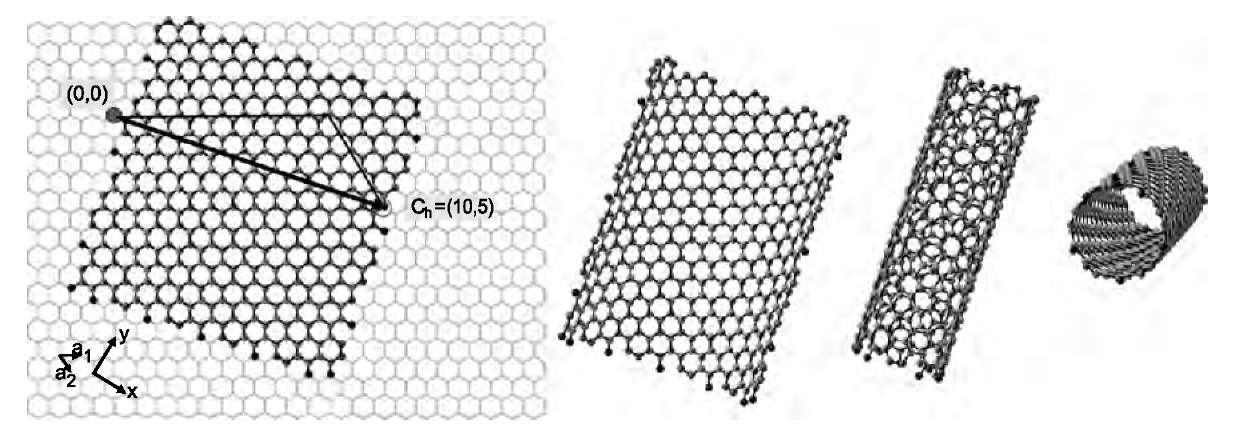
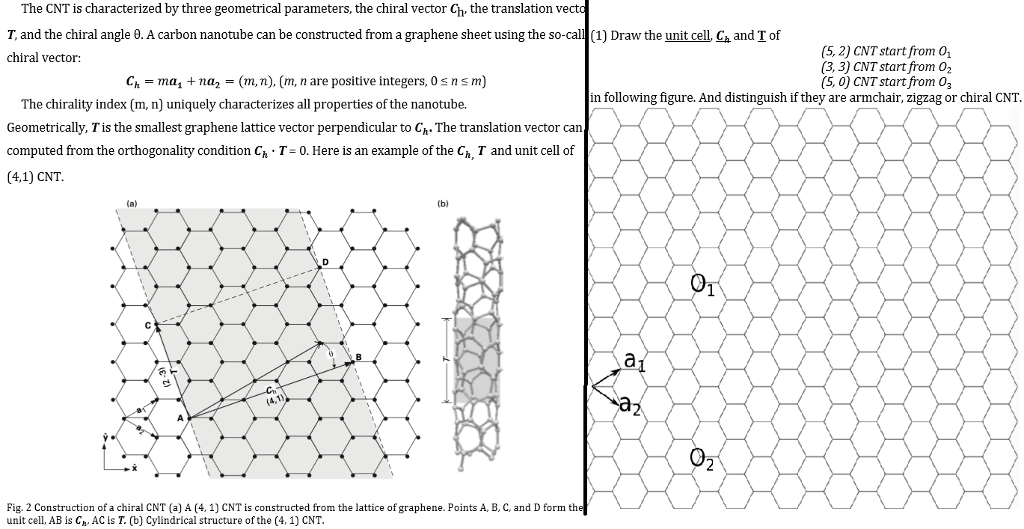
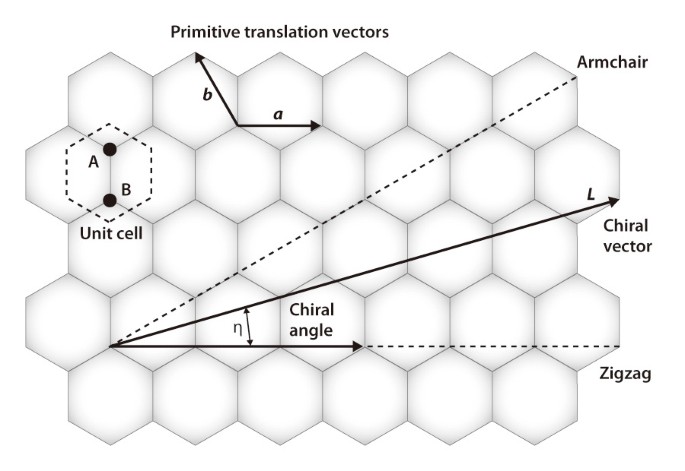
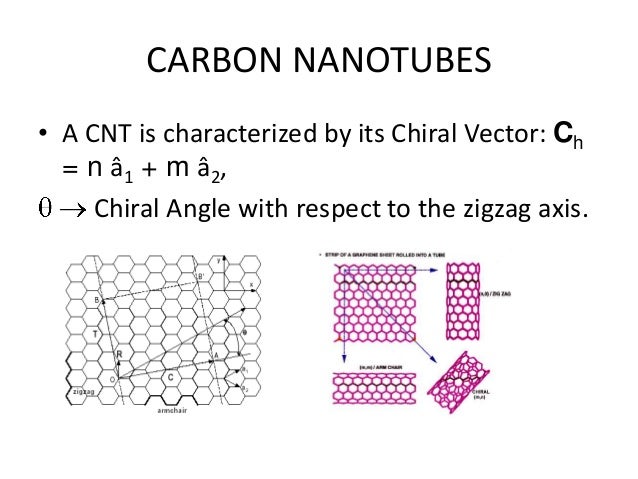
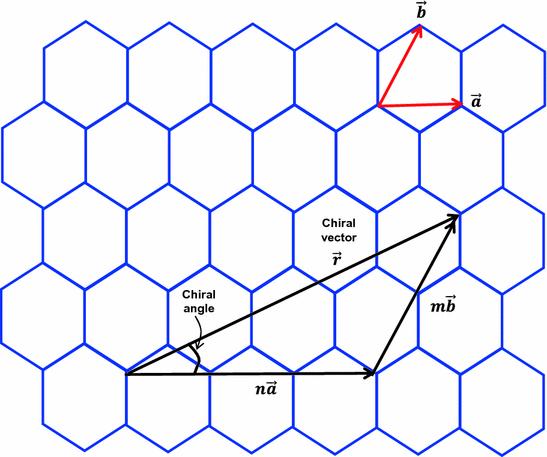
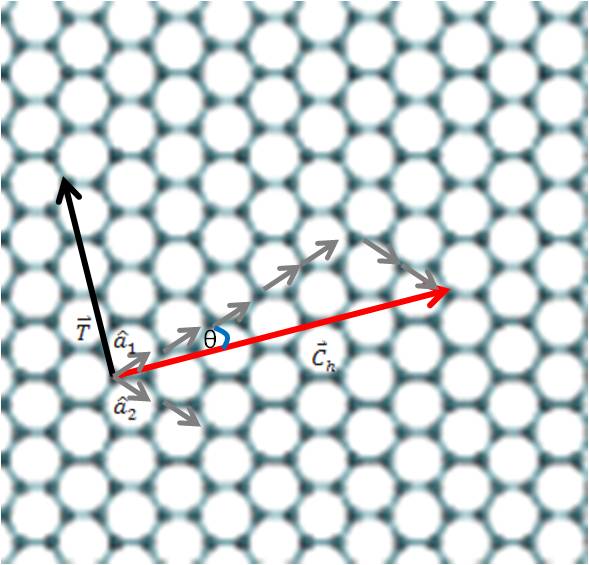
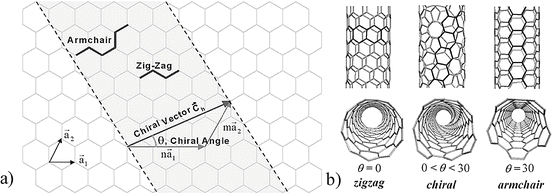
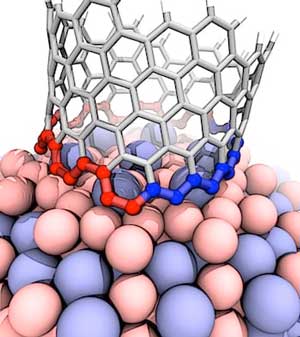
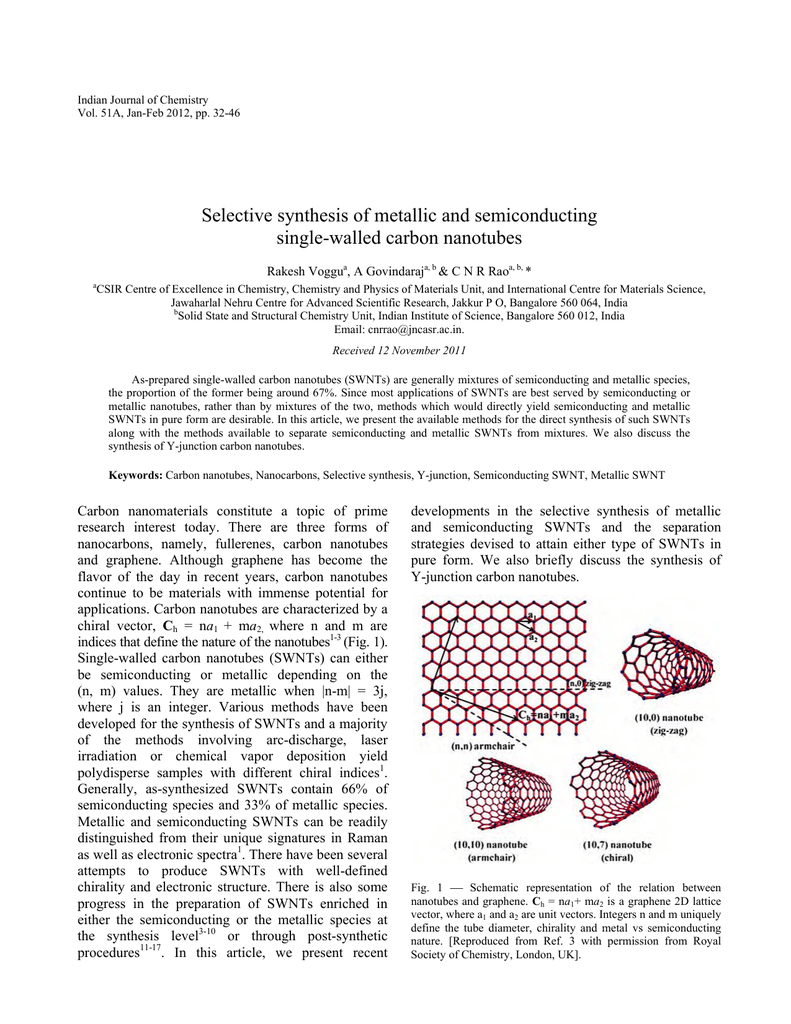
Chiral vector of carbon nanotubes. Along the longitude directions carbon nanotubes show superior mechanical strength with the highest known tensile strength and elastic modulus among known materials. The pair of integers nm is called the chiral index or just chirality. Chiral vector c can be written as c n a1 m a2where a1and a2are basis vectors of the graphene lattice. Pair of integers nm is called the chiral vector and uniquely defines the nanotube structure1 determining whether a carbon nanotube is conducting or nonconducting is crucial when considering their suitability for electronic or photonic device applications.
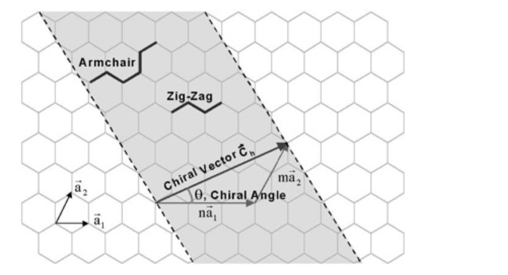
Instead of the type n m the structure of a carbon nanotube can be specified by giving the length of the vector w that is the circumference of the nanotube and the angle a between the directions of u and w which may range from 0 inclusive to 60 degrees clockwise exclusive. The atomic structure of a carbon nanotube can be defined by the chiral indices nm that specify its perimeter vector chiral vector with which the diameter and helicity are also determined. Considering a chiral vector with indices n m carbon nanotubes are metallic when n m or n m 3i i is an integer and semiconducting in other cases.




.jpg)

.jpg)