Cloning Vector Pagal6
Matt carter jennifer c.

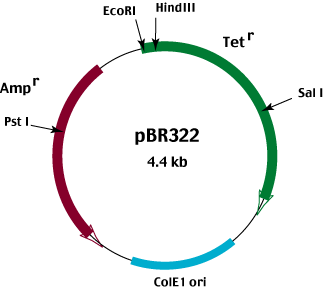
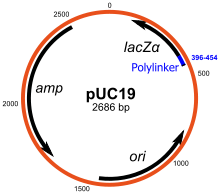
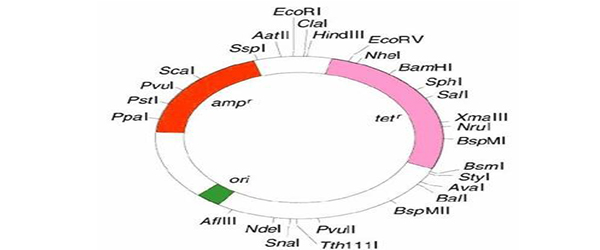
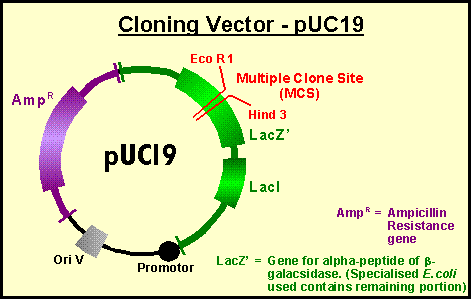
Cloning vector pagal6. Most vectors are genetically engineered. Types of cloning vectors bacteriophage. A cloning vector is also a fragment of dna which is capable of self replication and stable maintenance inside the host organism. Cloning vectors provide a basic backbone for the dna insert to be reproduced and generally have the common features just described but these vectors are useful only for cloning and not for expressing a protein product.
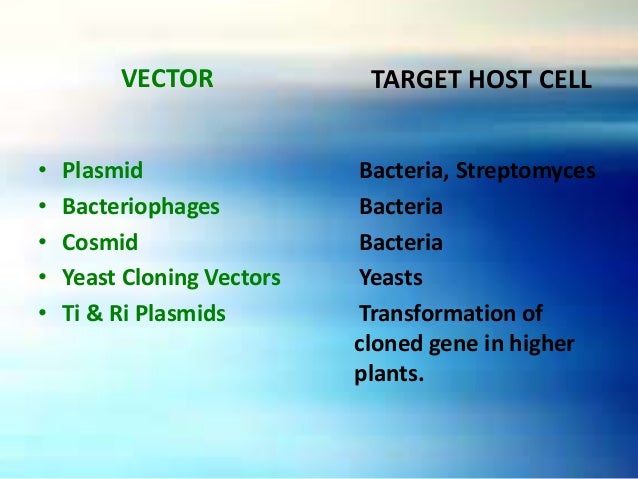
The bacteriophages used for cloning are the l phage and m13 phage. Vector is an important term in molecular biology. The cloning of a specific fragment of dna into a vector such as a plasmid is one of the foundational steps that enables additional characterization of that sequence. The dna insert in a cloning vector can be copied but not translated.
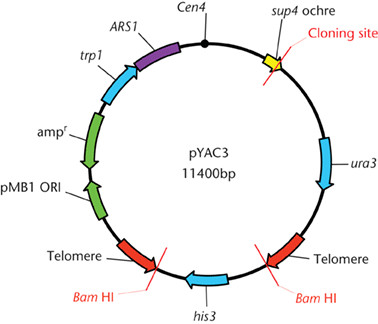
In recombinant dna technology the main role of a vector is to provide a mode of transport to a useful dna fraction to be inserted. Most of the cloning vectors are genetically engineered. Cosmids are plasmids that incorporate a segment of bacteriophage l dna that has the cohesive end site cos. Shieh in guide to research techniques in neuroscience 2010.
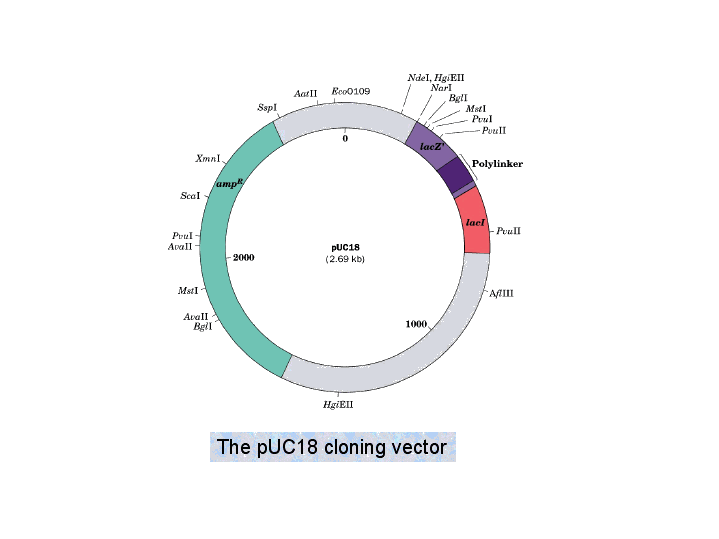
It is selected based upon the size and the kind of dna segment to be cloned. It can be extracted from a virus plasmid or cells of a higher organism. Vectors such as the pgem series contain multiple cloning sites to excerpt fragments generated by digestion with specific restriction enzymes. The cloning vector is chosen according to the size and type of dna to be cloned.
Genetic vectors are vehicles for delivering foreign dna into recipient cells. In molecular cloning a vector is a dna molecule used as a vehicle to artificially carry foreign genetic material into another cell where it can be replicated andor expressed.