Define Vector Quantity And Scalar Quantity With Examples
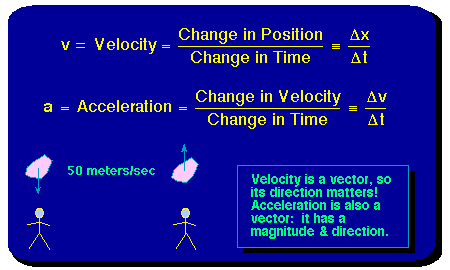
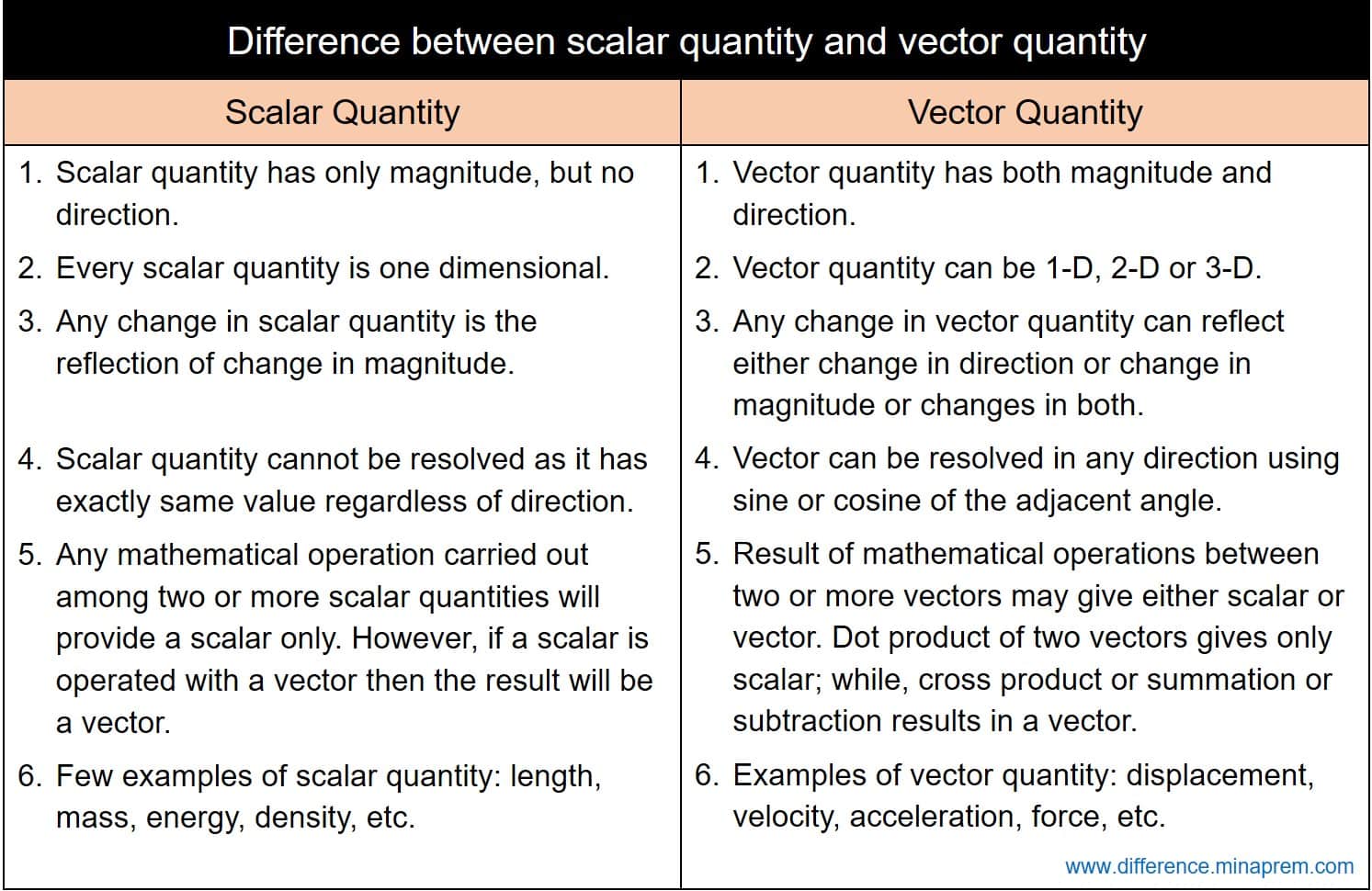
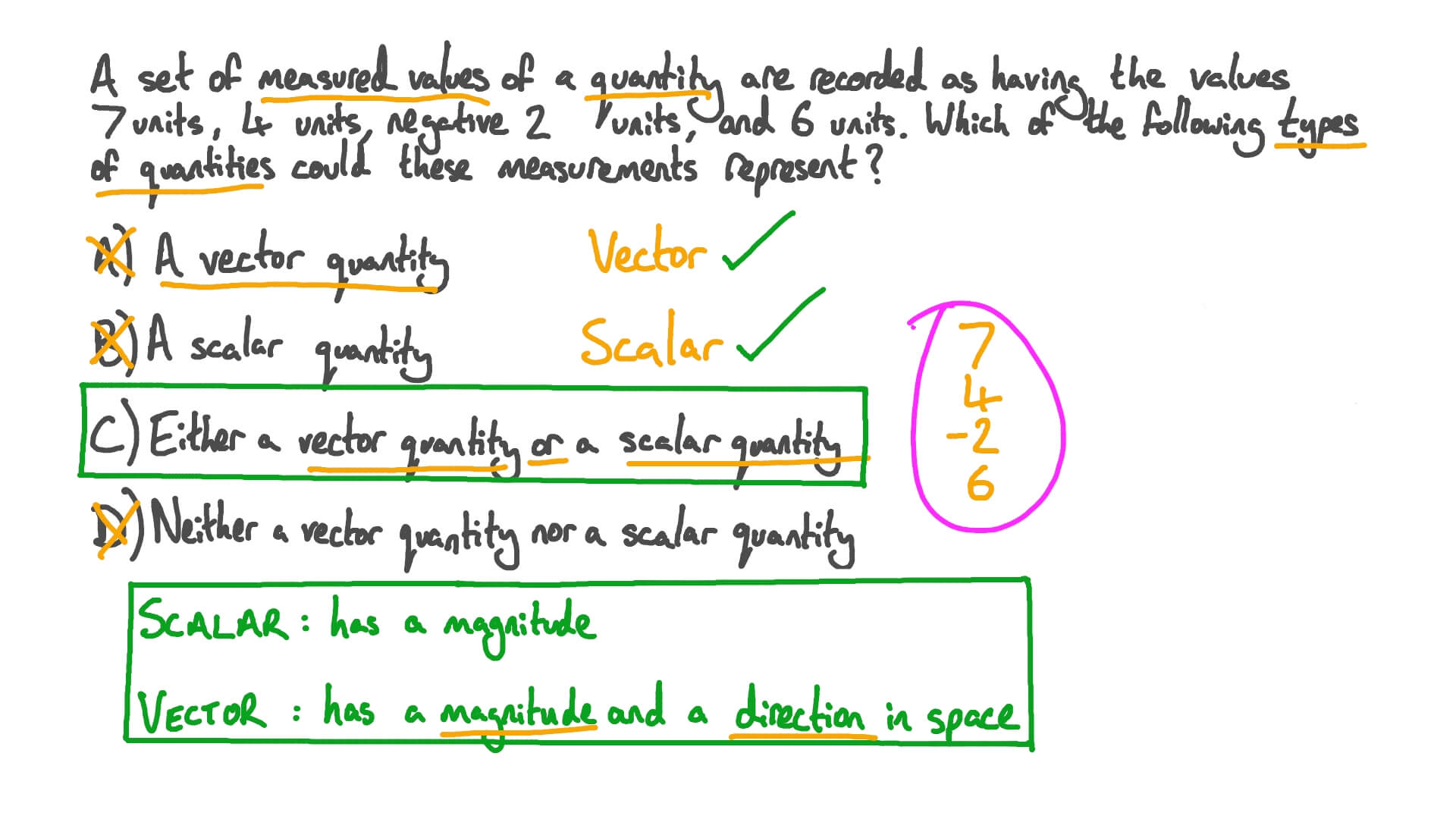
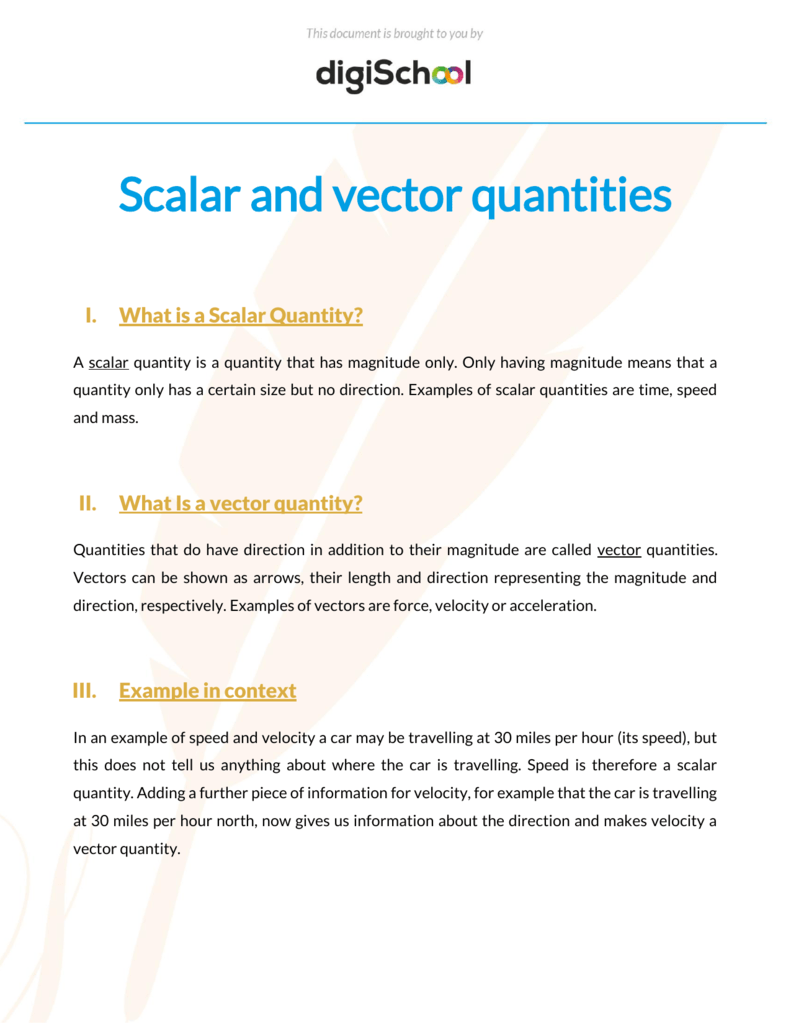
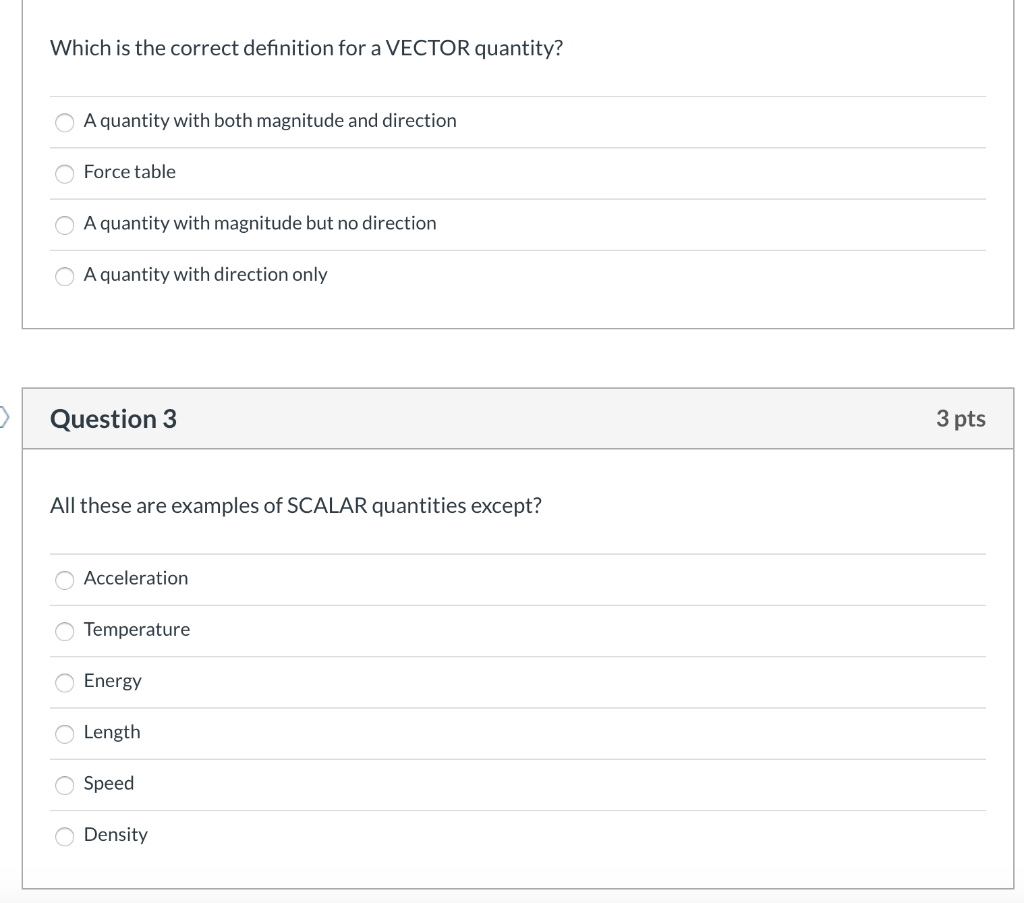
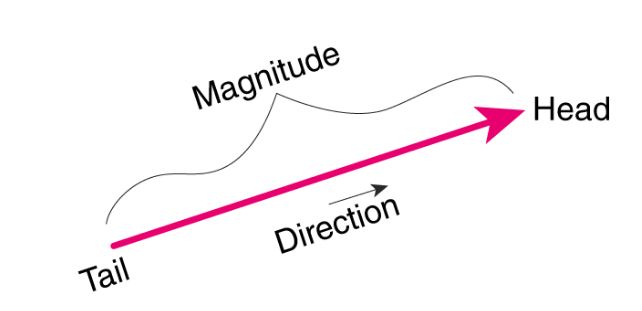
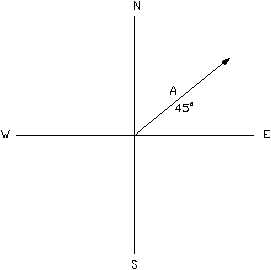
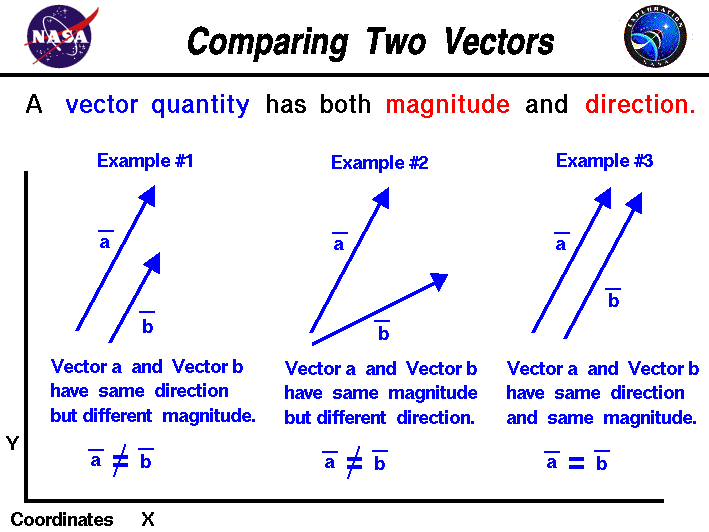
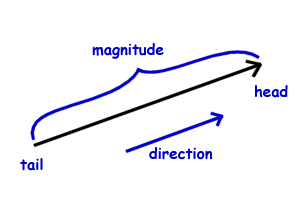
Any quantity that needs to be fully described by identifying its magnitude and direction is referred to as a vector quantity.

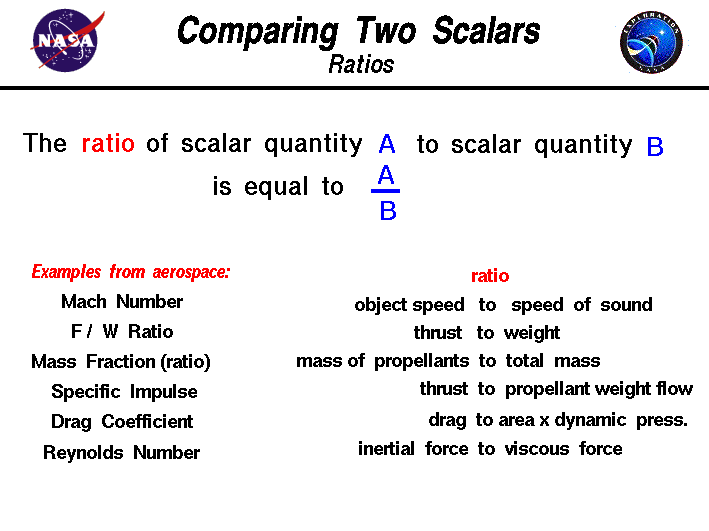
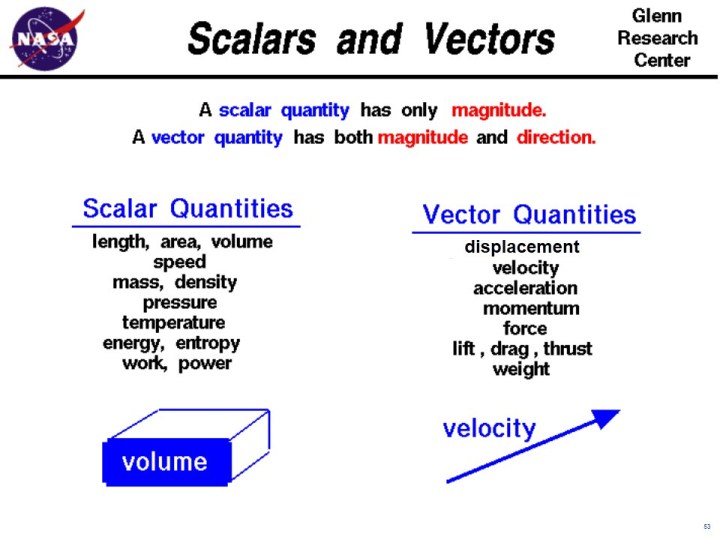
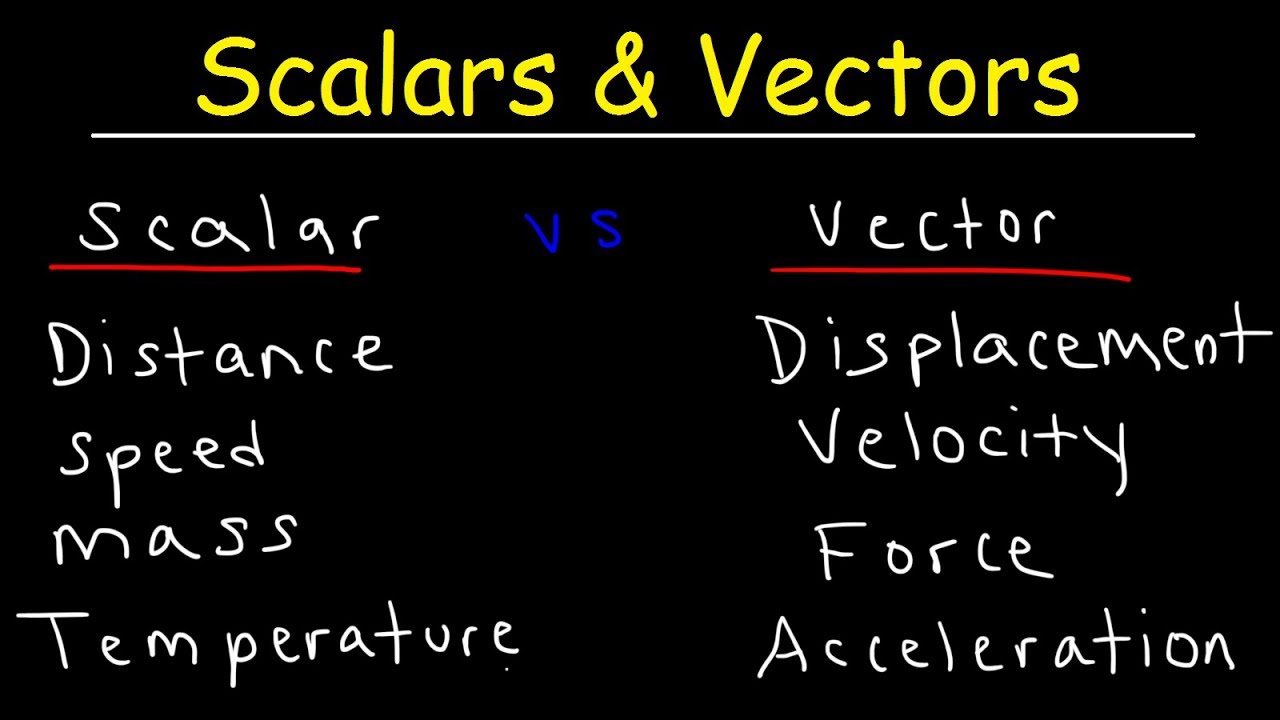
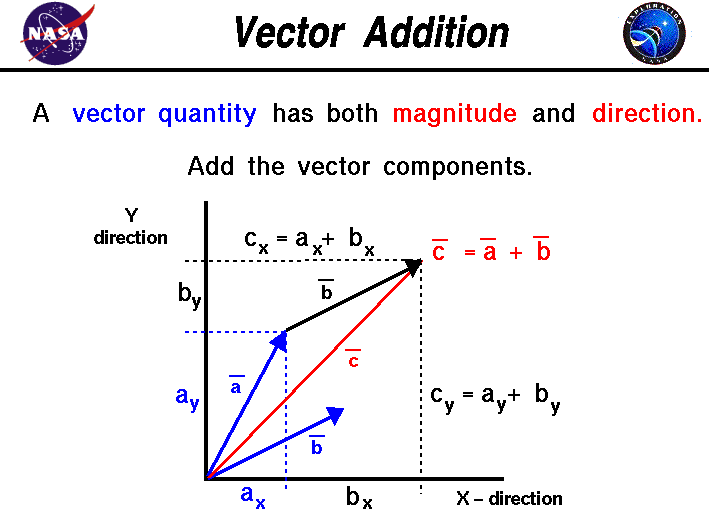
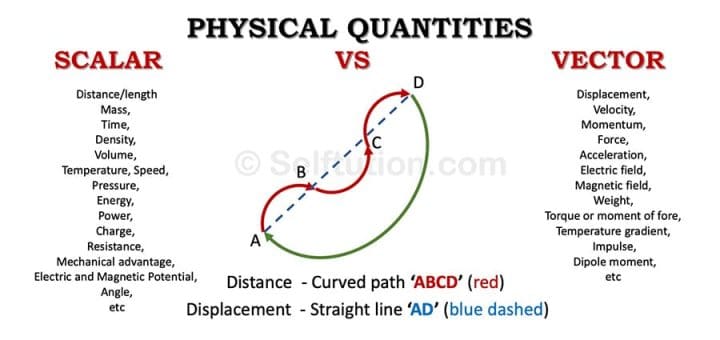
Define vector quantity and scalar quantity with examples. Examples of scalar and vector quantities some common examples of scalar quantities are mass time speed volume temperature density and many more. The vector quantities however involve much more information than simply representable in a figure often requiring a specific sense of direction within a specified coordinate system. Displacement velocity acceleration momentum force weight etc. It is important to note here that in addition to magnitude and direction two vector quantities of the same kind must compound according to the parallelogram law of vector addition.
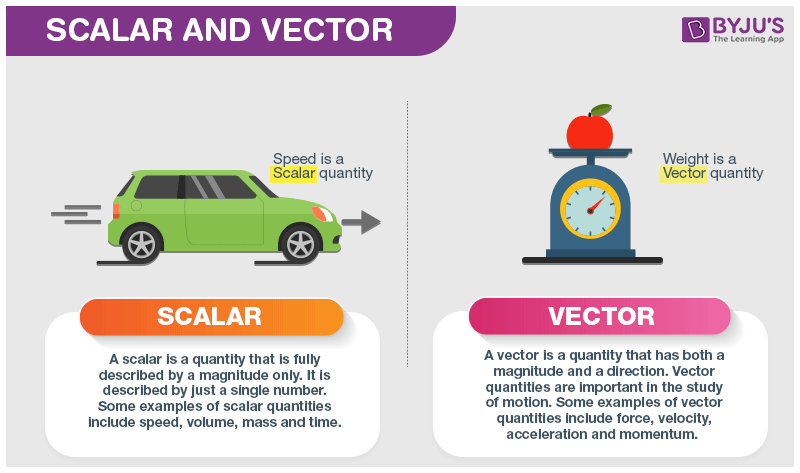
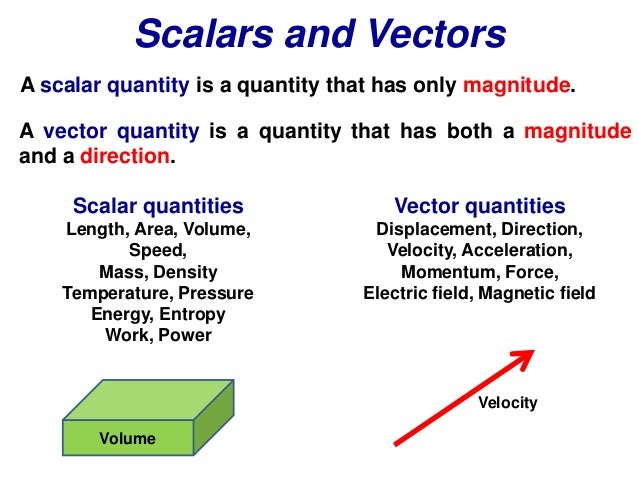
Definition of a scalar quantity scalar quantities are those physical quantities which are expressed only by their magnitude along with the unit required for the measurement. A scalar quantity is defined as the physical quantity that has only magnitude for example mass and electric charge. The magnitude of velocity and its. 20 examples of vector quantities and scalars quantities.
Other examples of scalar quantities are mass speed distance time energy density volume temperature distance work and so on. On the other hand a vector quantity is defined as the physical quantity that has both magnitude as well as direction like force and weight. On the other hand multi dimensional quantities are explained by vector quantity. Scalar is the measurement of a medium strictly in magnitude.
Quantities are represented by vectors. For example displacement force etc are vector quantity. Defining scalar and vector quantity. By definition a vector quantity is a physical quantity with magnitude and direction whereas a scalar quantity only has magnitude.
The scalar quantities are those representable by a numerical scale in which each specific value accuses a greater or lesser degree of the scale. These quantities are often described as being a scalar or a vector quantity. The physical quantities for which both magnitude and direction are defined distinctly are known as vector quantities. Vector is a measurement that refers to both the magnitude of the medium as well as the direction of the movement the medium has taken.
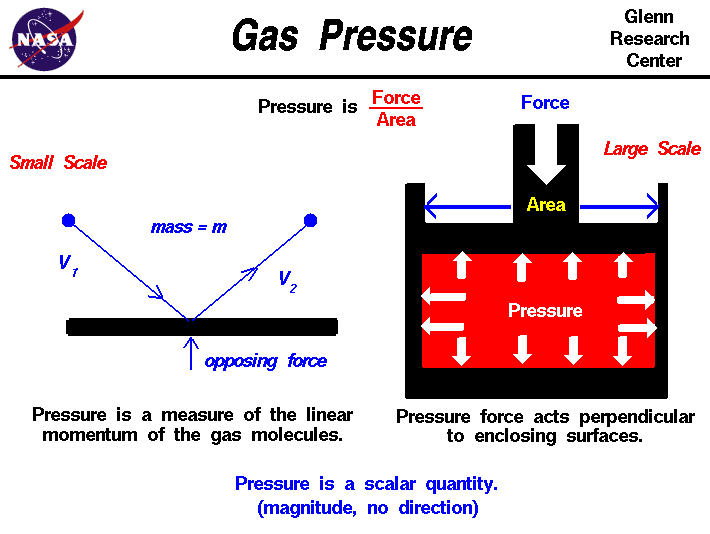
Scalars and vectors are differentiated depending on their definition. Vector quantity definition physical quantities which have both magnitude and direction are known as vector quantities. For example if we say that the mass of a bag is 50 kg it has complete meaning and we are completely expressing the mass of the bag. By magnitude we mean size of the quantity such as length or strength.
September 20 2018 1227 am. For example a boy is riding a bike with a velocity of 30kmhr in a north east direction. Scalar quantity changes only when there is a change in their magnitude. Then as we see for defining the velocity we need two things ie.
Scalar quantities explain one dimensional quantities.