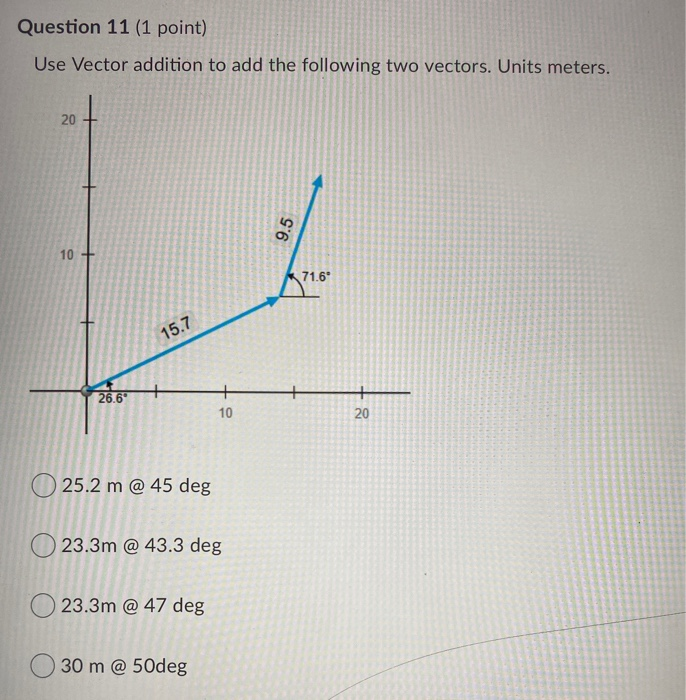
Point Vector Addition
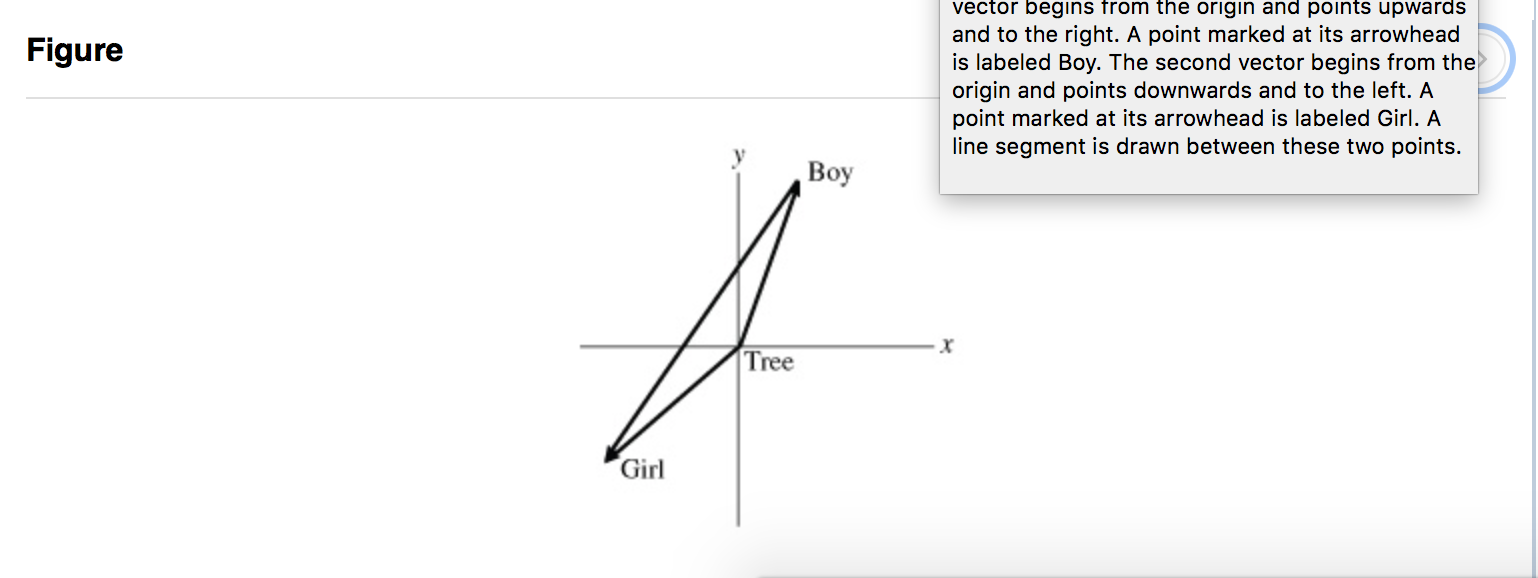
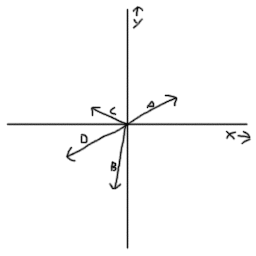
Now imagine a scenario where a boy moves from point a to b and then from point b to c.
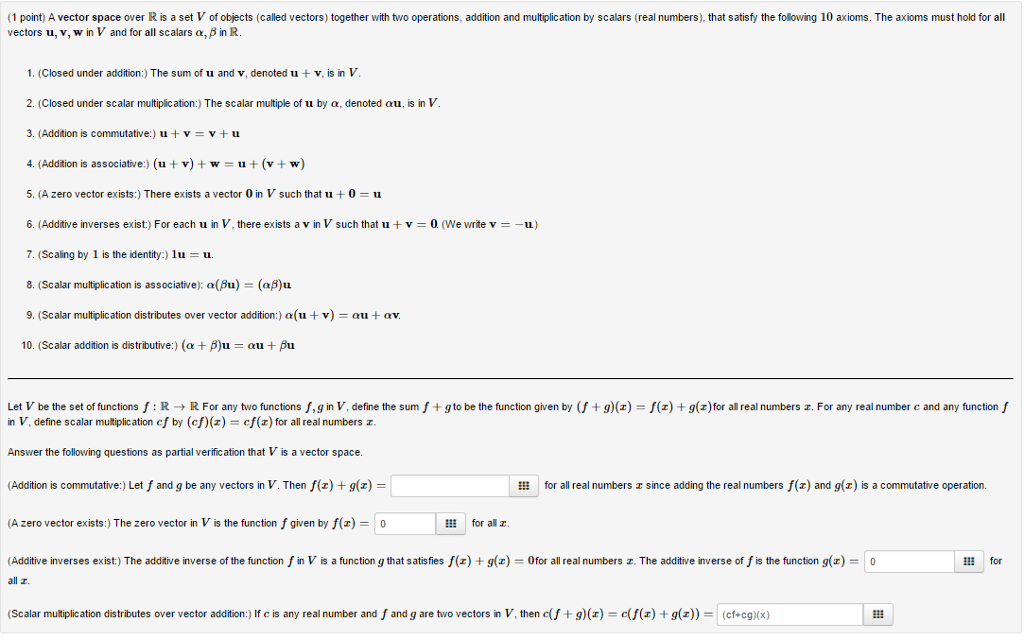
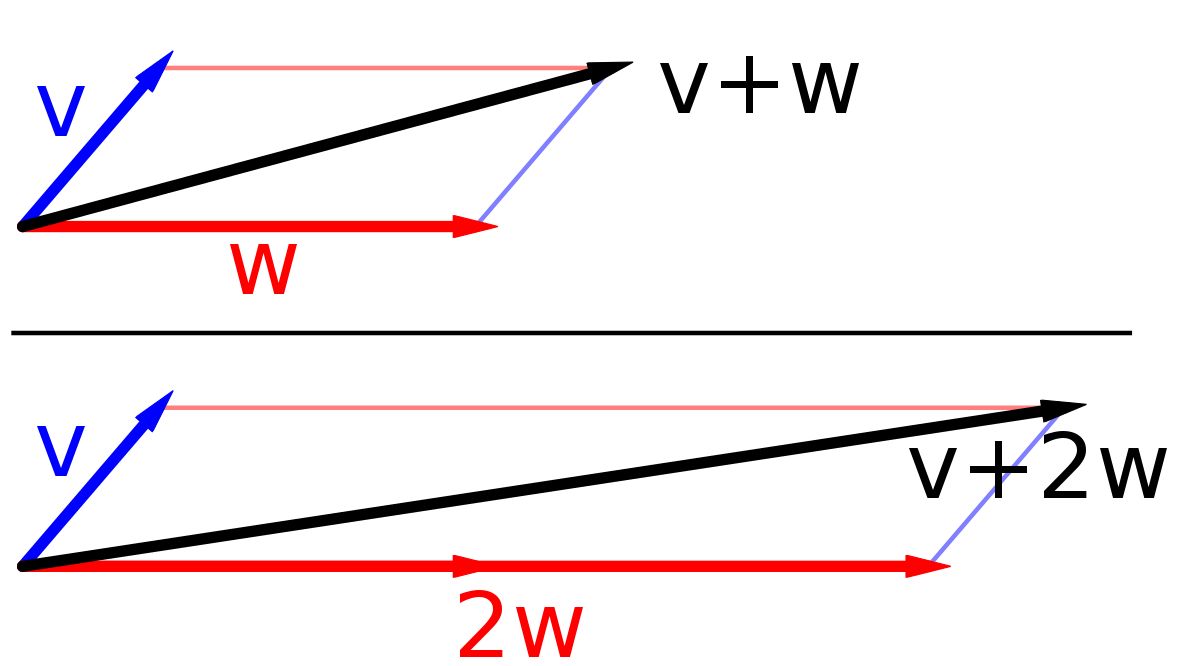
Point vector addition. Experiment with vector equations and compare vector sums and differences. 4 4 t 1 2 t 5 6 t. A tuple can be regarded as a function and a vector is a tuple. This blue vector the sum of the two is what results where you start with vector a.
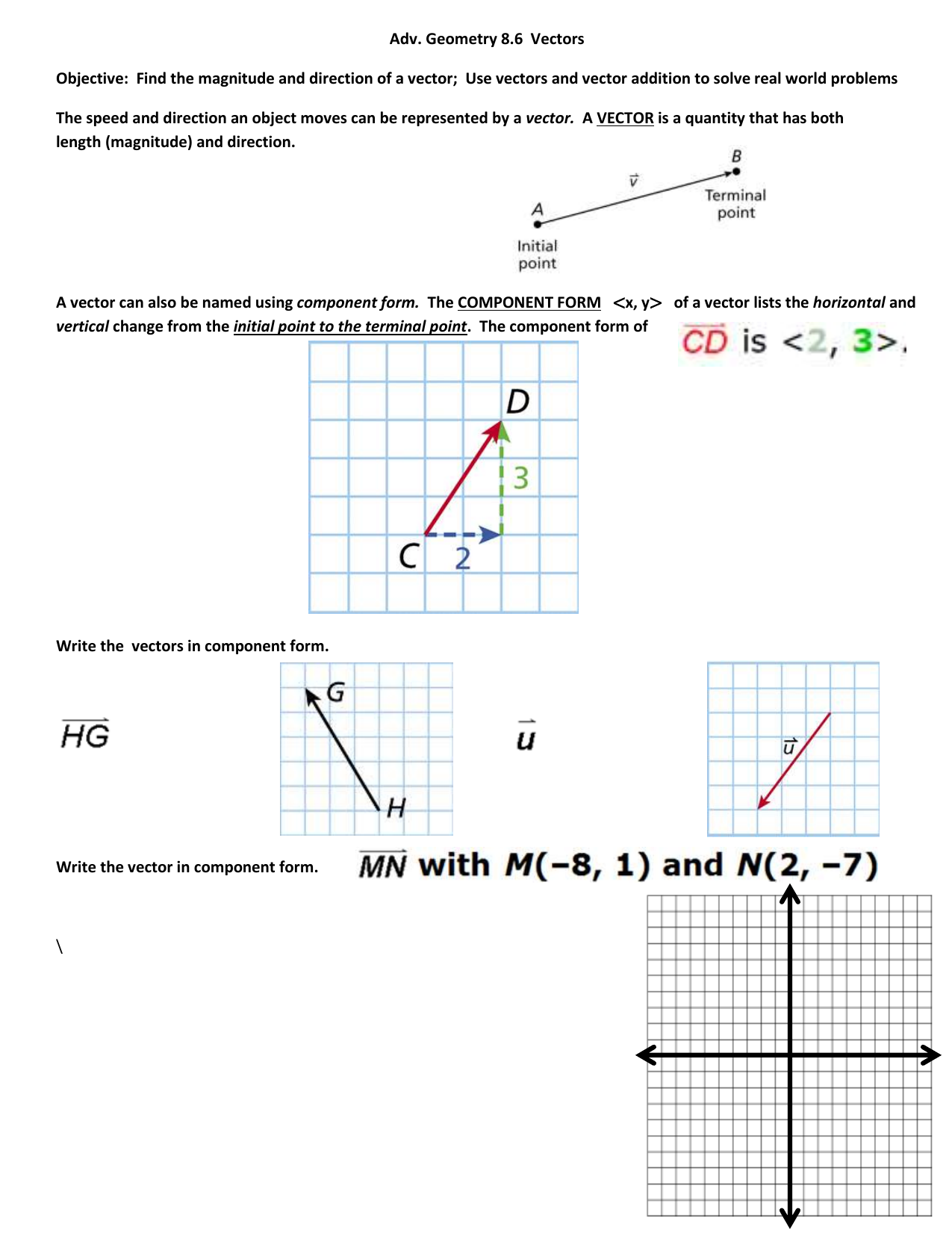
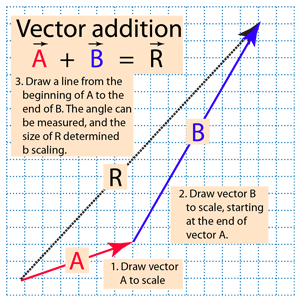
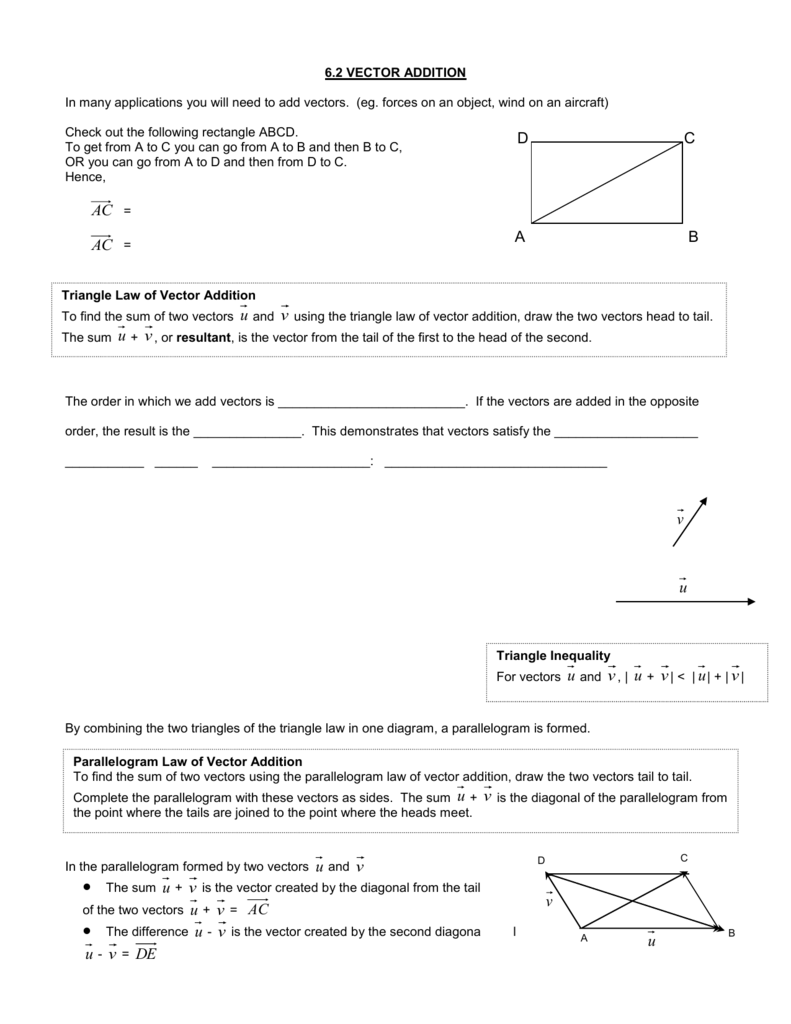
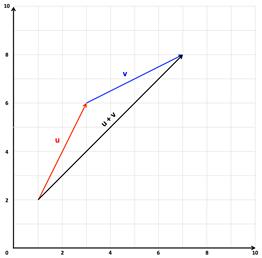
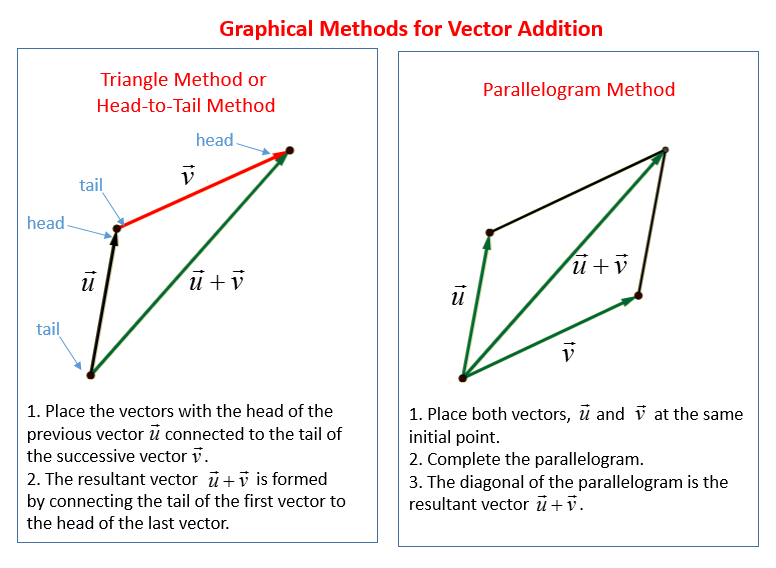
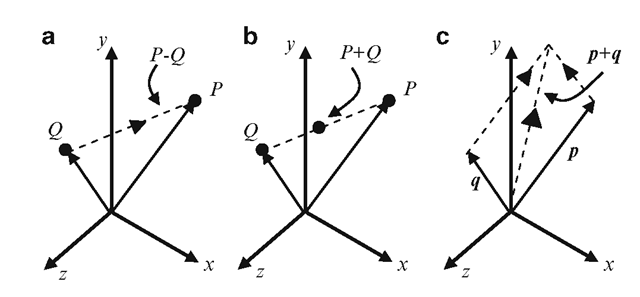
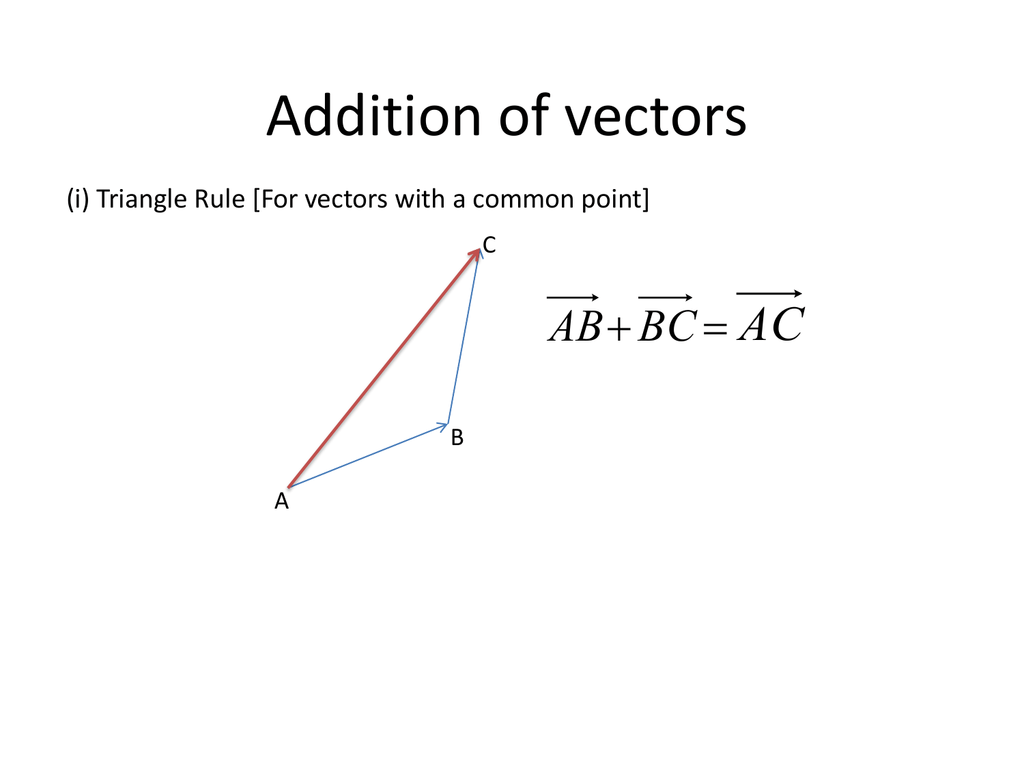
Vec ab ab in simple words means the displacement from point a to point b. Place both vectors u and v at the same initial point. Triangle law of vector addition. Add point to a vector using the overloaded operator.
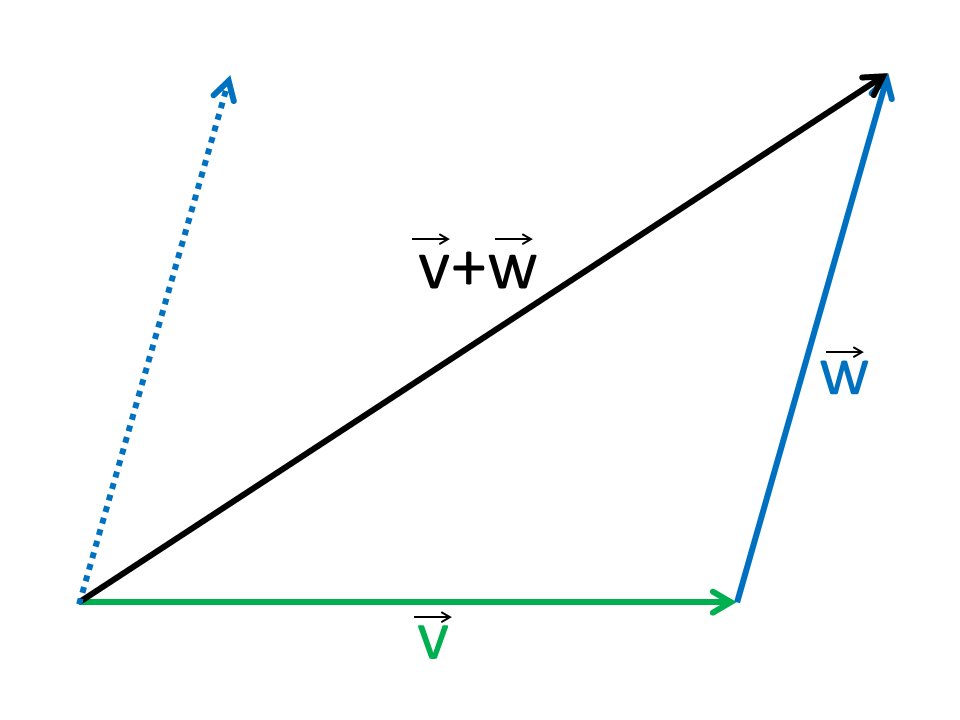
The following example shows how to add a point to a vector using the overloaded operator. Matrix addition where is a componentwise operation while matrix multiplication is not. At that point right over there vector a takes you there then you take vector bs tail start over there and it takes you to the tip of the sum. Now one question you might be having is well vector a plus vector b is this but what is vector b plus vector a.
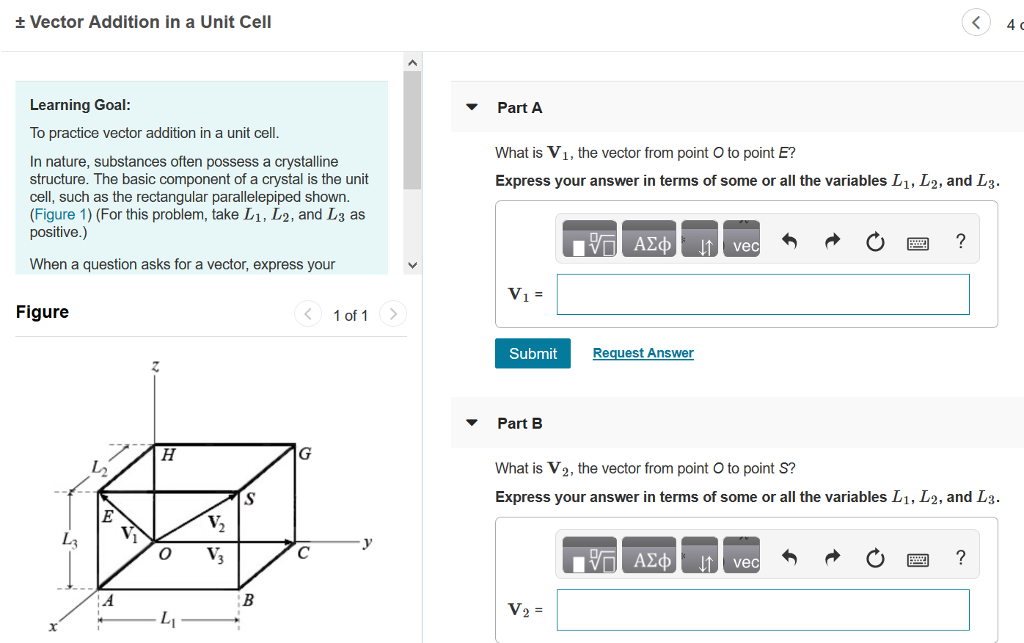
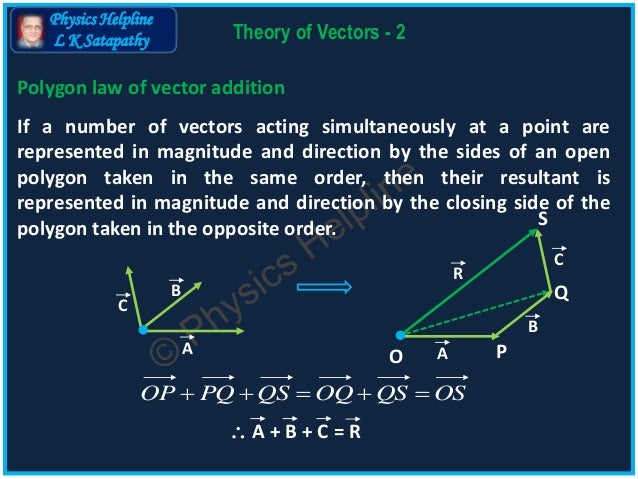
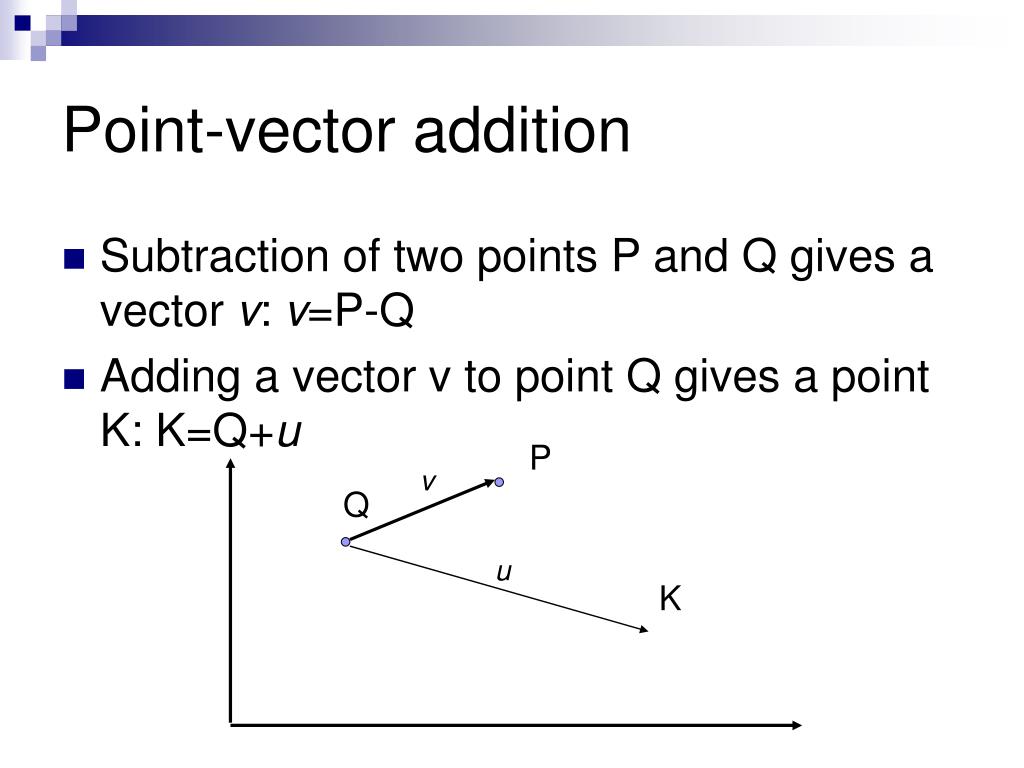
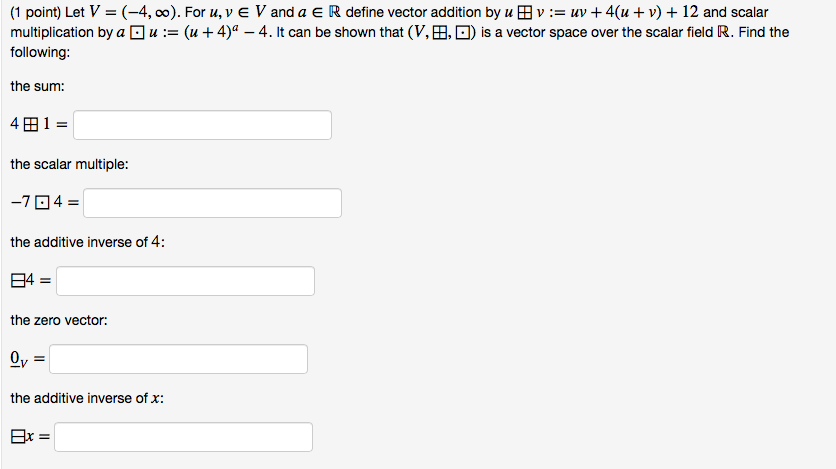
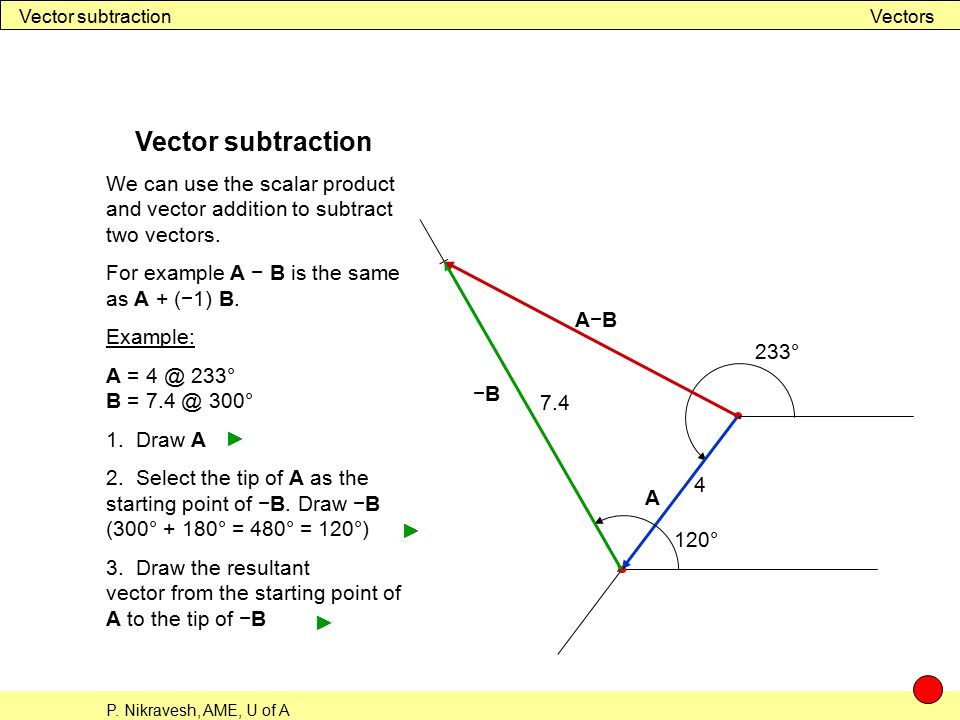
One such operation is the addition of vectors. Pointresult is equal to 3035. Adding points and vectors if the vector 1 2 t is a displacement ie an amount by which to change x and an amount by which to change y then the result must be a point in a new location. This process of adding two or more vectors has already been discussed in an earlier unit.
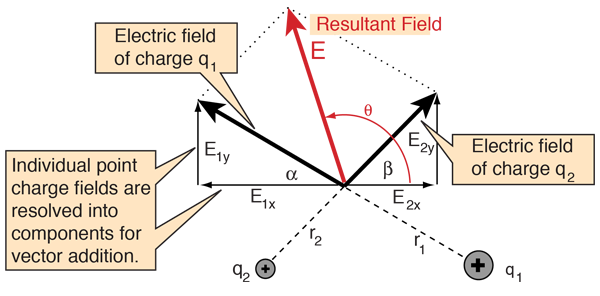
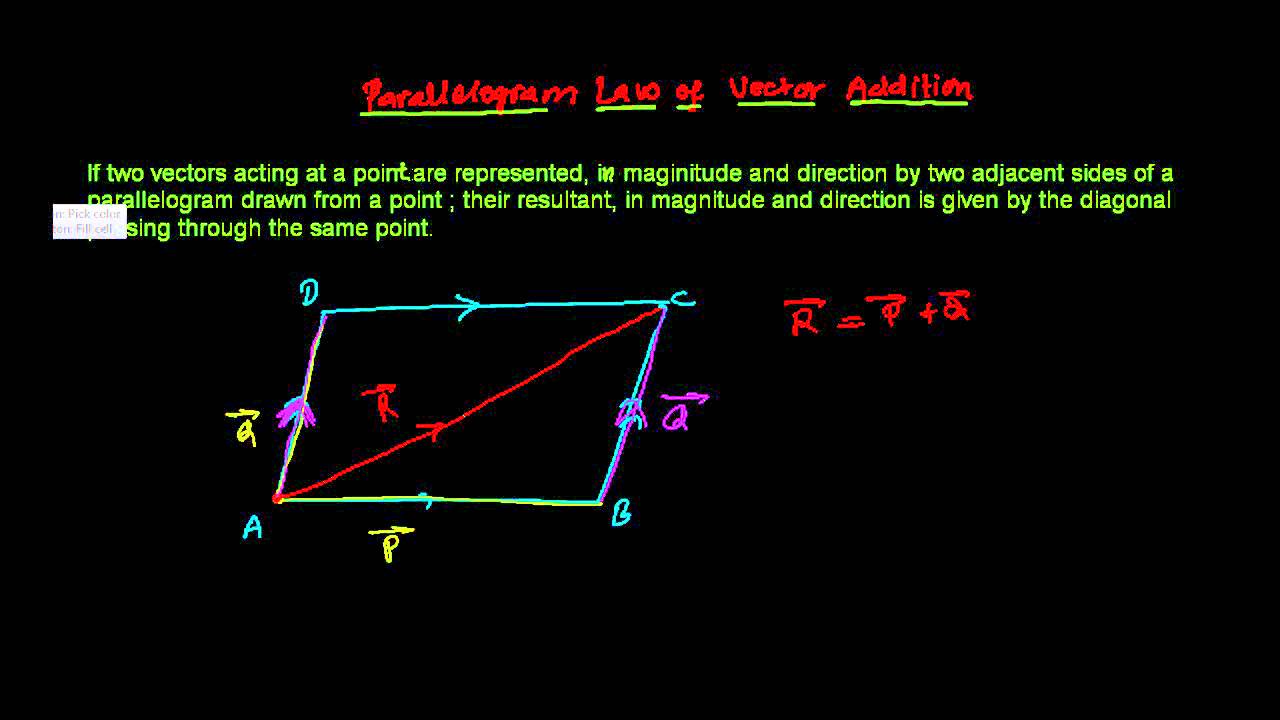
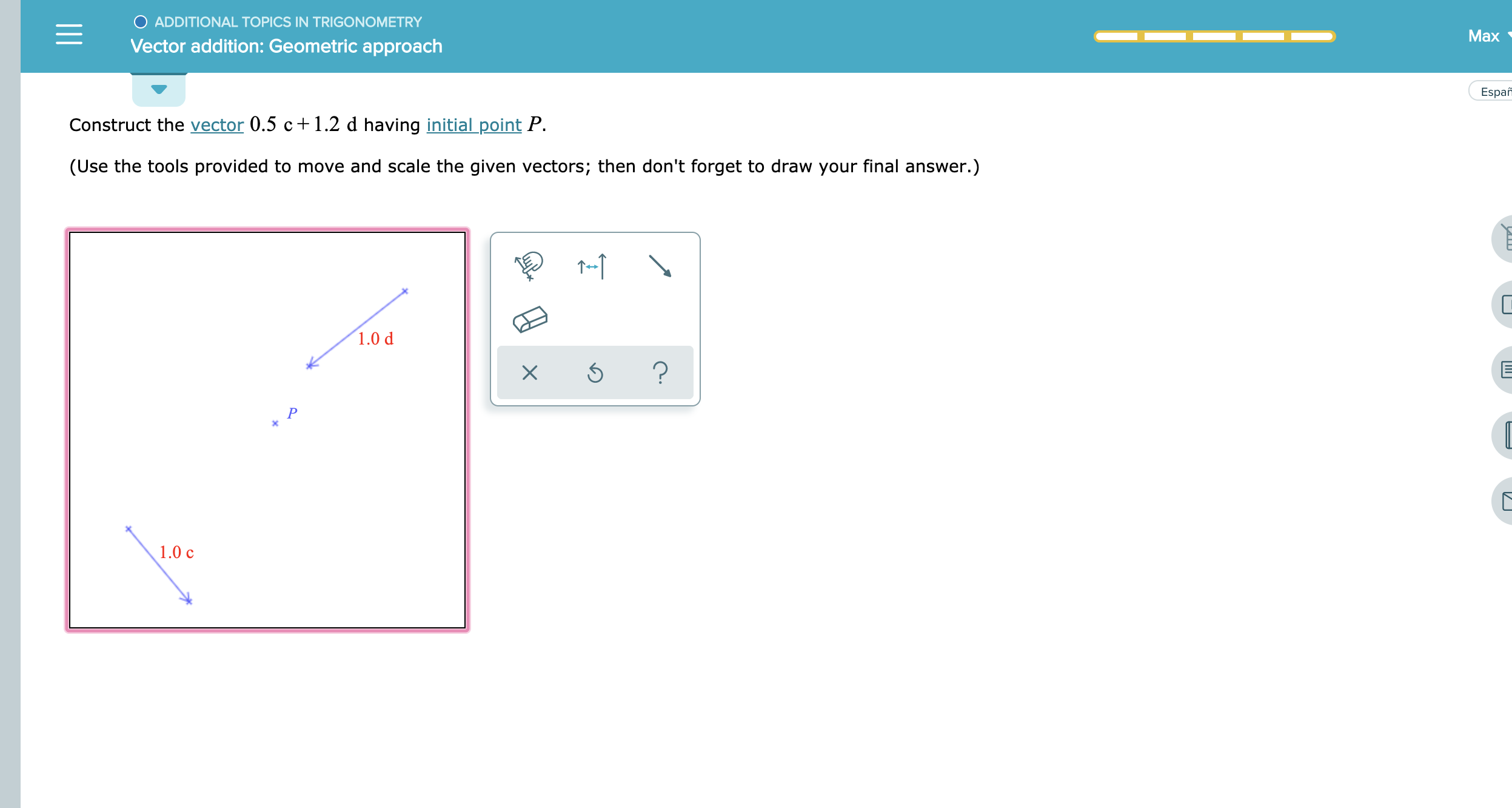
Specify vectors in cartesian or polar coordinates and see the magnitude angle and components of each vector. A variety of mathematical operations can be performed with and upon vectors. Vector addition satisfies the following properties. The resultant vector u v is the diagonal of the.
Two vectors can be added together to determine the result or resultant. N k displaystyle fnto k such that f i v i displaystyle fivi and any componentwise operation on vectors is the pointwise operation on functions corresponding to those vectors. Vector addition association commutation pointvector association. Private point overloadedadditionoperatorexample point point1 new point10 5.
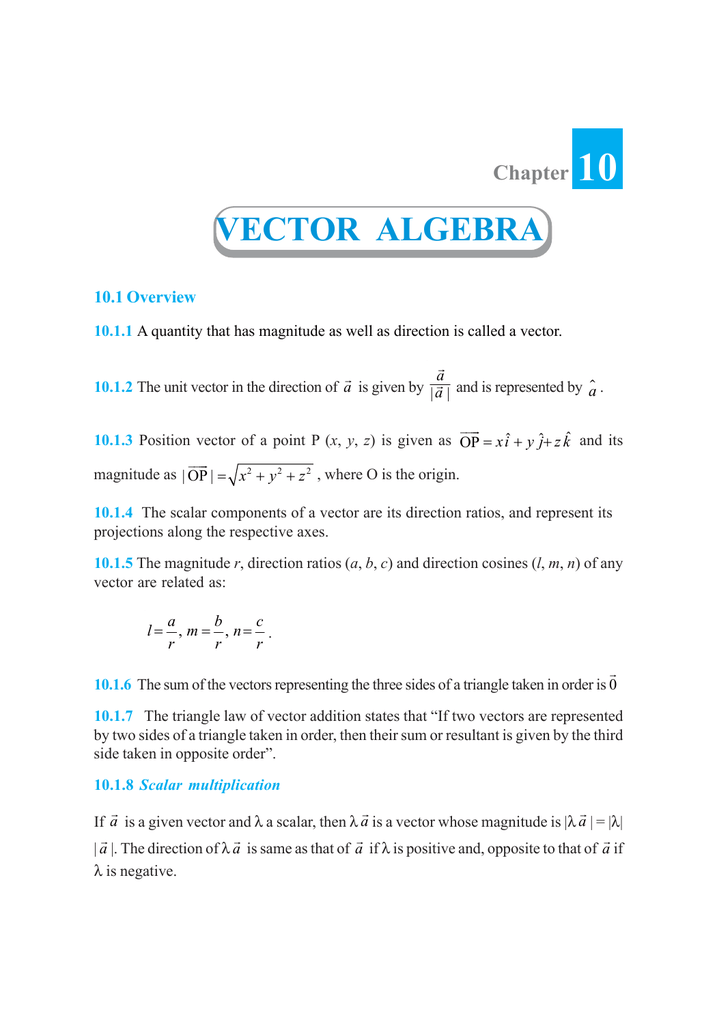
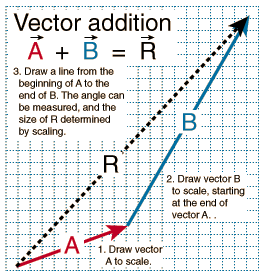
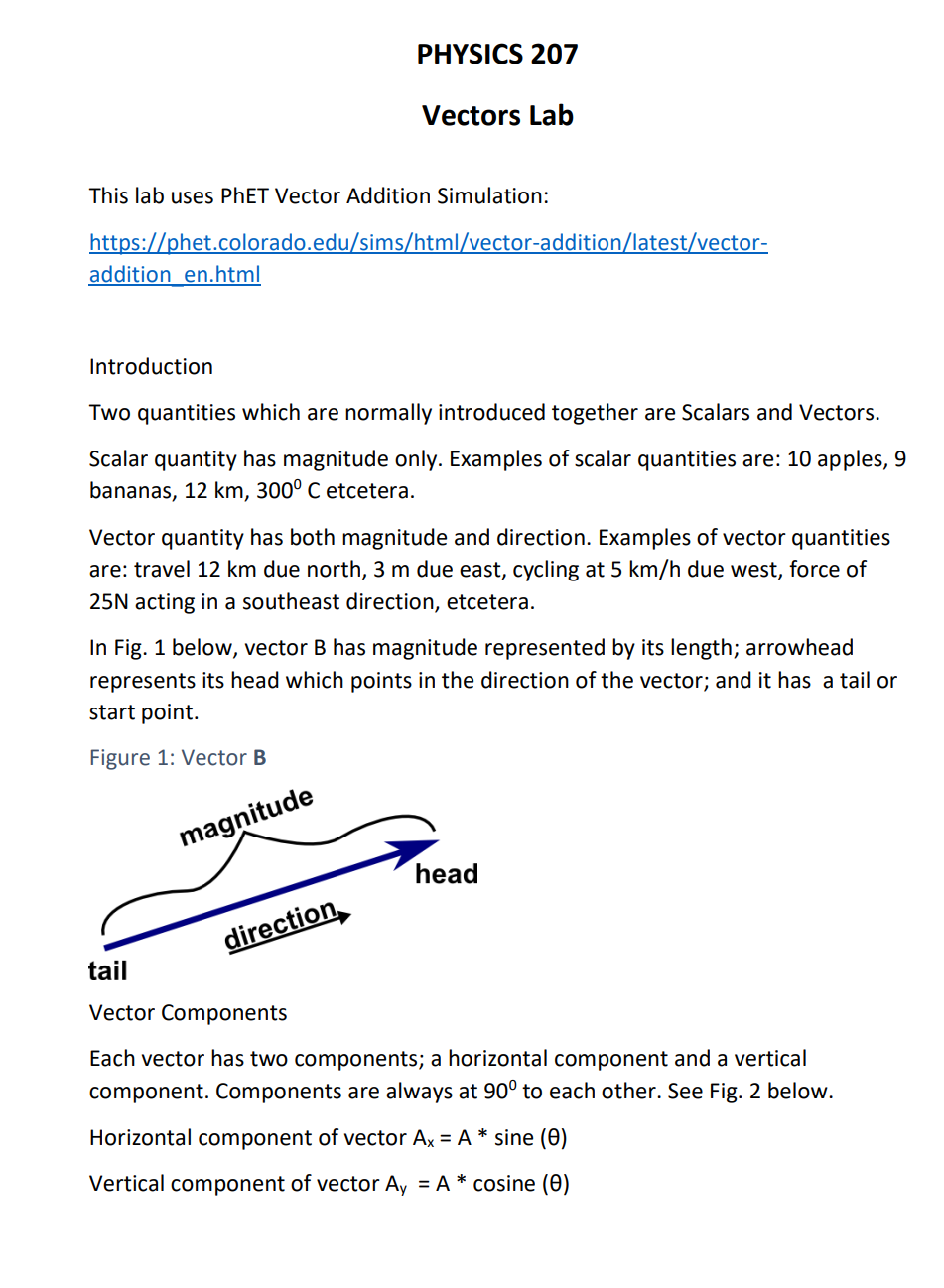
This is a vector. The resulting point q is considered to be the displacement or translation of the point p in the direction of and by the magnitude of the vector. We can add two vectors by joining them head to tail. The length of the line shows its magnitude and the arrowhead points in the direction.
Therefore any vector v displaystyle v corresponds to the function f.