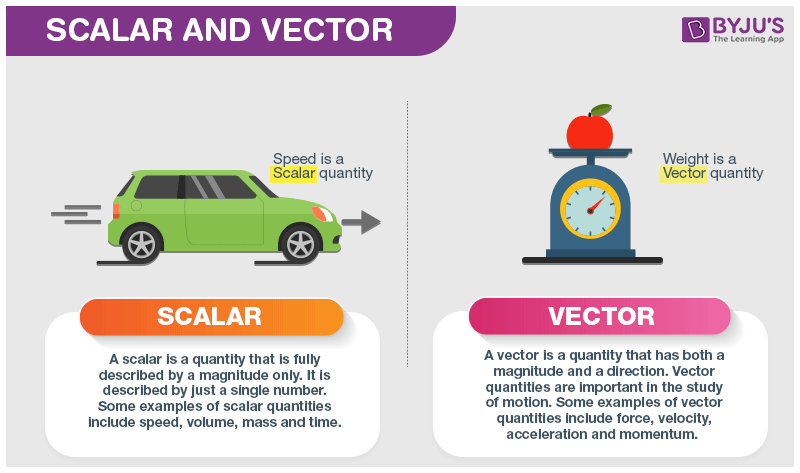
A Vector Is A Quantity That Has
Vectors often represent displacement speed acceleration or force.

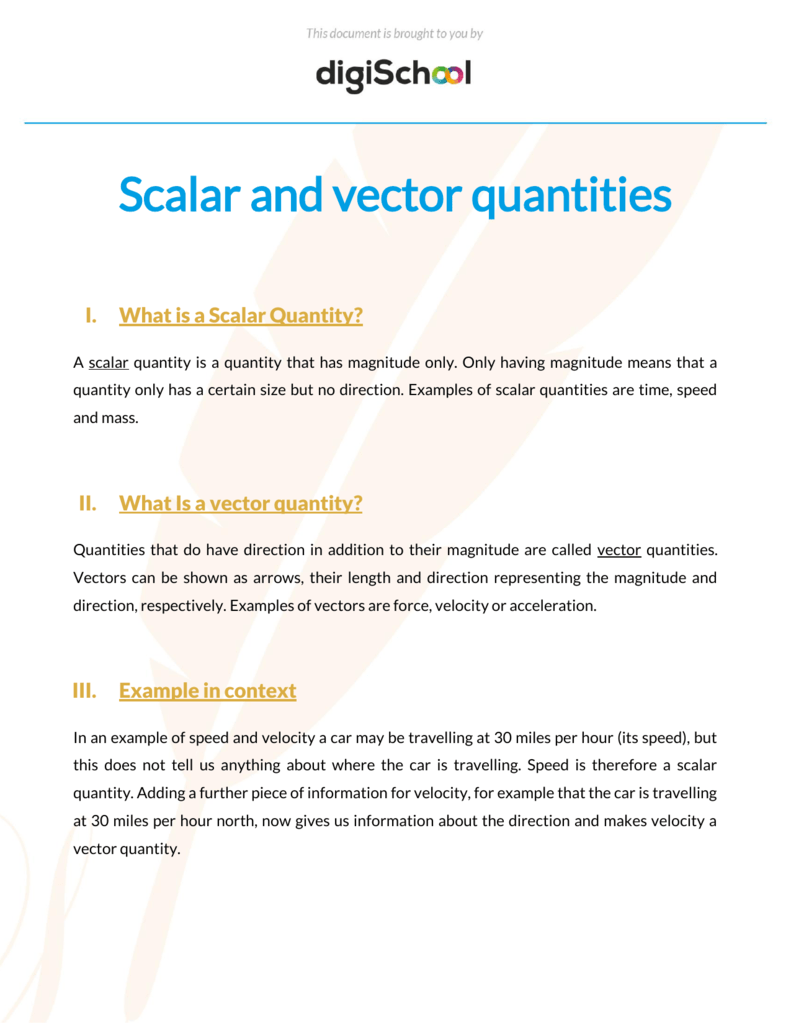
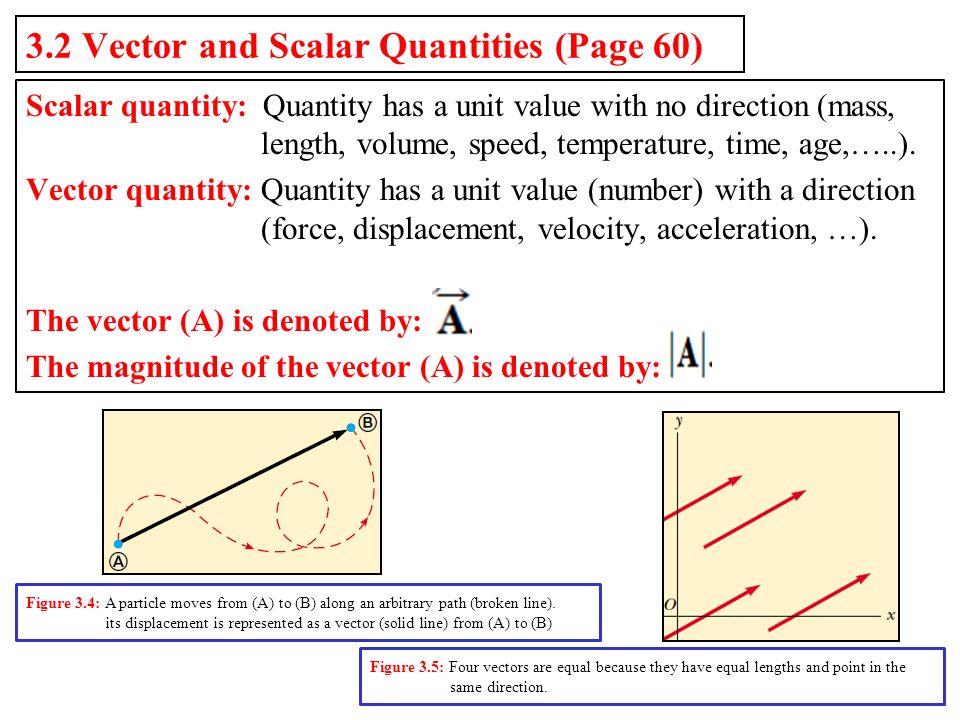
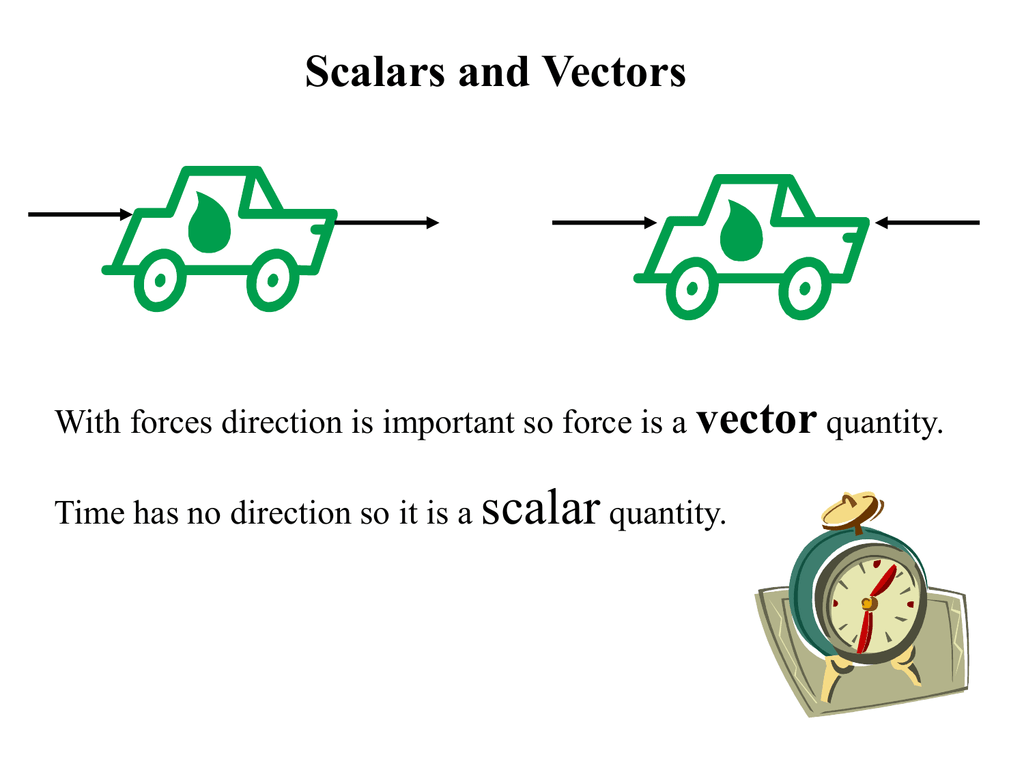
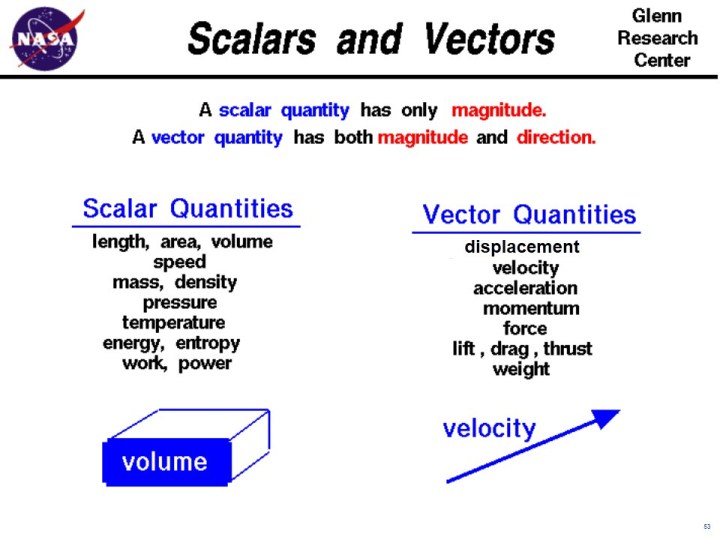
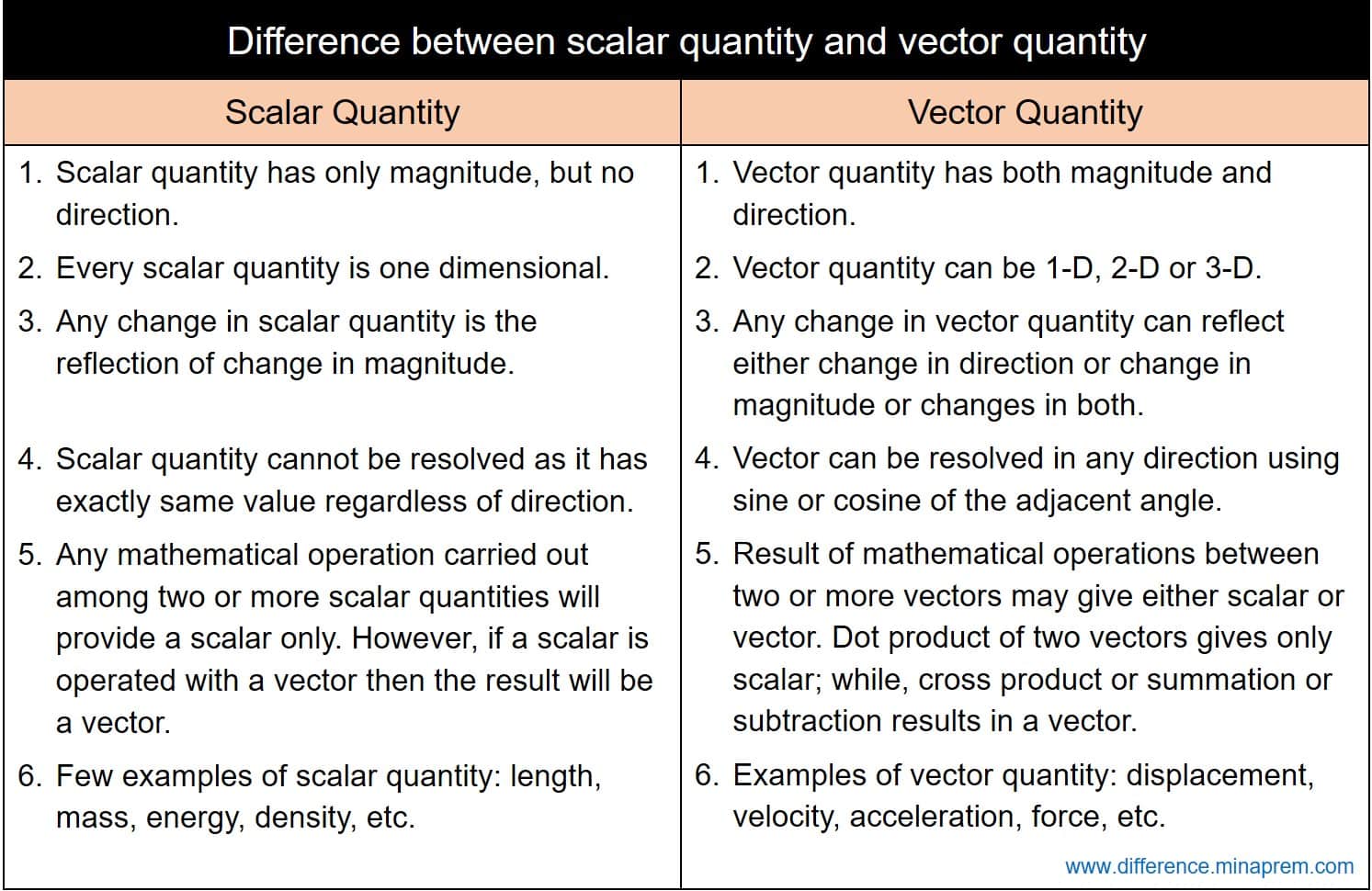
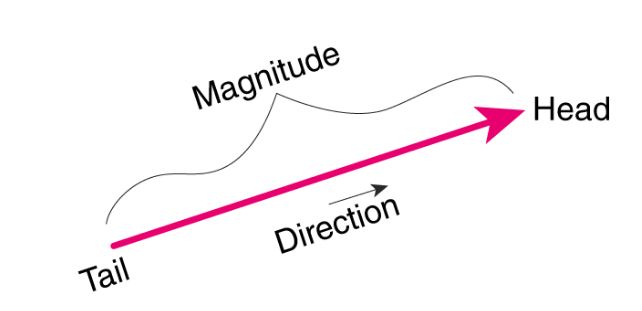
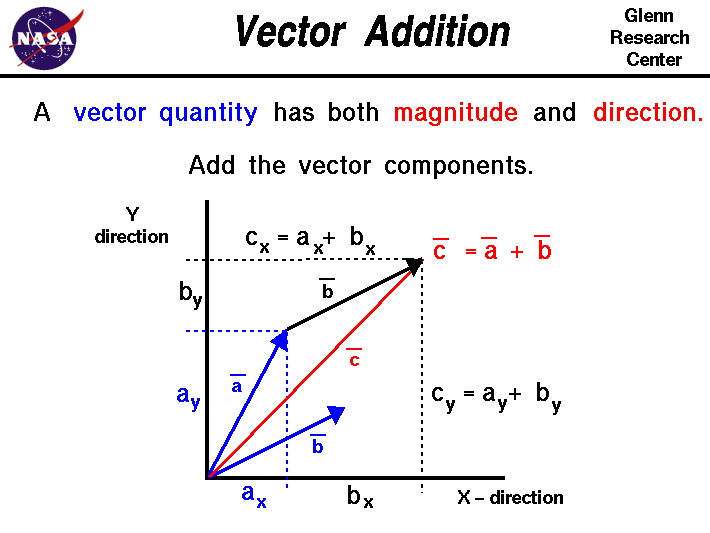
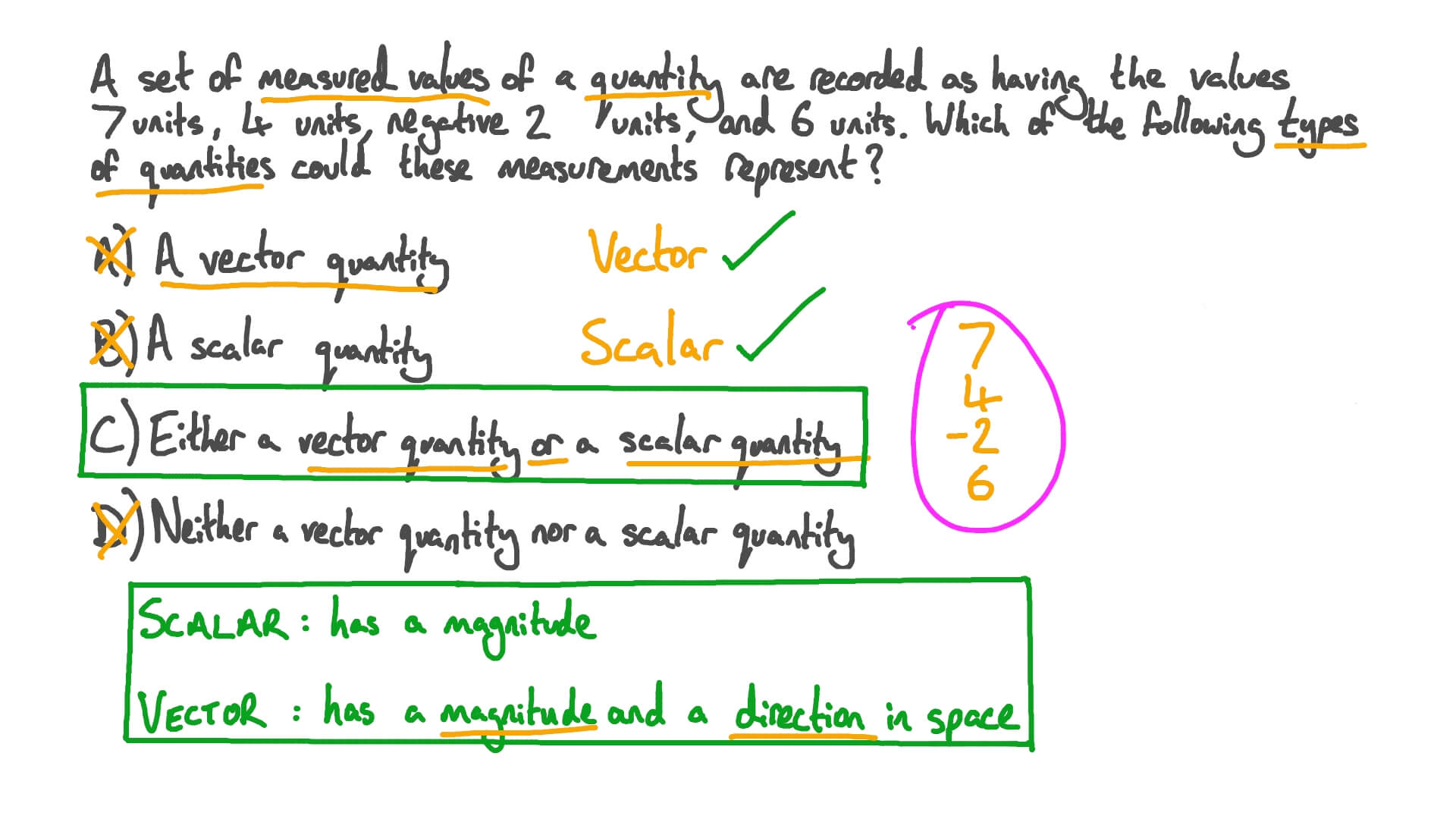
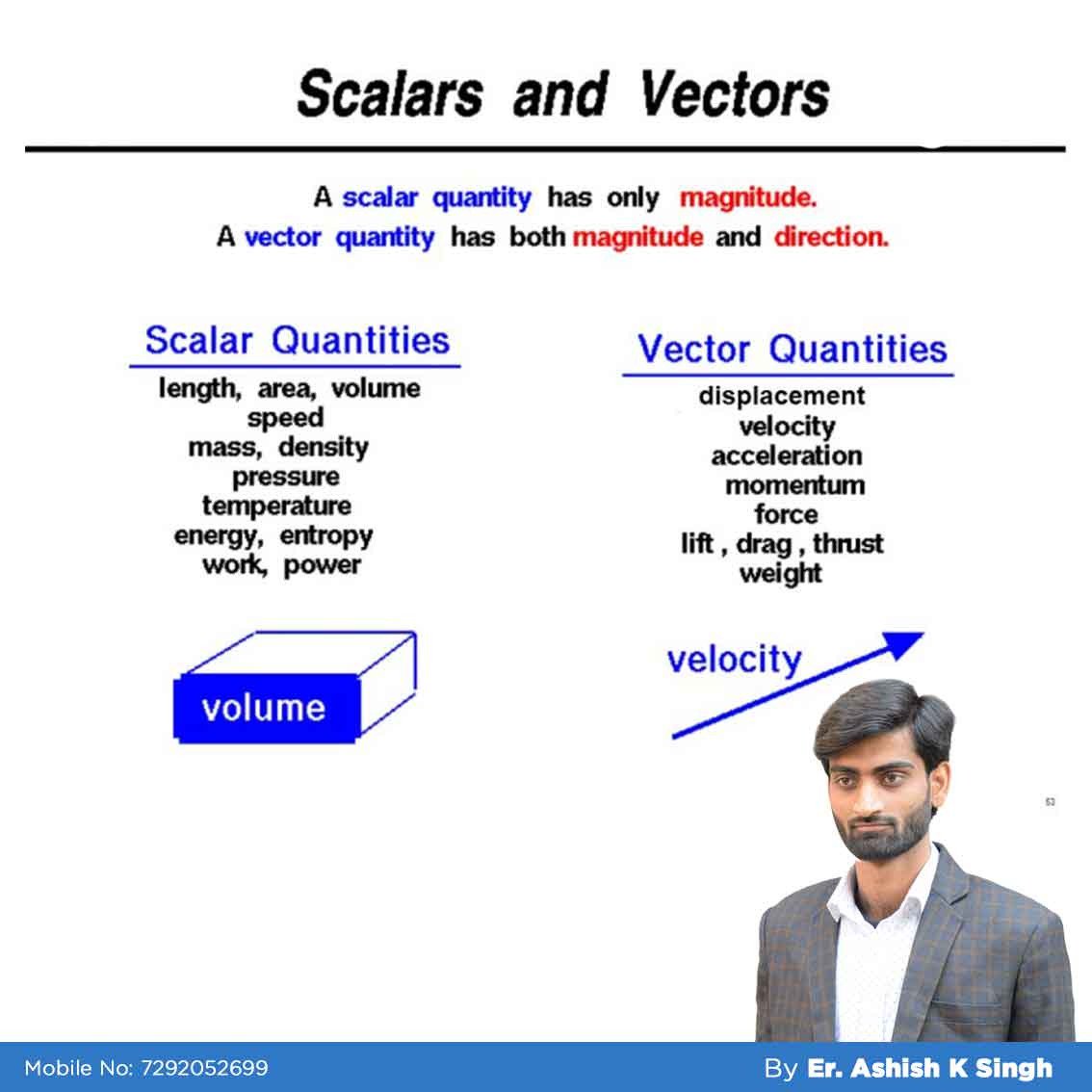
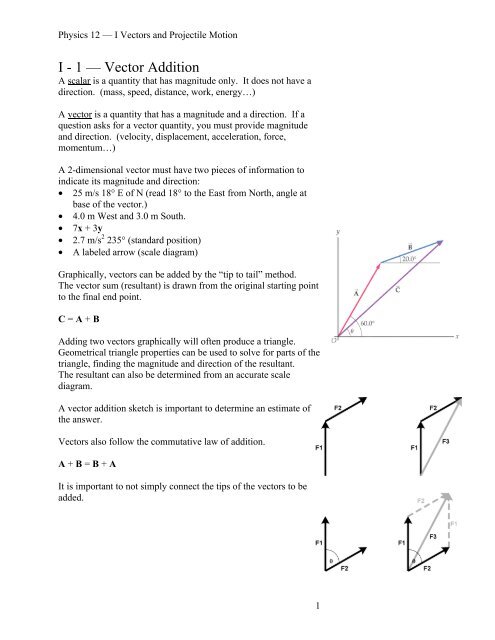
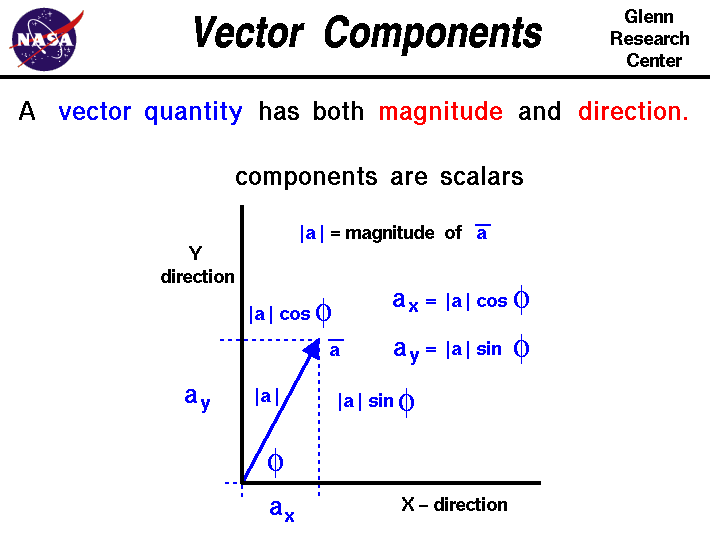
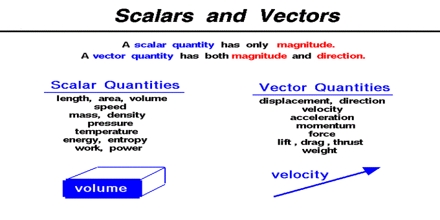
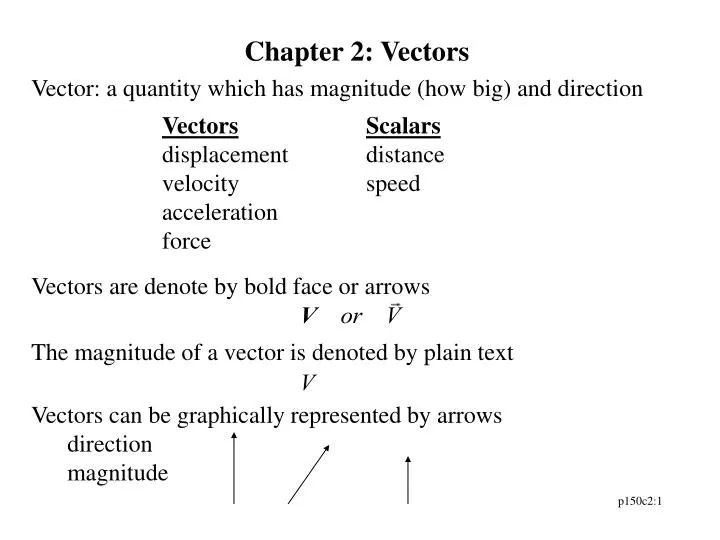
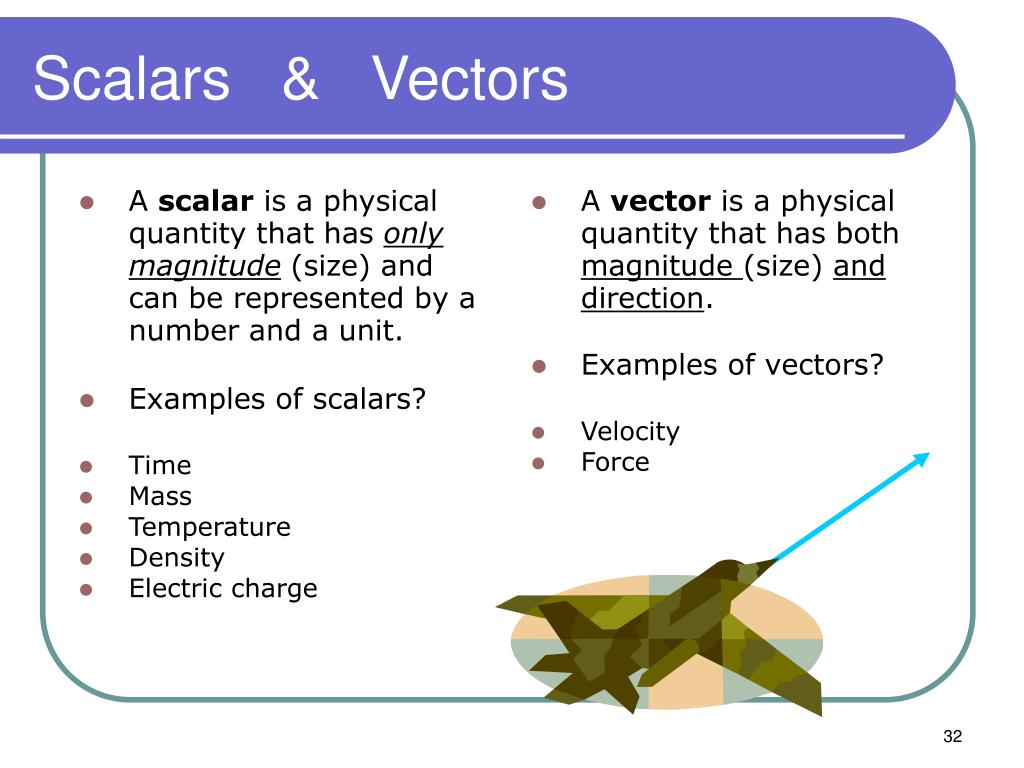
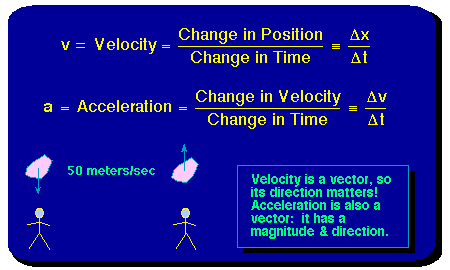
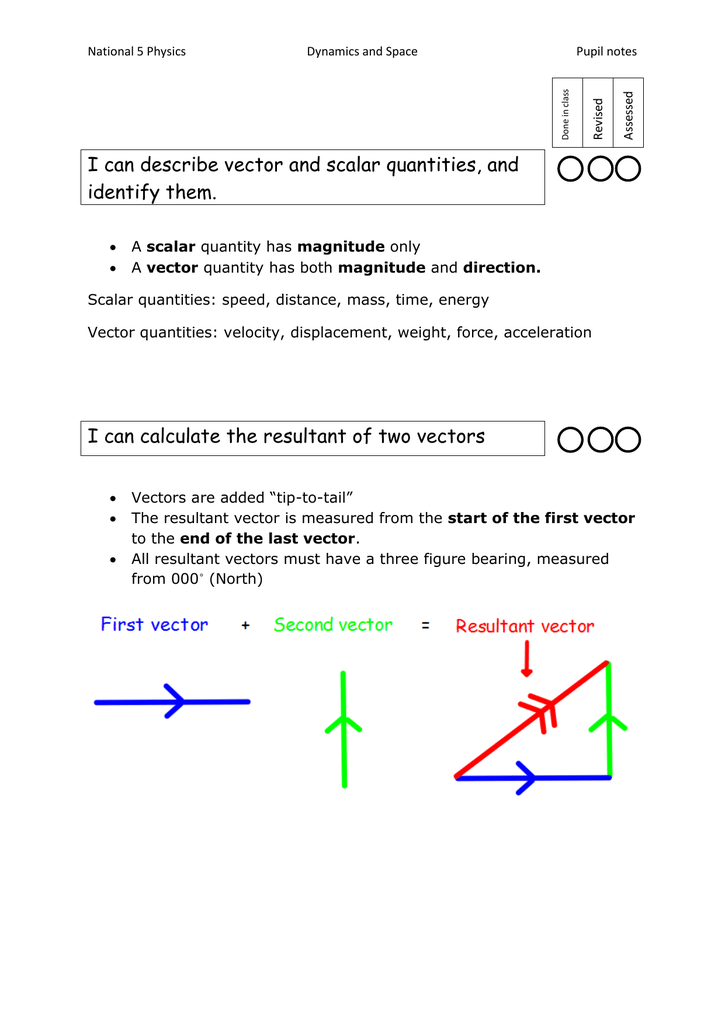
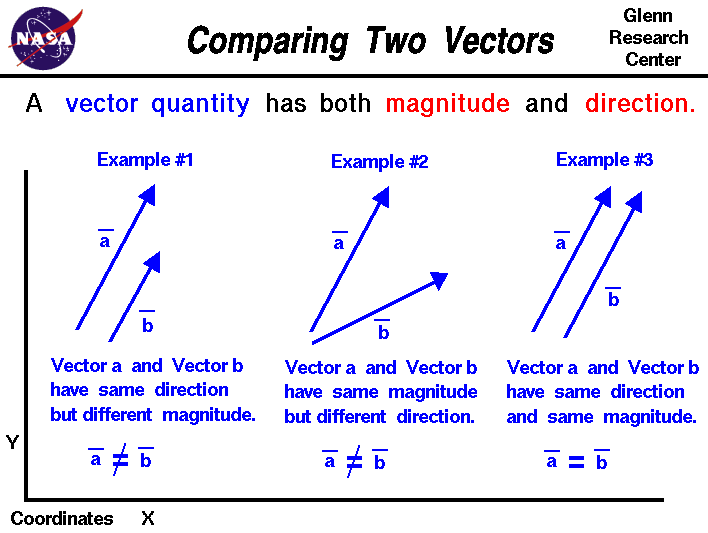
A vector is a quantity that has. Vector quantities have two characteristics a magnitude and a direction. Examples of vectors in nature are velocity momentum force electromagnetic fields and weight. A quantity which does not depend on direction is called a scalar quantity. That makes velocity a vector quantity.
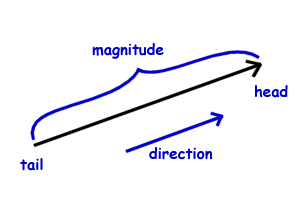
A vector is a quantity that has a. The direction of the arrow shows the direction of motion. The term also denotes the mathematical or geometrical representation of such a quantity. You can think about a vector as a directed line segment.
In this example the vector is called a displacement vector. A vector with the value of magnitude equal to one and direction is called unit vector represented. Momentum is a vector quantity. A vector is a quantity or phenomenon that has two independent properties.
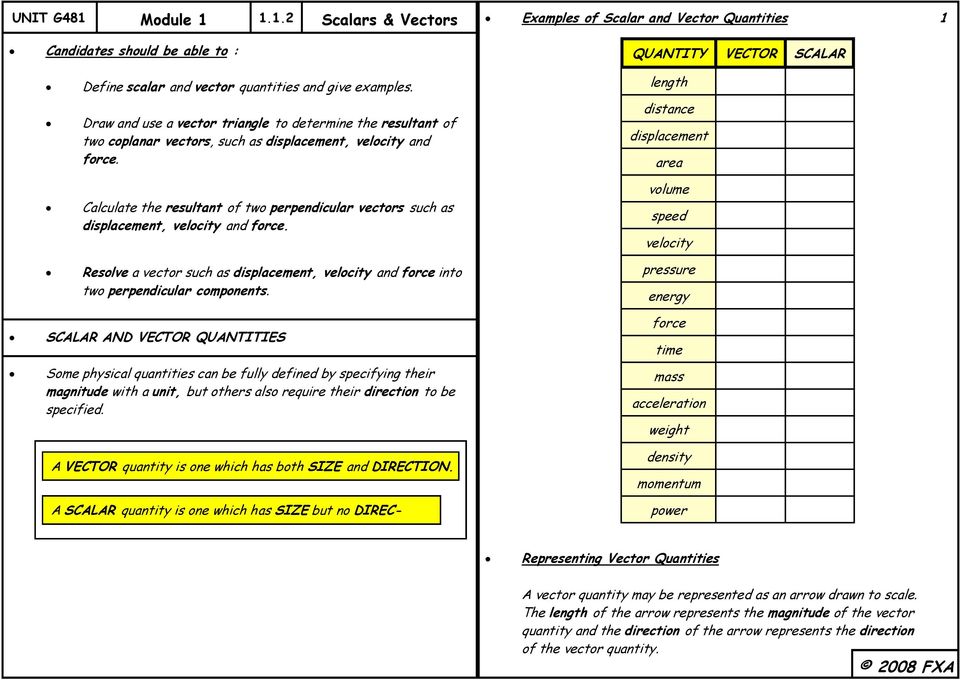
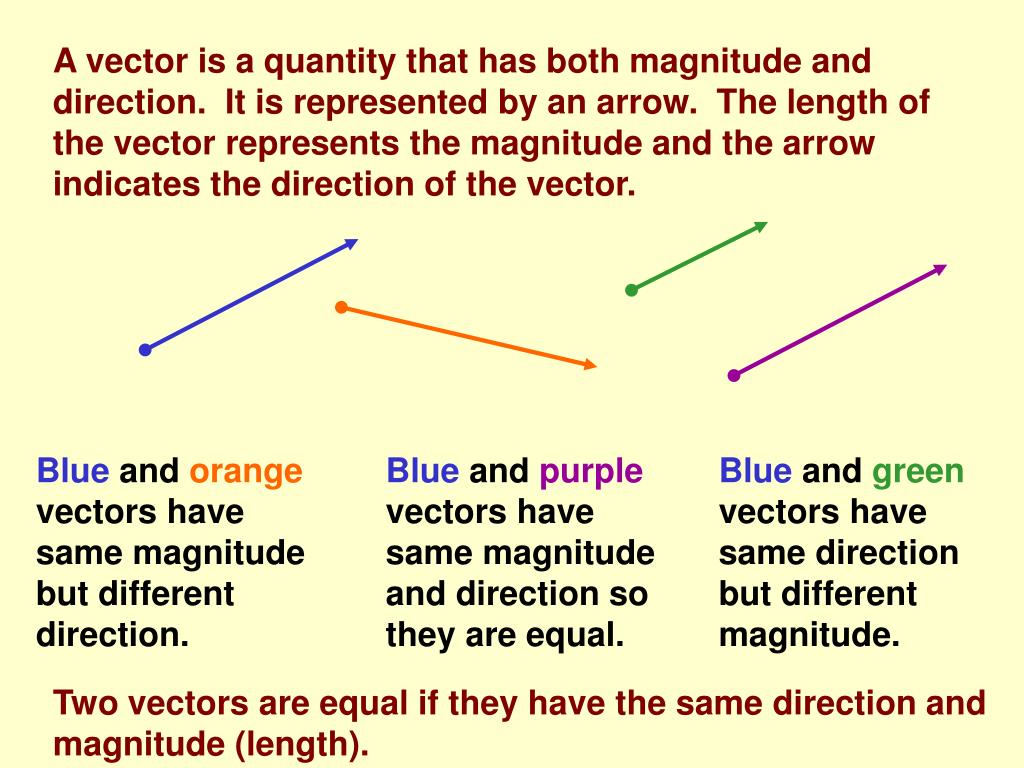
Although a vector has magnitude and direction it does not have position. That is as long as its length is not changed a vector is not altered if it is displaced parallel to itself. Magnitude and time b. A quantity that has magnitude and acts in a particular direction is described as vector.
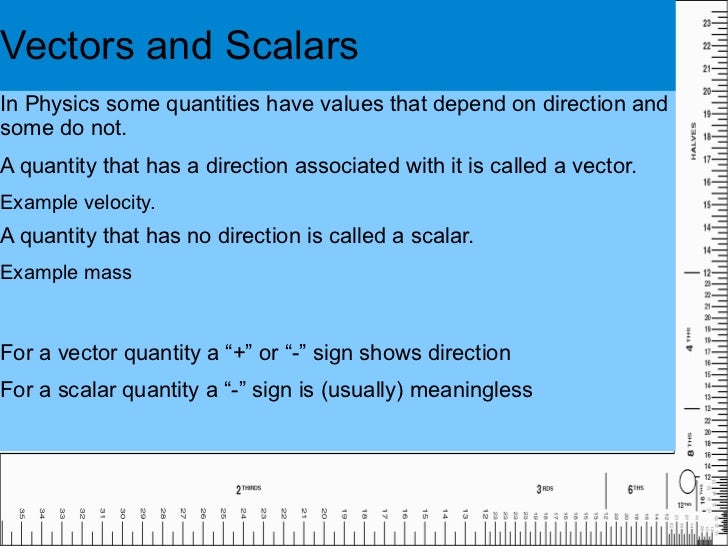
Mathematicians and scientists call a quantity which depends on direction a vector quantity. Scalar quantities only have magnitude size. A vector is a quantity that has magnitude and direction. We know that momentum is the product of mass and velocity and velocity has direction.
For example if you travel 20 miles northwest 20 miles is the magnitude and northwest is the direction. Vector in physics a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A vector quantity is defined as the physical quantity that has both direction as well as magnitude. A scalar is a quantity that has a.
When representing velocity as a vector a. Vector quantity in physics.



















































/GettyImages-533596181-1--57a0e6103df78c3276e56e07.jpg)