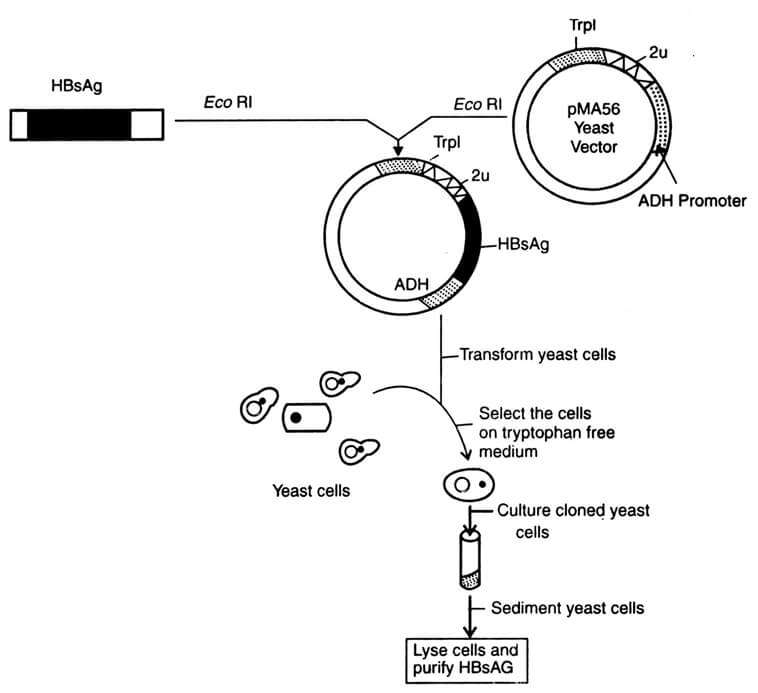
Recombinant Vector Vaccines Advantages And Disadvantages
Know more advantages and disadvantages of clinical trials.

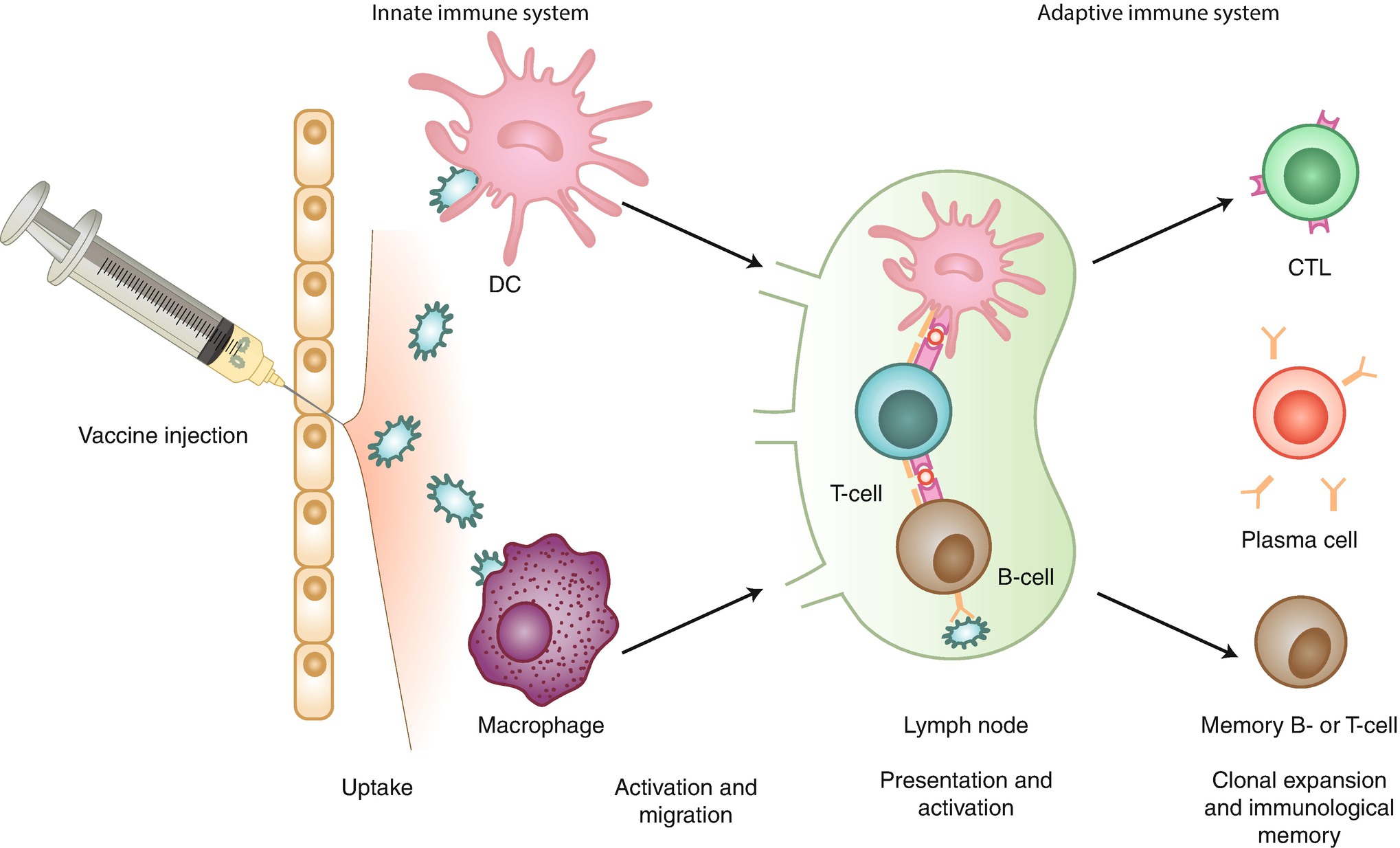
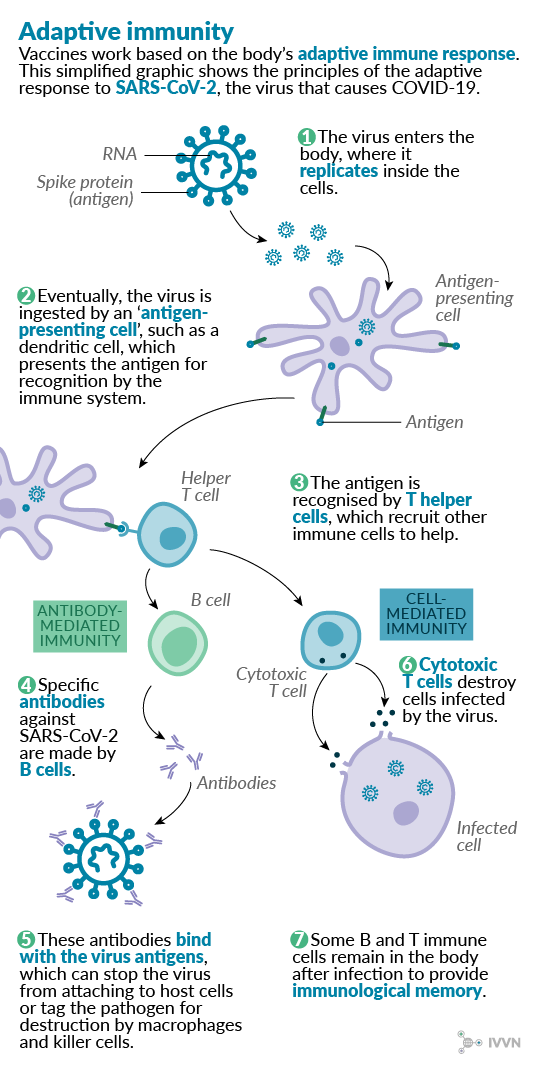
Recombinant vector vaccines advantages and disadvantages. Most modern vaccines introduce a small piece of a disease into the body so the body can develop ways to fight that particular disease. The vaccine to combat ebola is an example of a recombinant vaccine. From the perspective of viral replication the transgene is not only dispensable but may even be detrimental. All the approved vaccines have relatively low risk factors and are not produced with the real virus in any way.
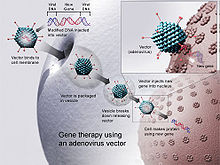
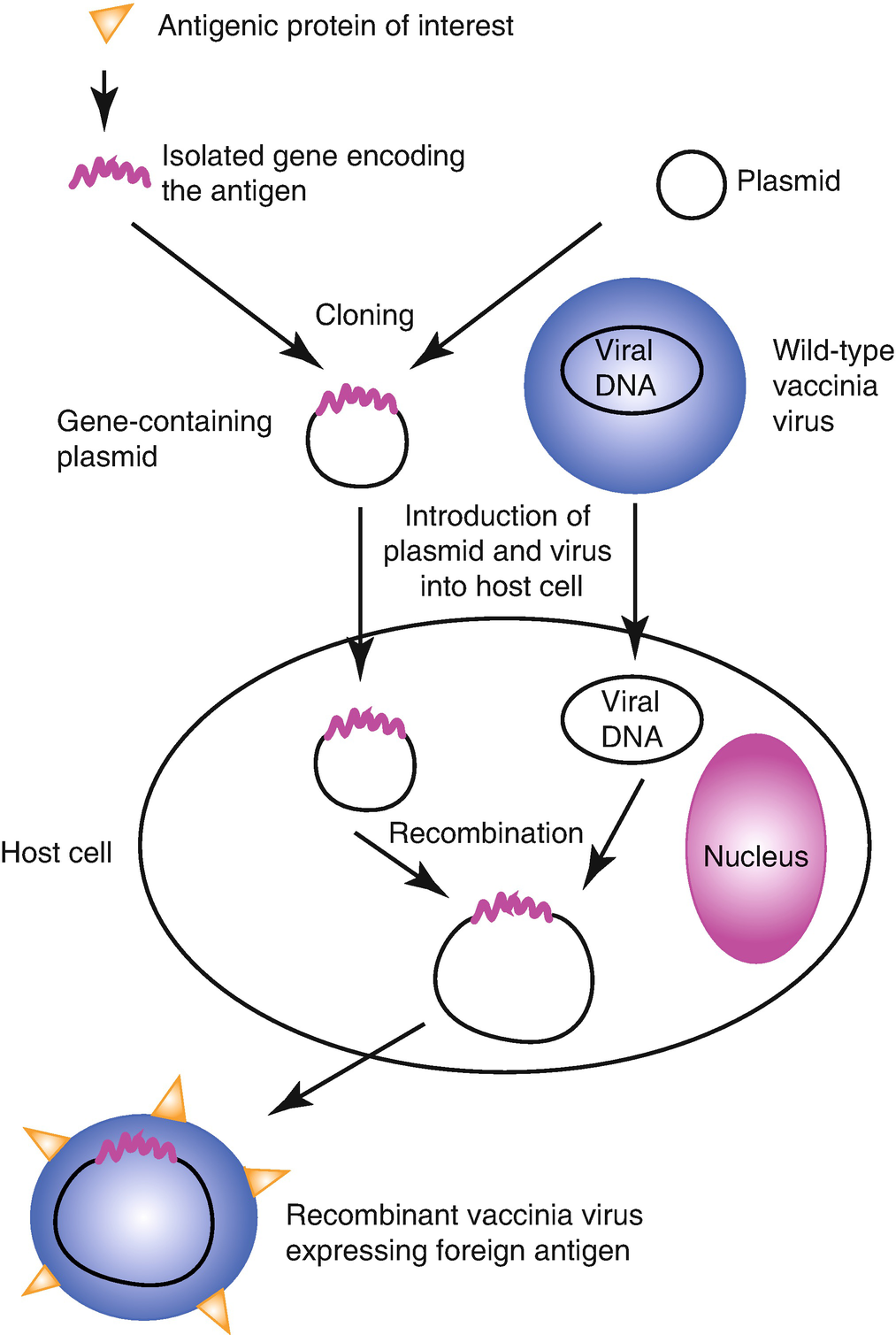
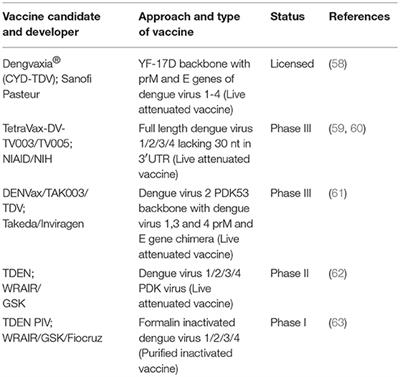
Several such recombinant vector vaccines are approved to protect animals from infectious diseases including rabies and distemper. Many of these veterinary vaccines are based on a technology developed by niaid researchers in the 1980s that uses weakened versions of a poxvirus to deliver the pathogens genetic material. They have protected so many children young adults and adults from hpv measles and many other viruses. Advantages of vaccines life saving.
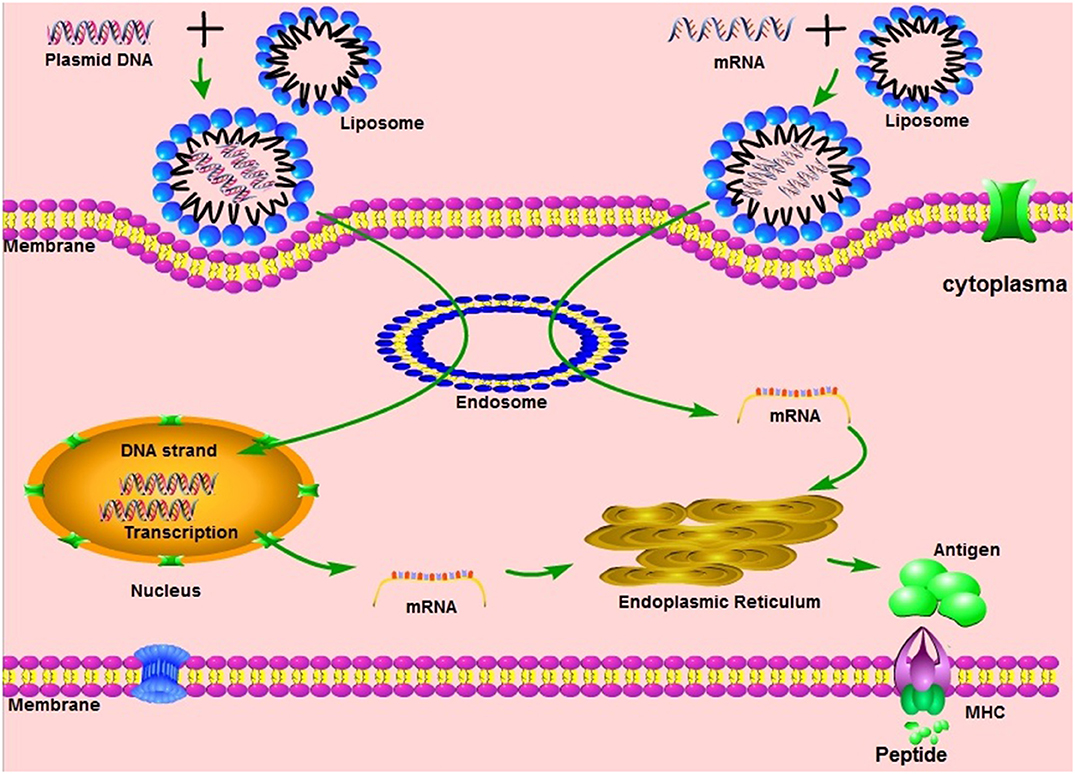
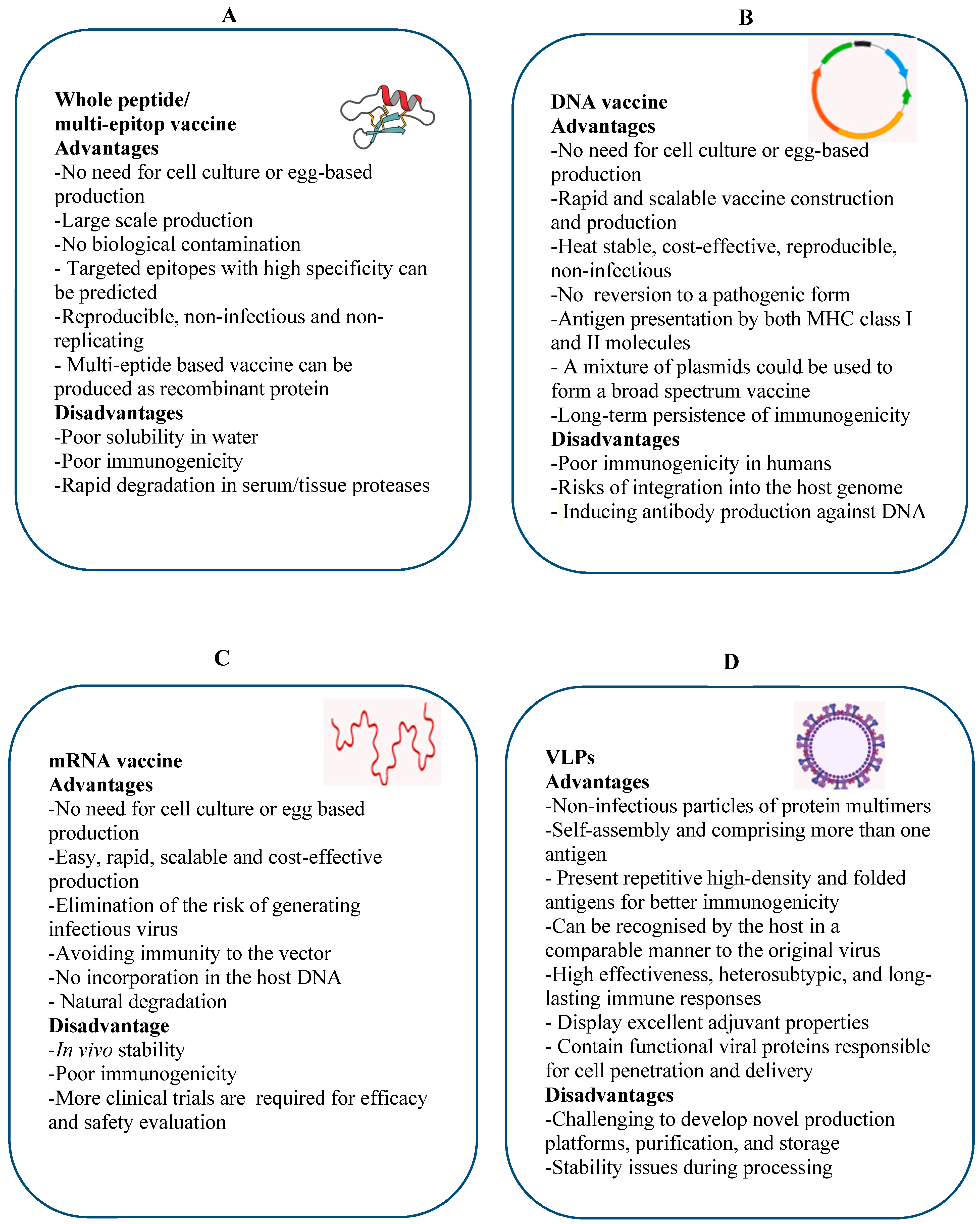
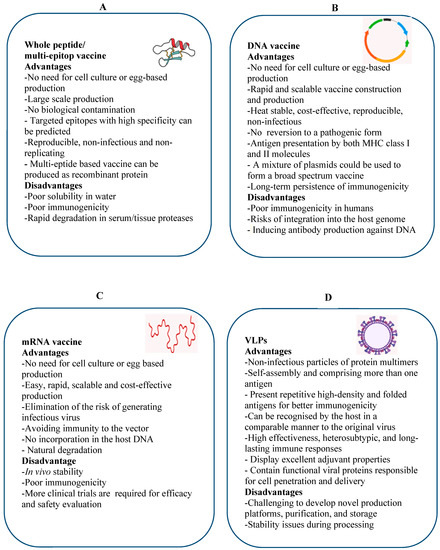
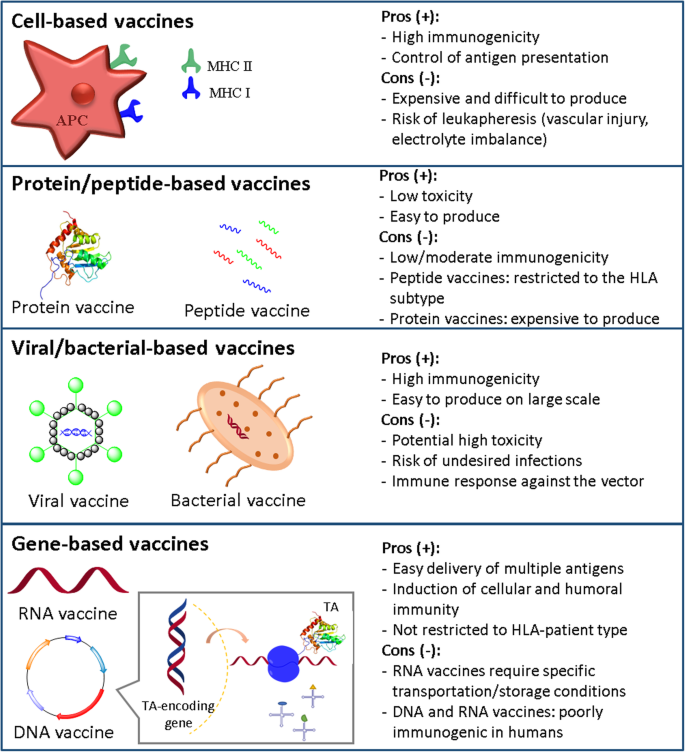
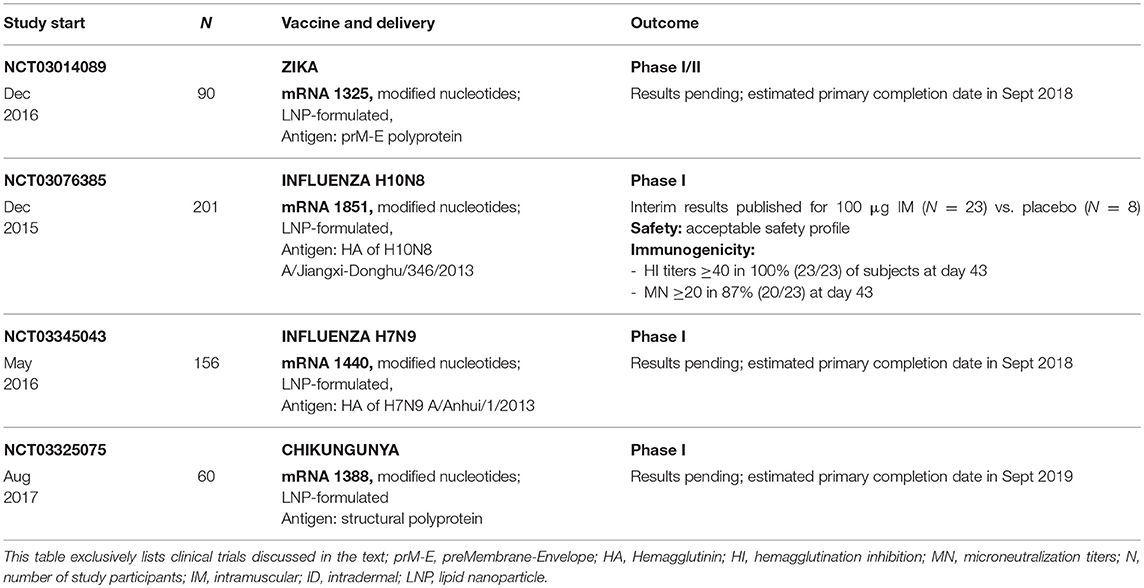
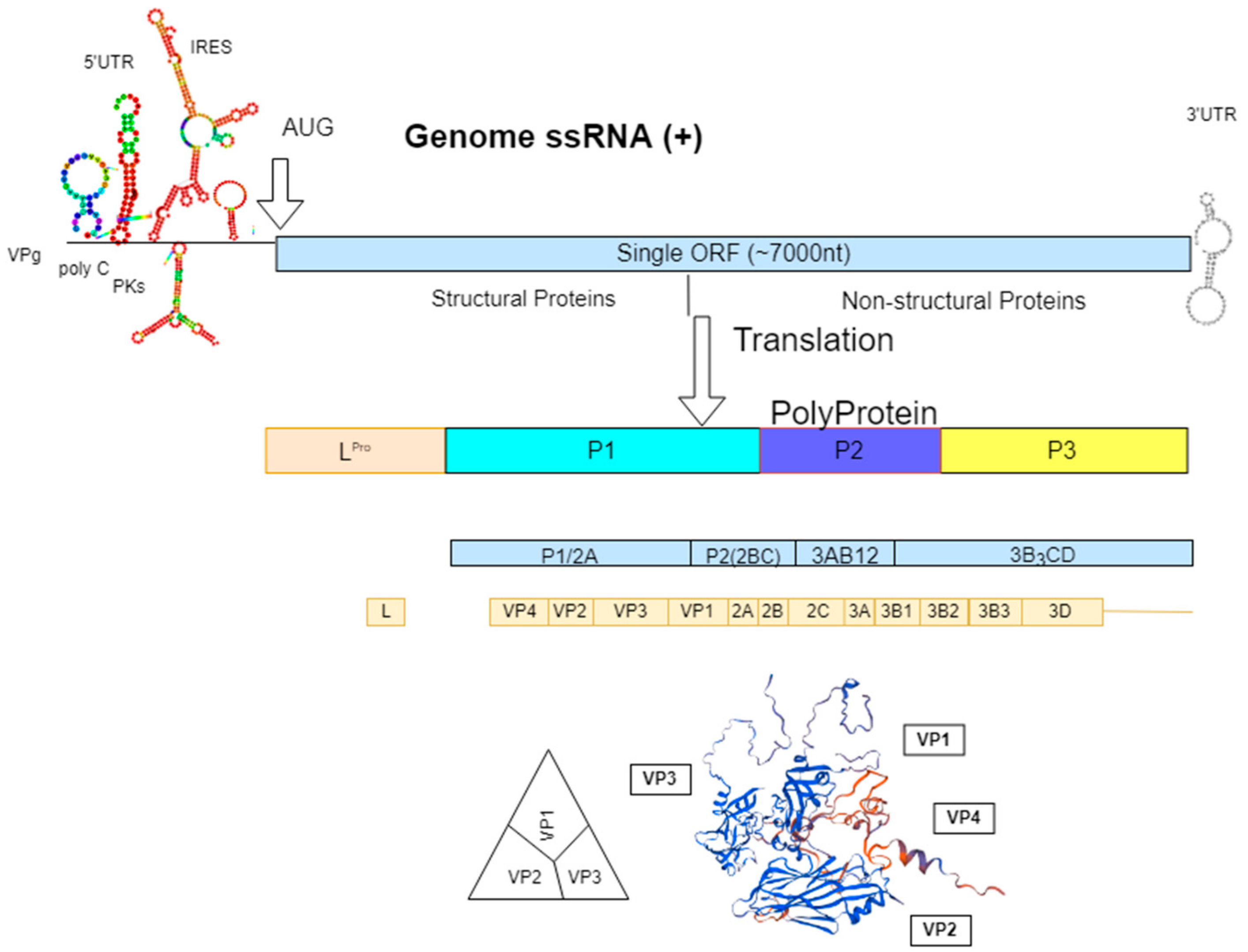
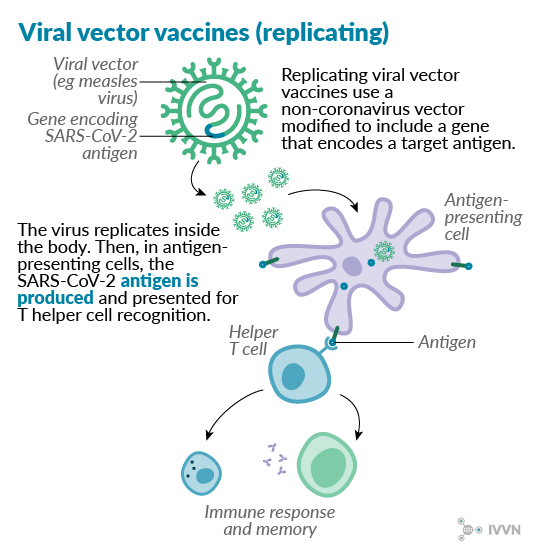
Scientists have been working to improve vaccines and produce new ones using recombinant dna technology. Replicating recombinant vector vaccines consist of a fully competent viral vector backbone engineered to express an antigen from a foreign transgene. The disadvantage is that a recombinant antigen on its own doesnt stimulate the immune system very well and needs to be supplemented with adjuvants to stimulate generation of antibodies against it. Dna vaccines are not in use yet.


































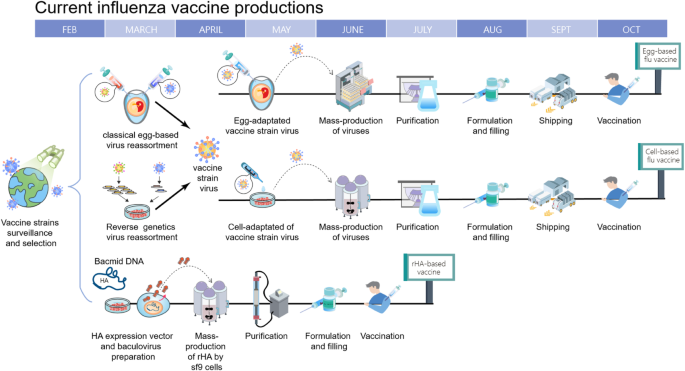

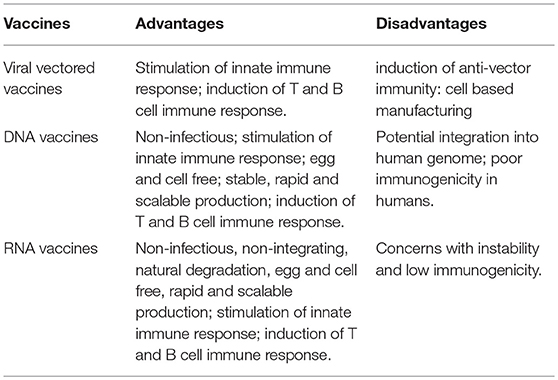
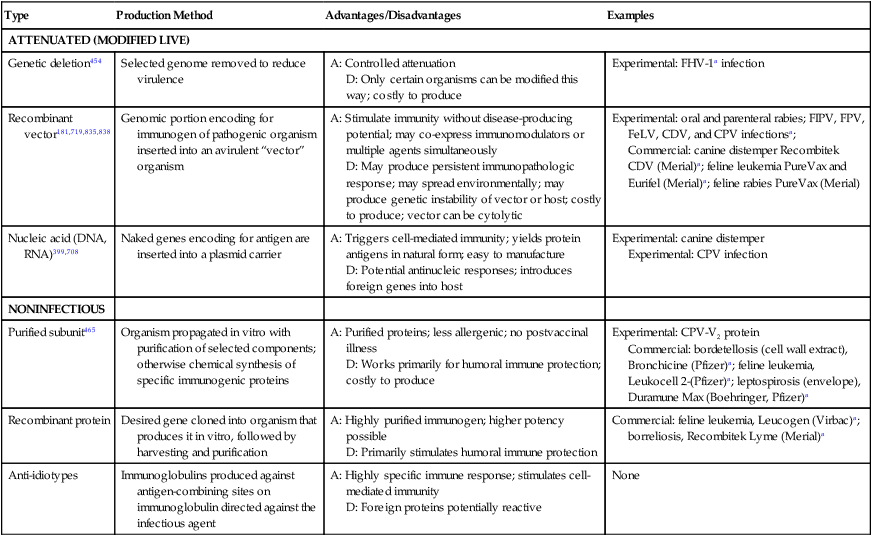

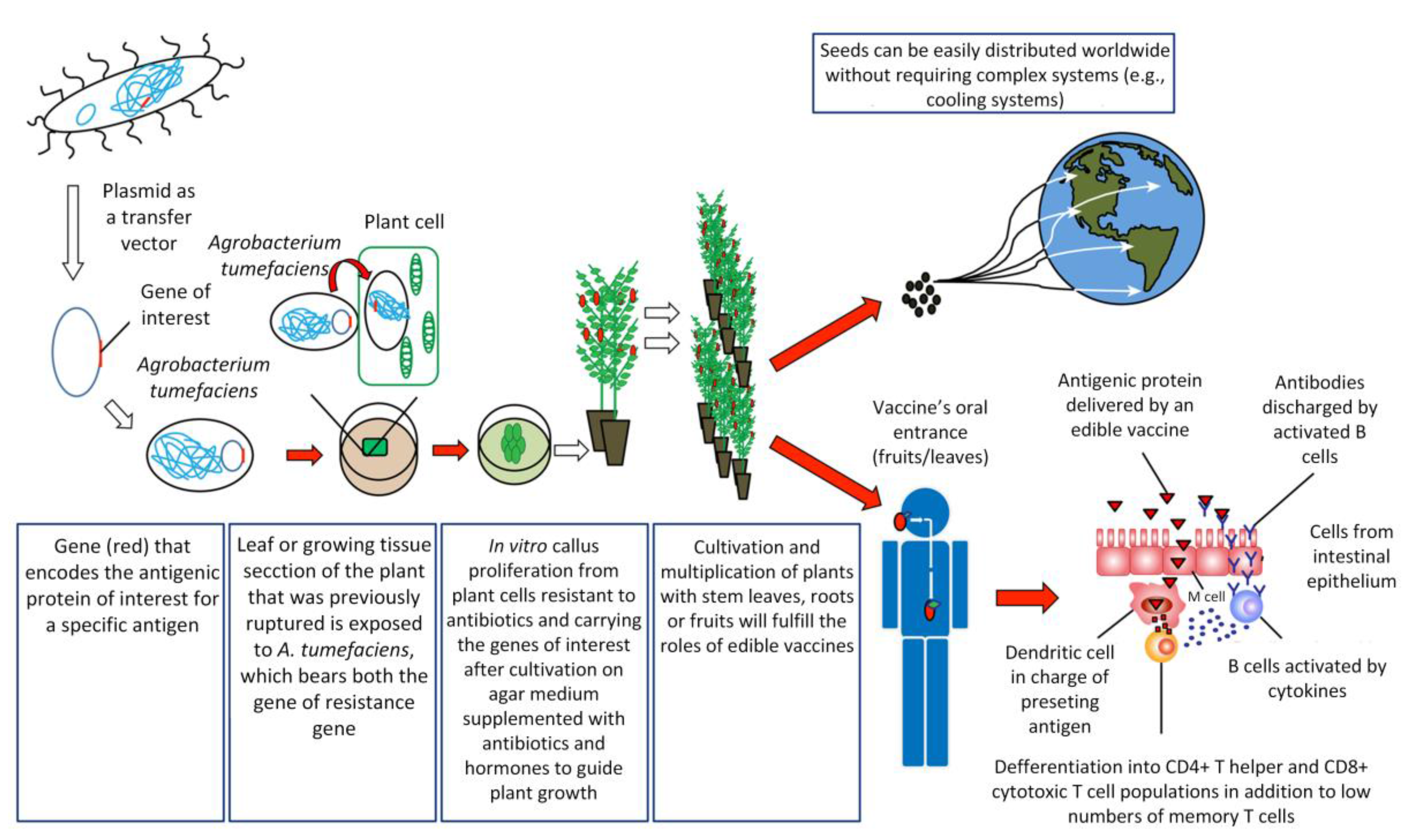



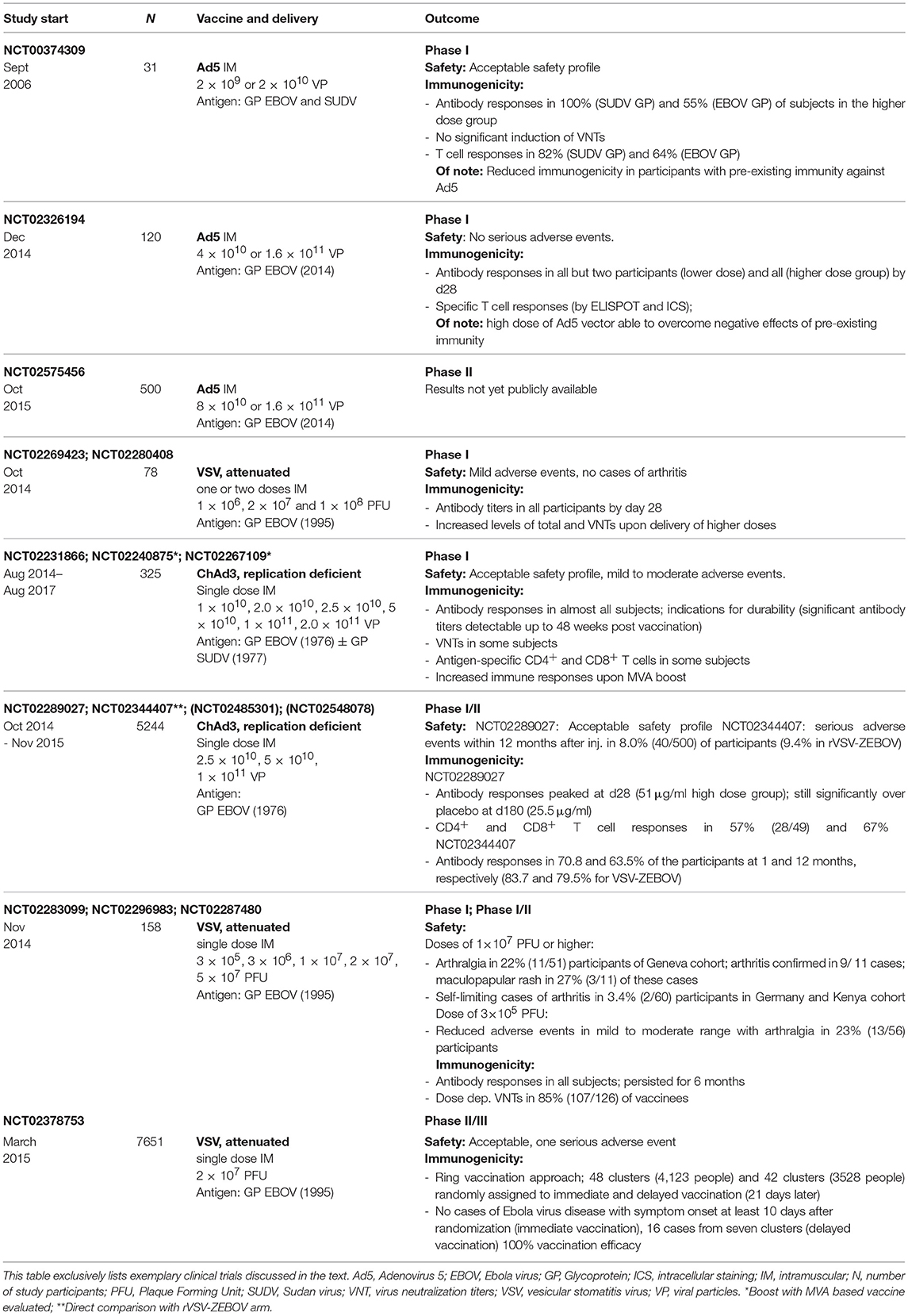










.jpg)