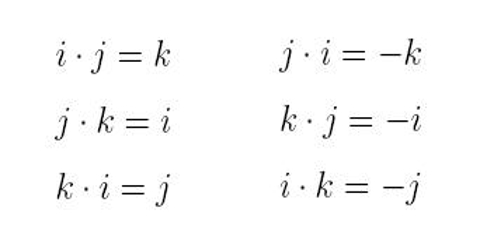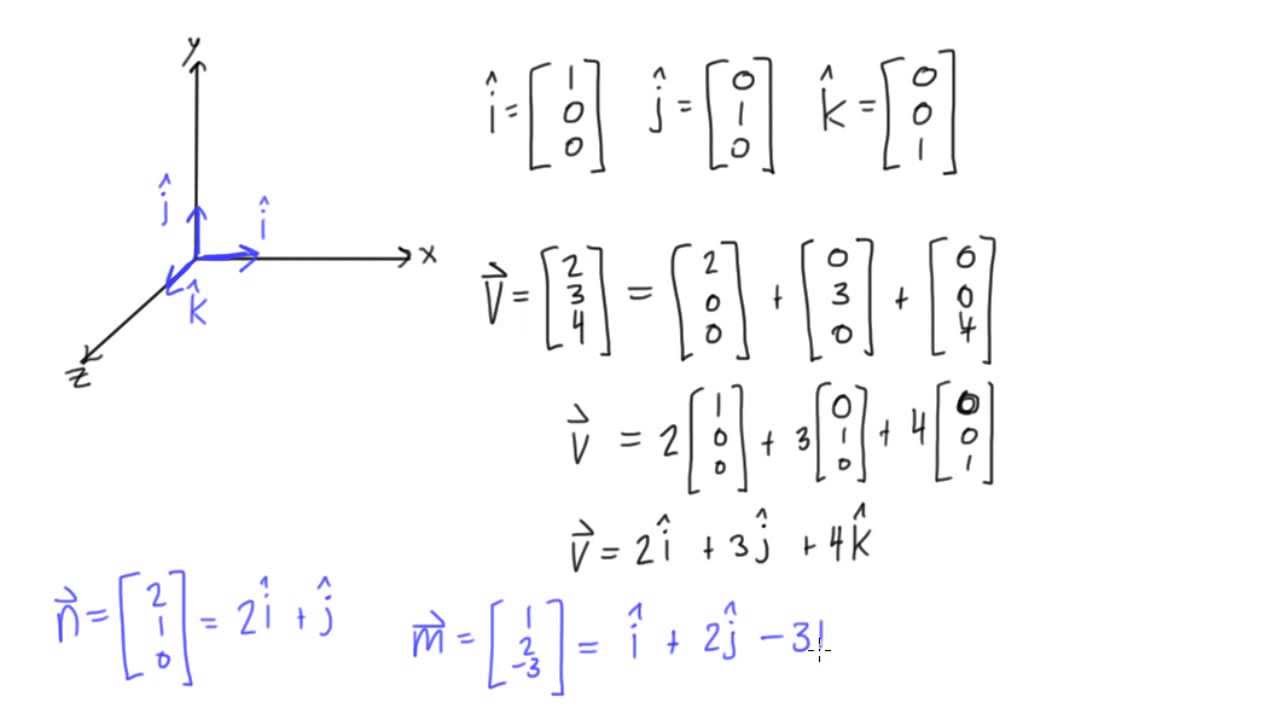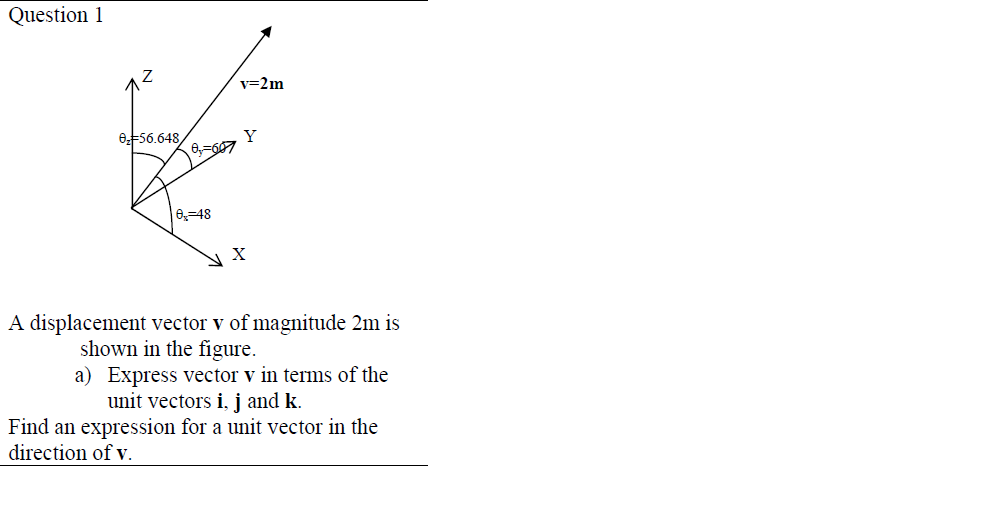Unit Vector I
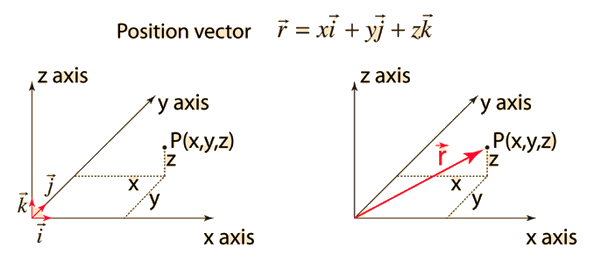
Vectors are often written in xyz coordinates.

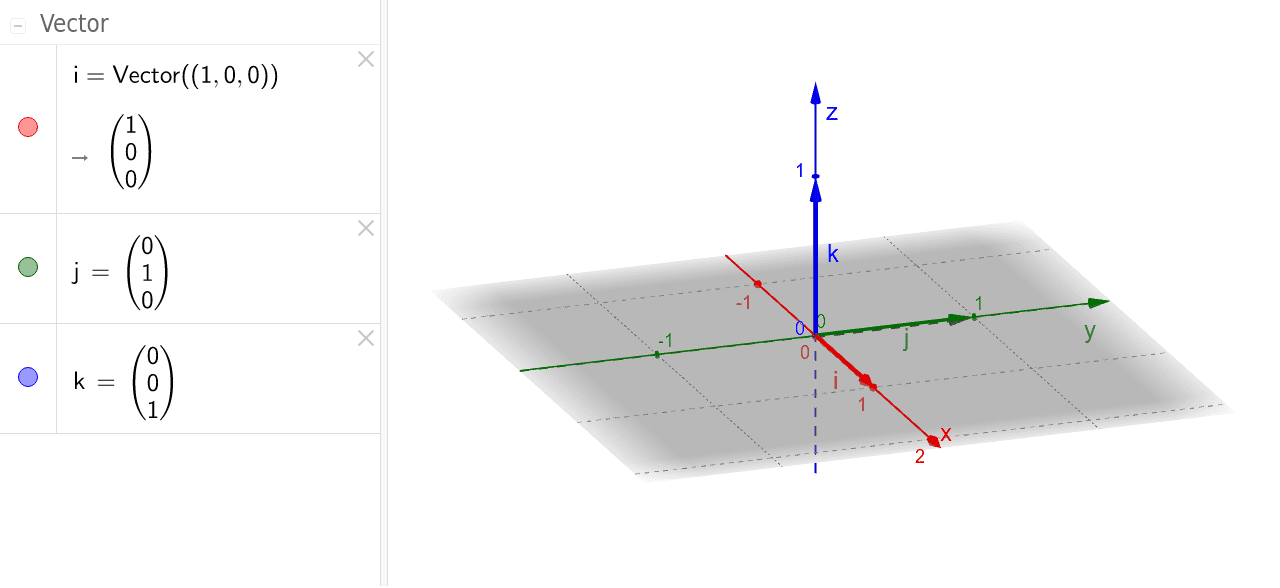
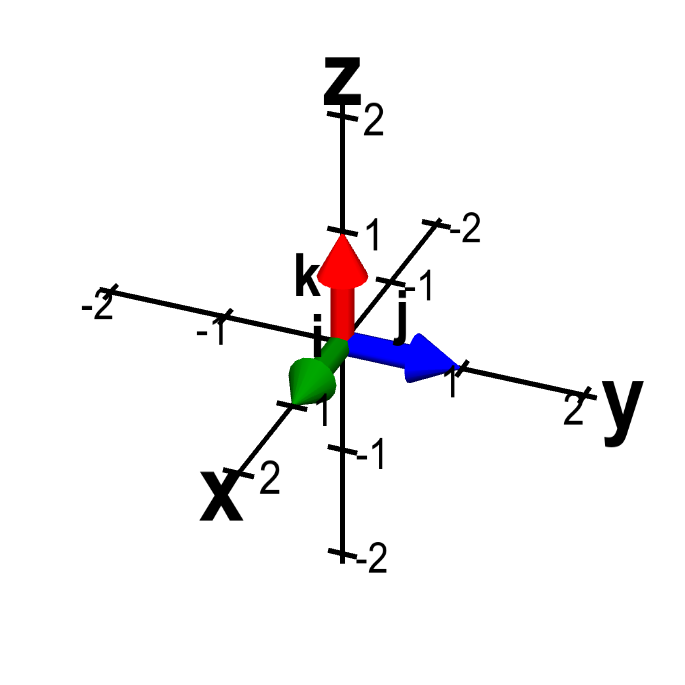
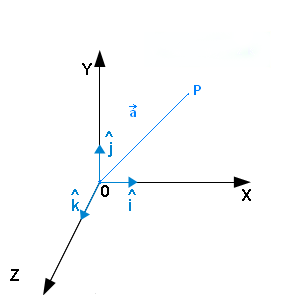
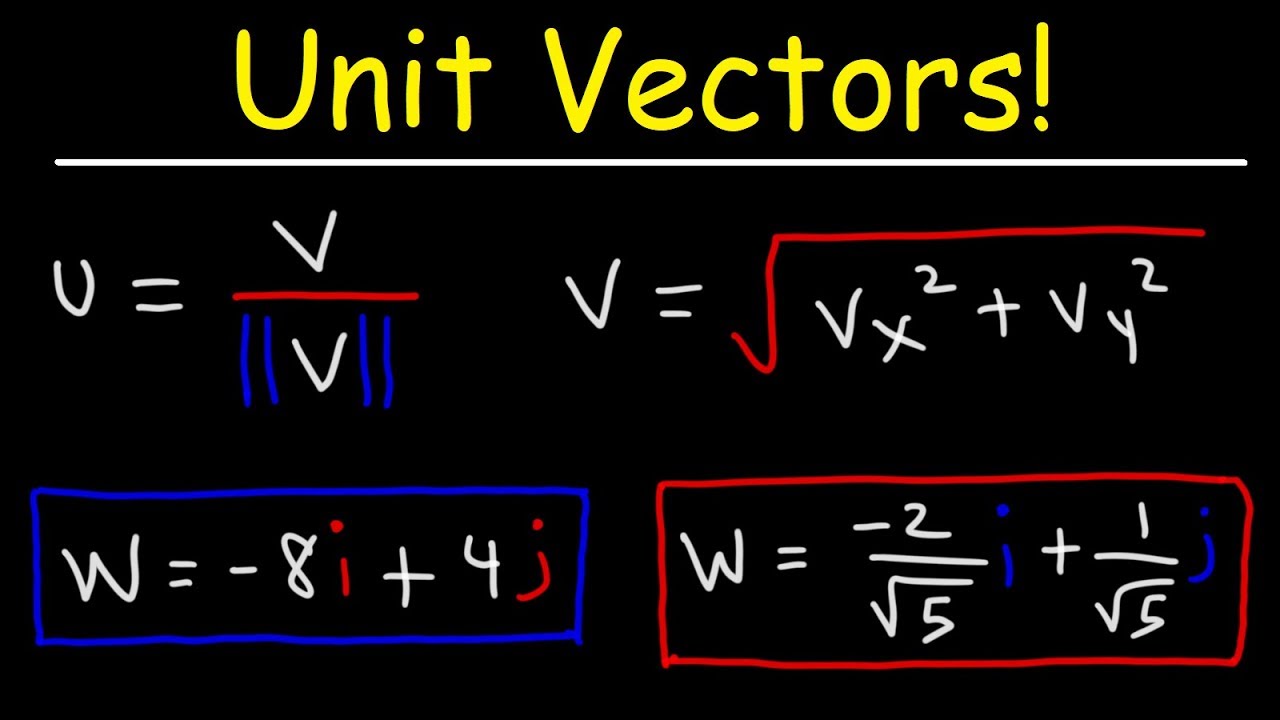
Unit vector i. I 10 and j 10 are called standard unit vectors. Note that this formula uses scalar multiplication because the numerator is a vector and the denominator. Unit vector in mathematics unit vector refers to the normal vector space often a spatial vector of length 1. A vector can be scaled off the unit vector.
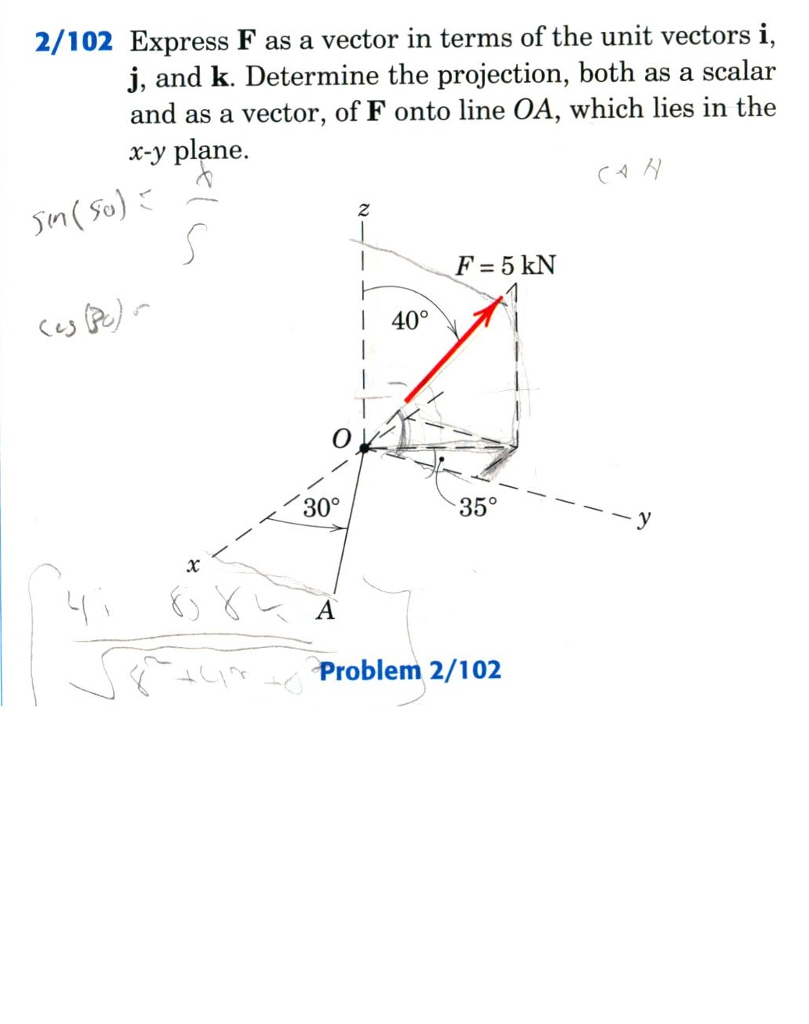
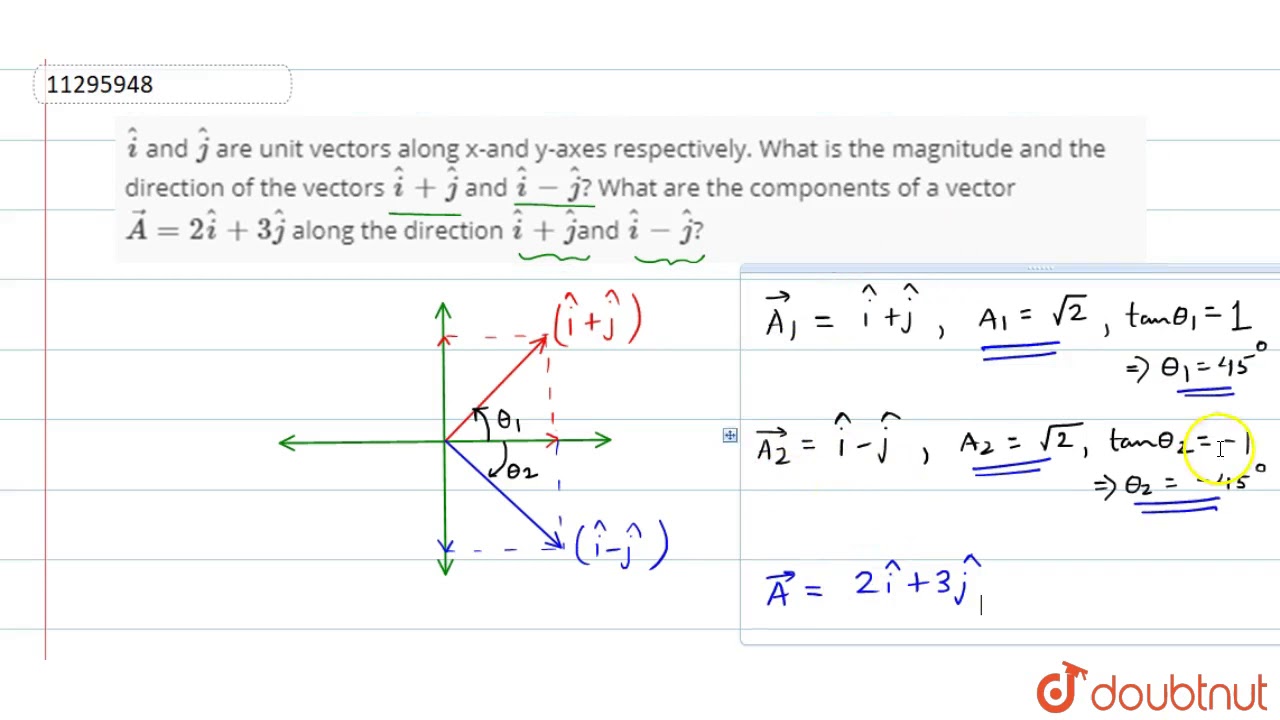
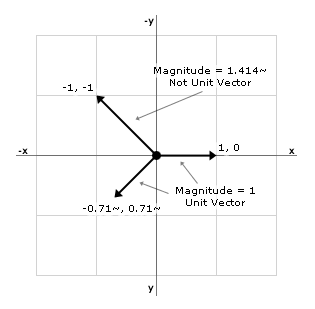
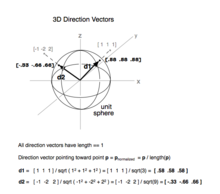
Unit vectors are useful in defining the direction of any vector. A unit vector is a vector that has a magnitude of 1. They are labeled with a for example. I 10 is a unit vector in the direction of the x axis.
We define two special unit coordinate vectors. Usually we use the term direction vector to describe a unit vector to represent the spatial vector. In mathematics a unit vector in a normed vector space is a vector often a spatial vector of length 1. Moreover we use a lowercase letter with a circumflex or hat pronunciation i hat.
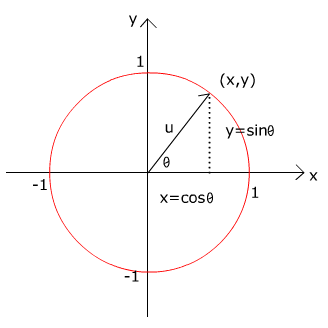
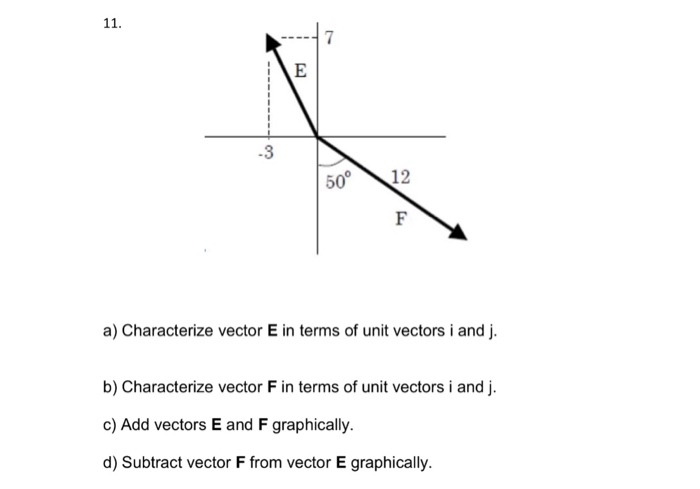
Unit vectors can be used in 2 dimensions. Here vector a is shown to be 25 times a unit vector. Displaystyle hat imath pronounced i hat. It is also known as direction vector.
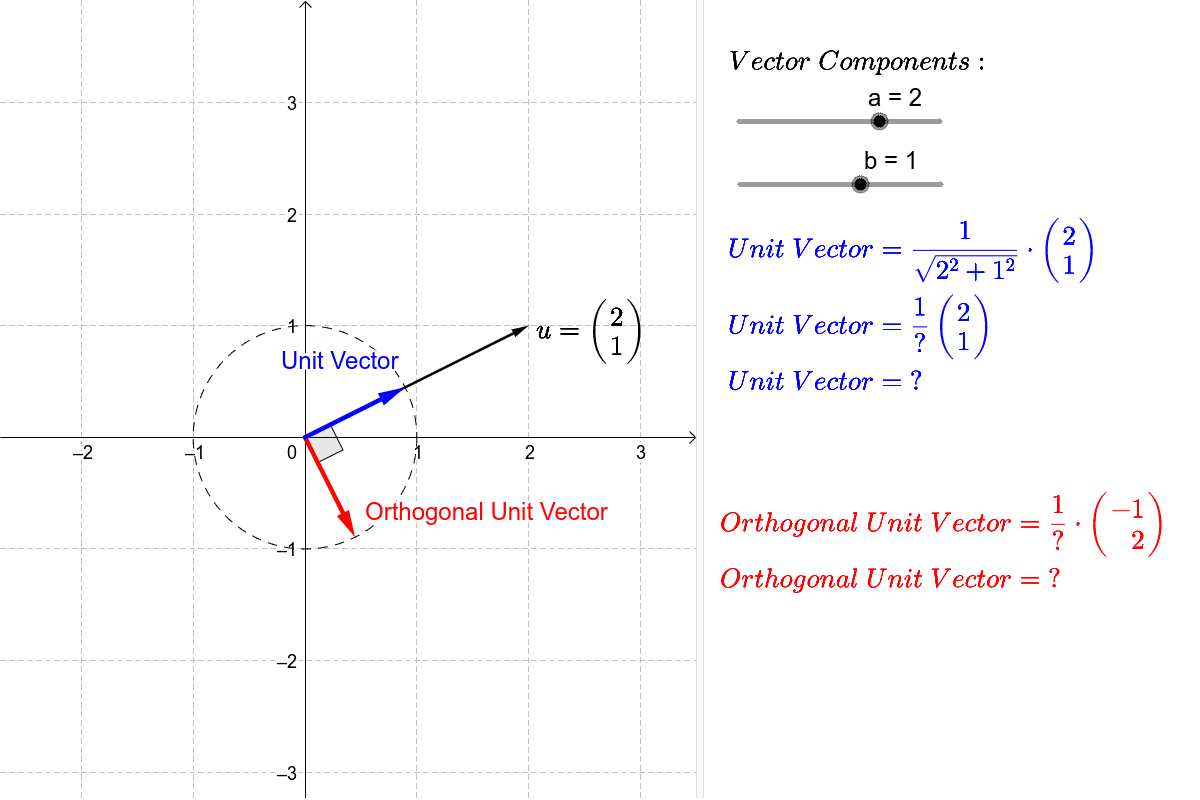
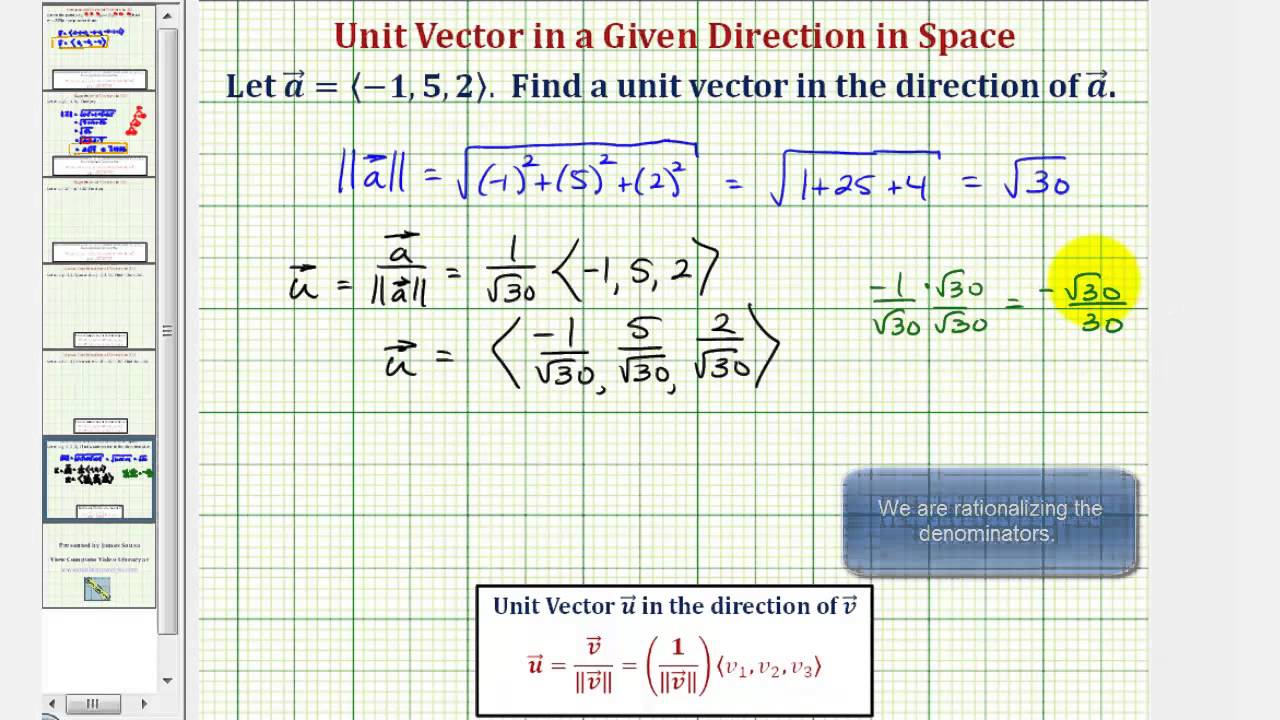
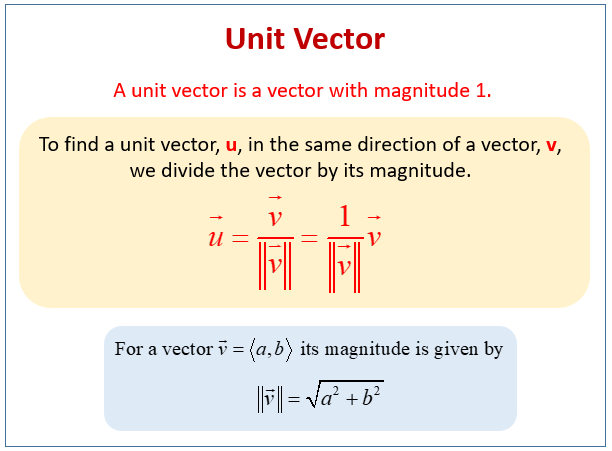
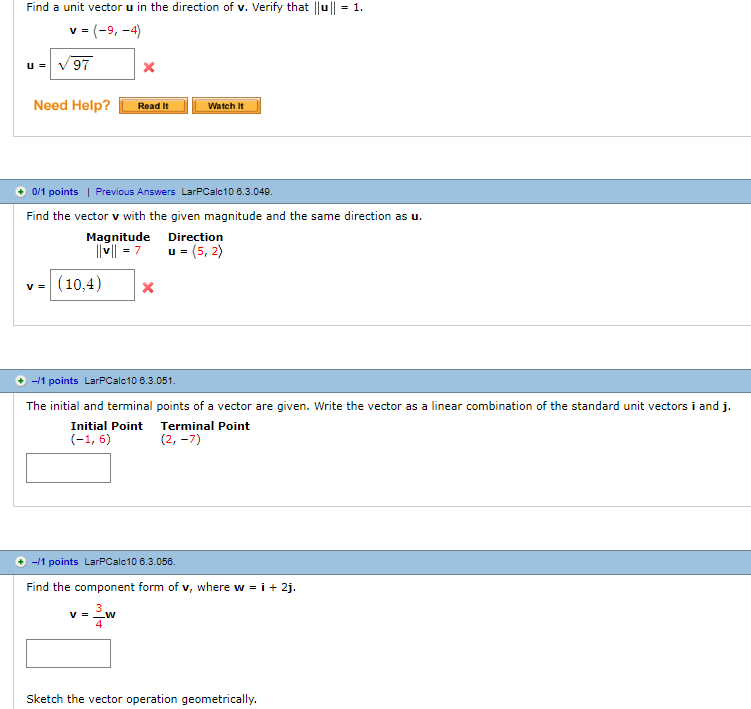
Notice they still point in the same direction. A vector which has a magnitude of 1 is a unit vector. To find the unit vector u of the vector you divide that vector by its magnitude as follows. Unit vector a vector is a quantity which has both magnitudes as well as direction.
Every nonzero vector has a corresponding unit vector which has the same direction as that vector but a magnitude of 1. This can be done in two ways. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumflex or hat.