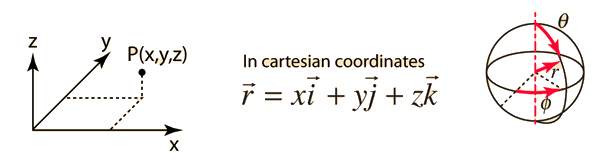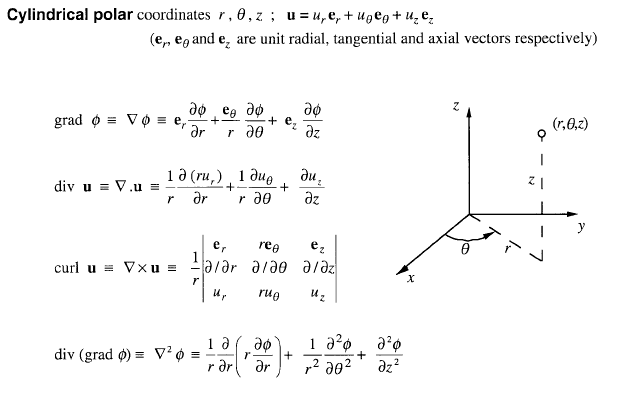Unit Vectors In Polar Coordinates
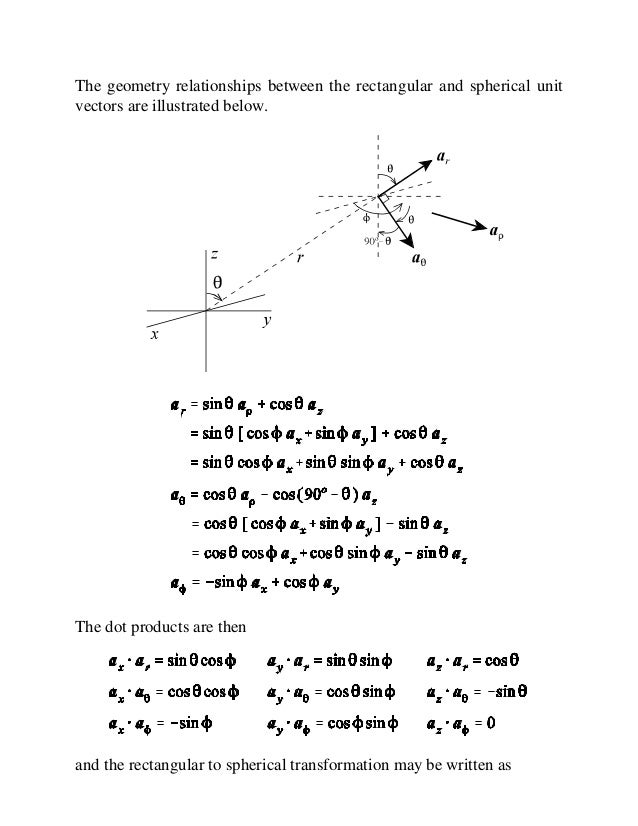
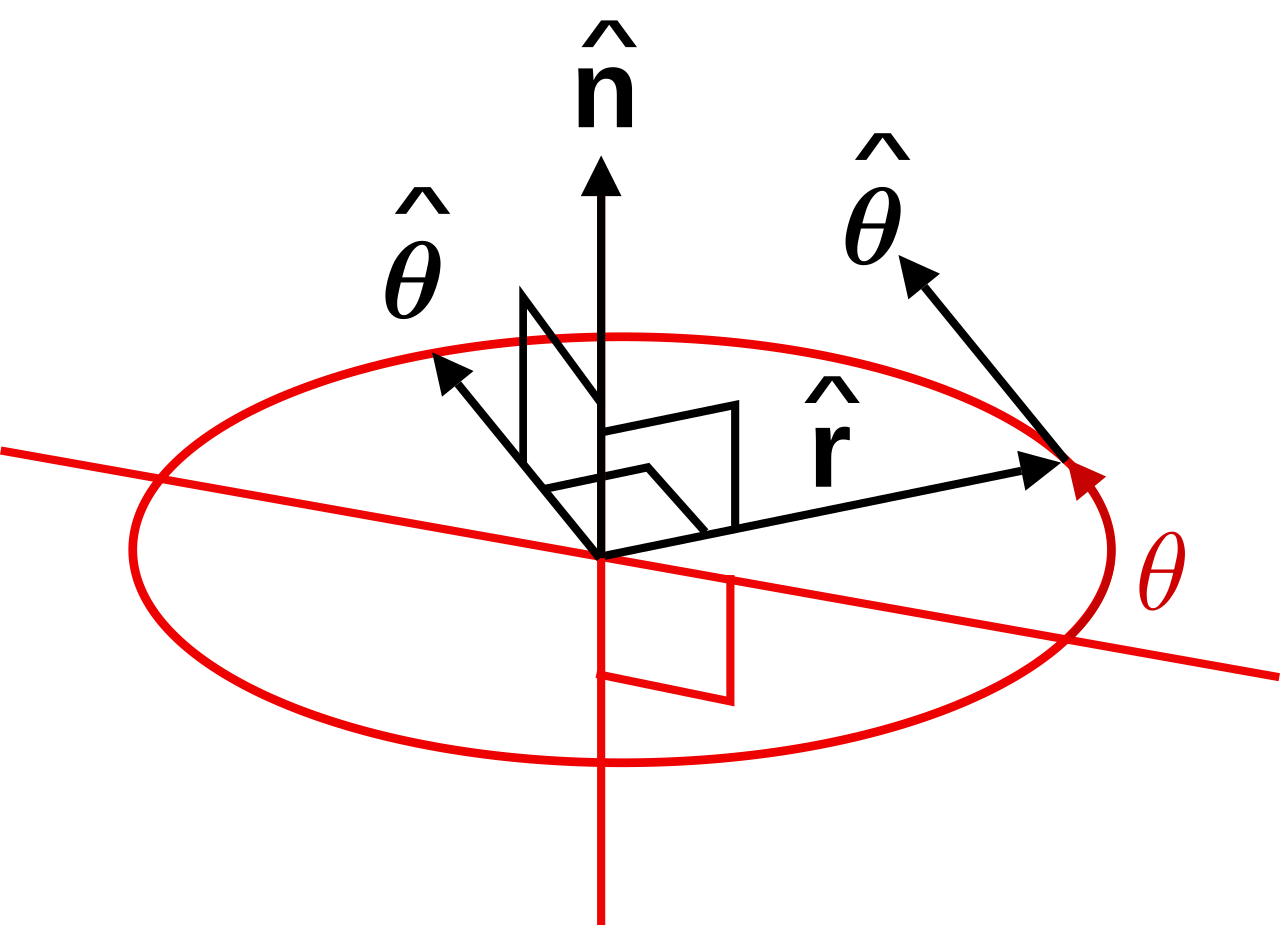
Specifically they are chosen to depend on the colatitude and azimuth angles.

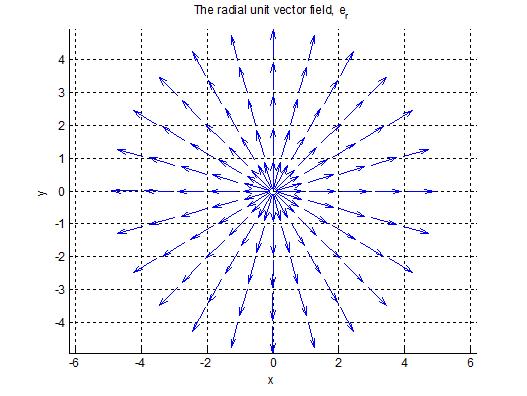
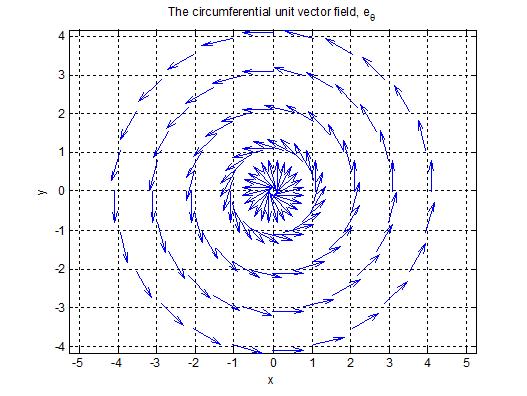
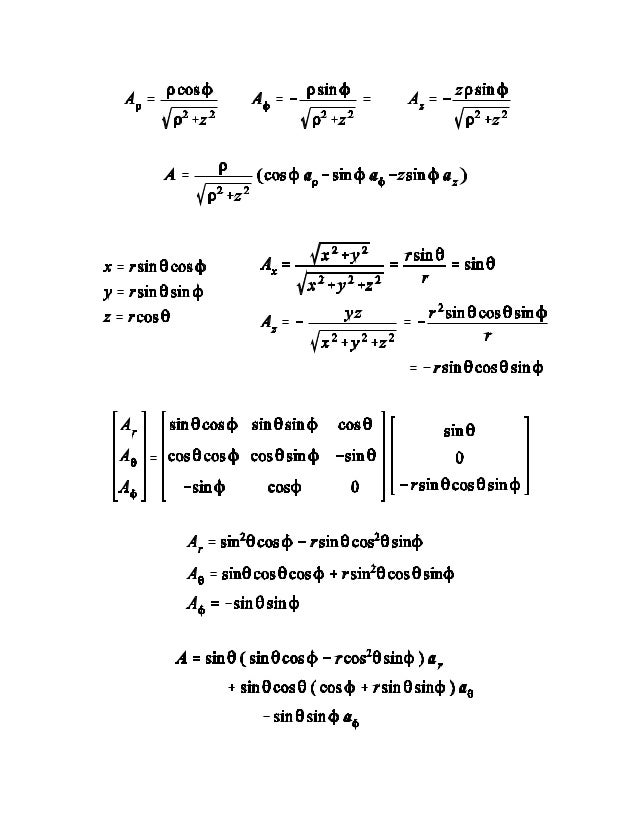
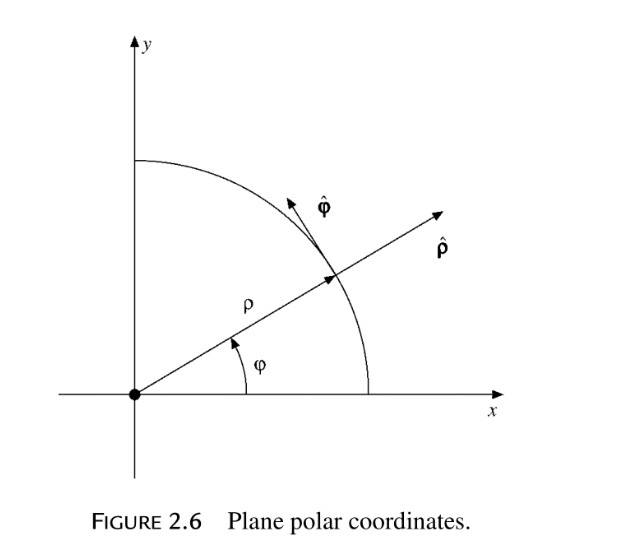
Unit vectors in polar coordinates. By substituting the formulas 4 and 5 for the polar unit vectors into this equation and simplifying you can verify that the equation is correct. Fo example p3 hat r. Velocity in polar coordinate. Ved a vector field in polar coordinates has the form ft0ft0u grug where the unit vectors are u cos isin e j and ug sinicos ej for r 0.
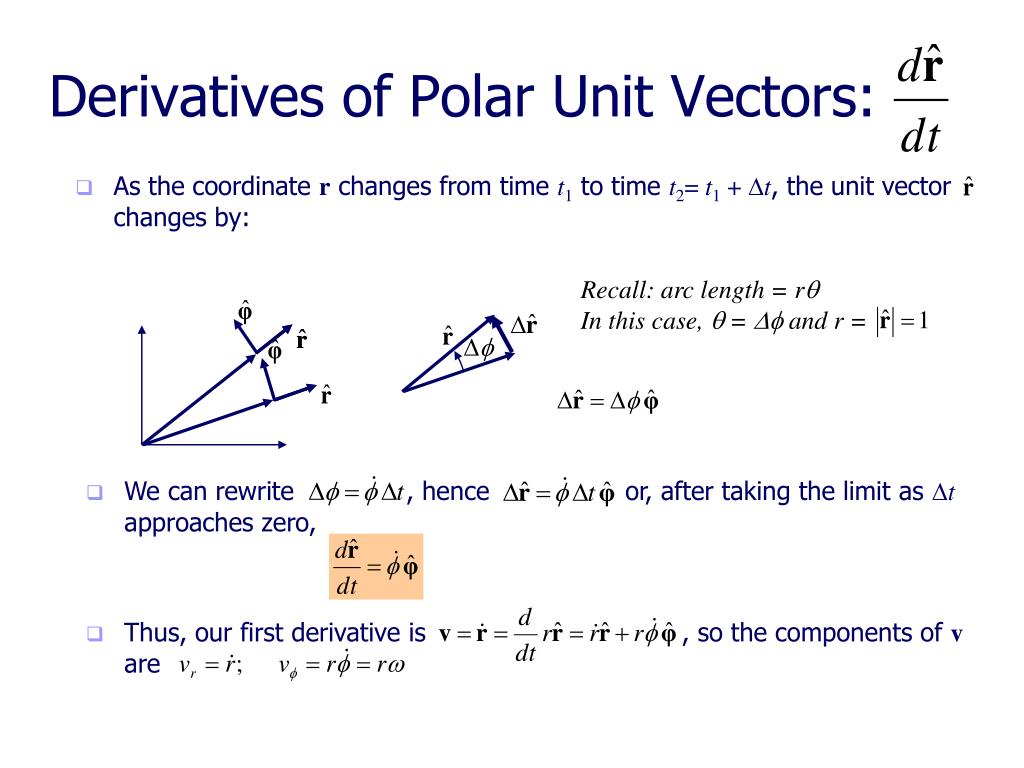
Roeoe t sinoe oeoe r dr oe oe dt tt therefore the velocity is given by. The radial coordinate is often denoted by r or r and the angular coordinate by f o or t. We only know it is 3 units away from the origin but dont know in which direction. E 3 cos d sin dir 3 sin d cos did.
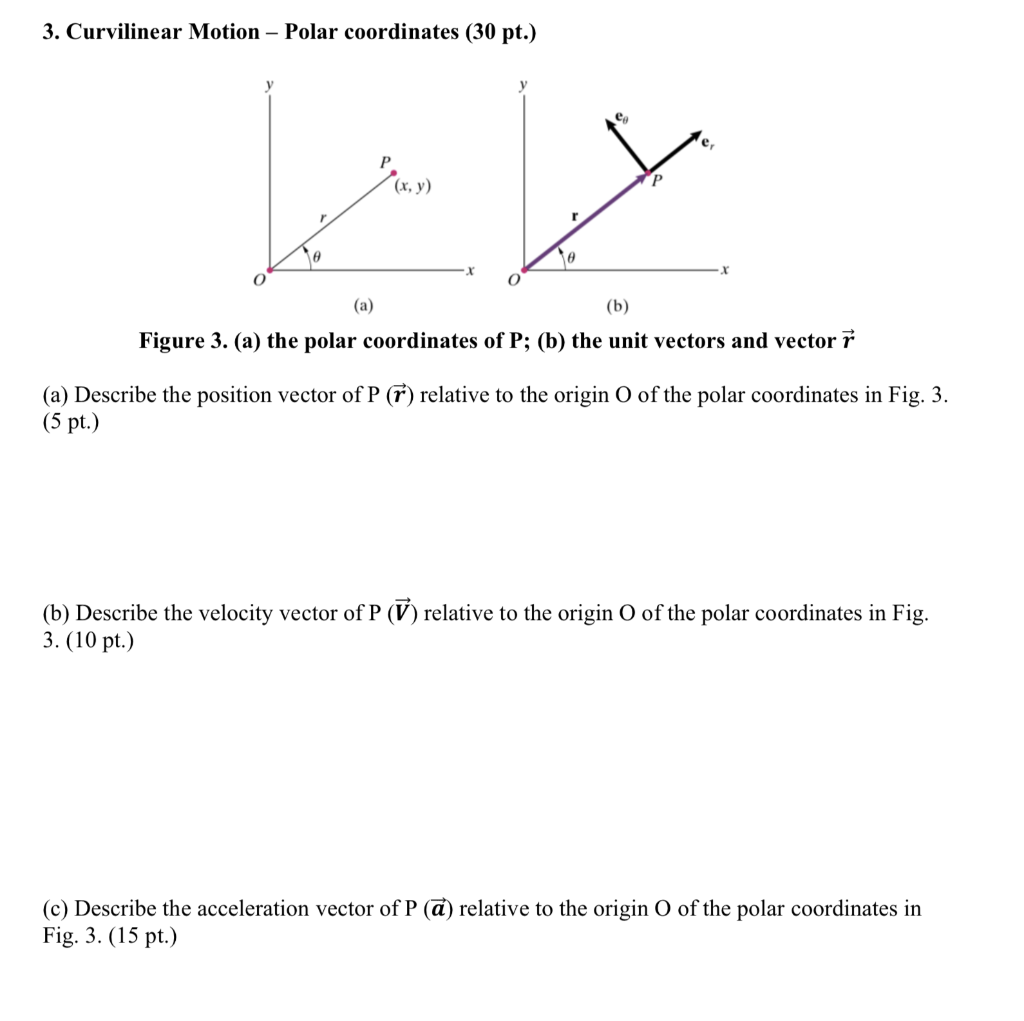
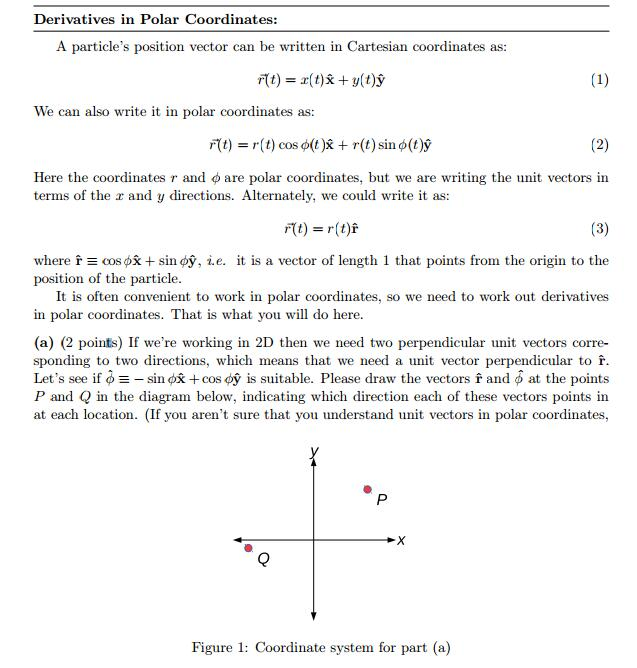
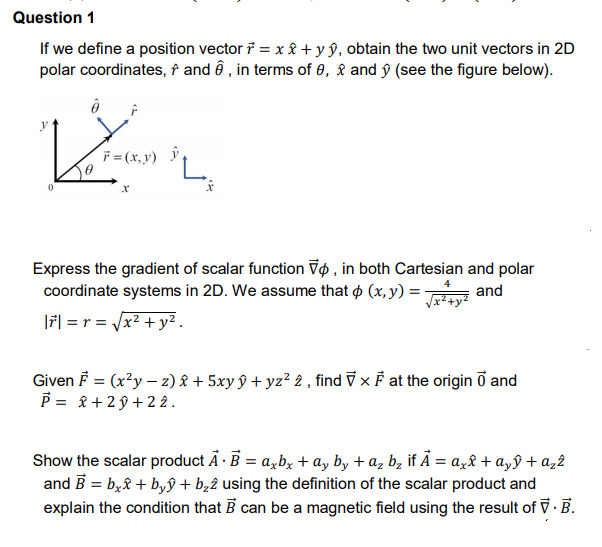
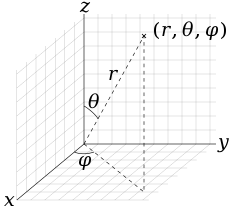
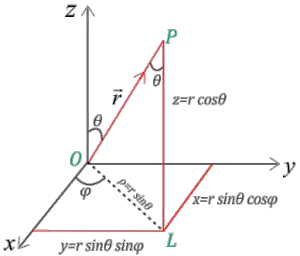
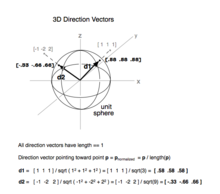
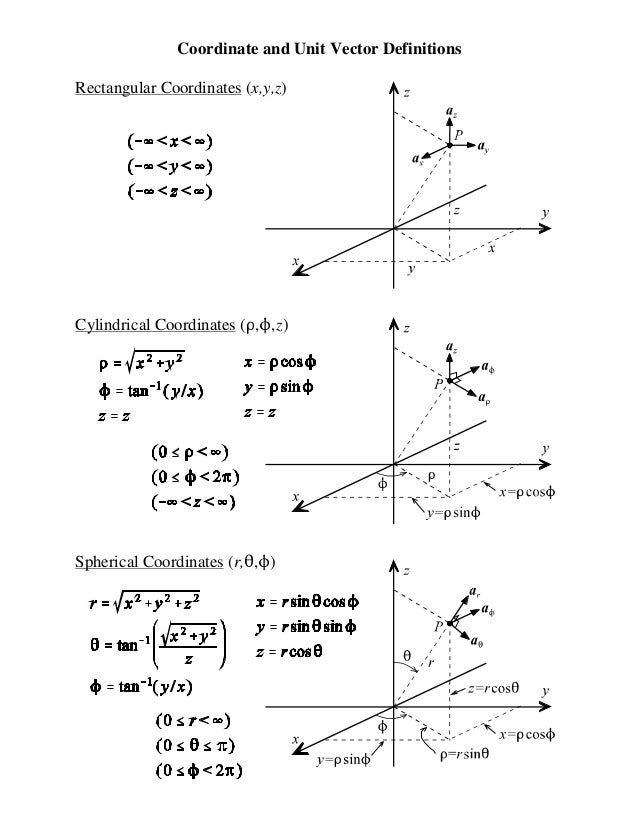
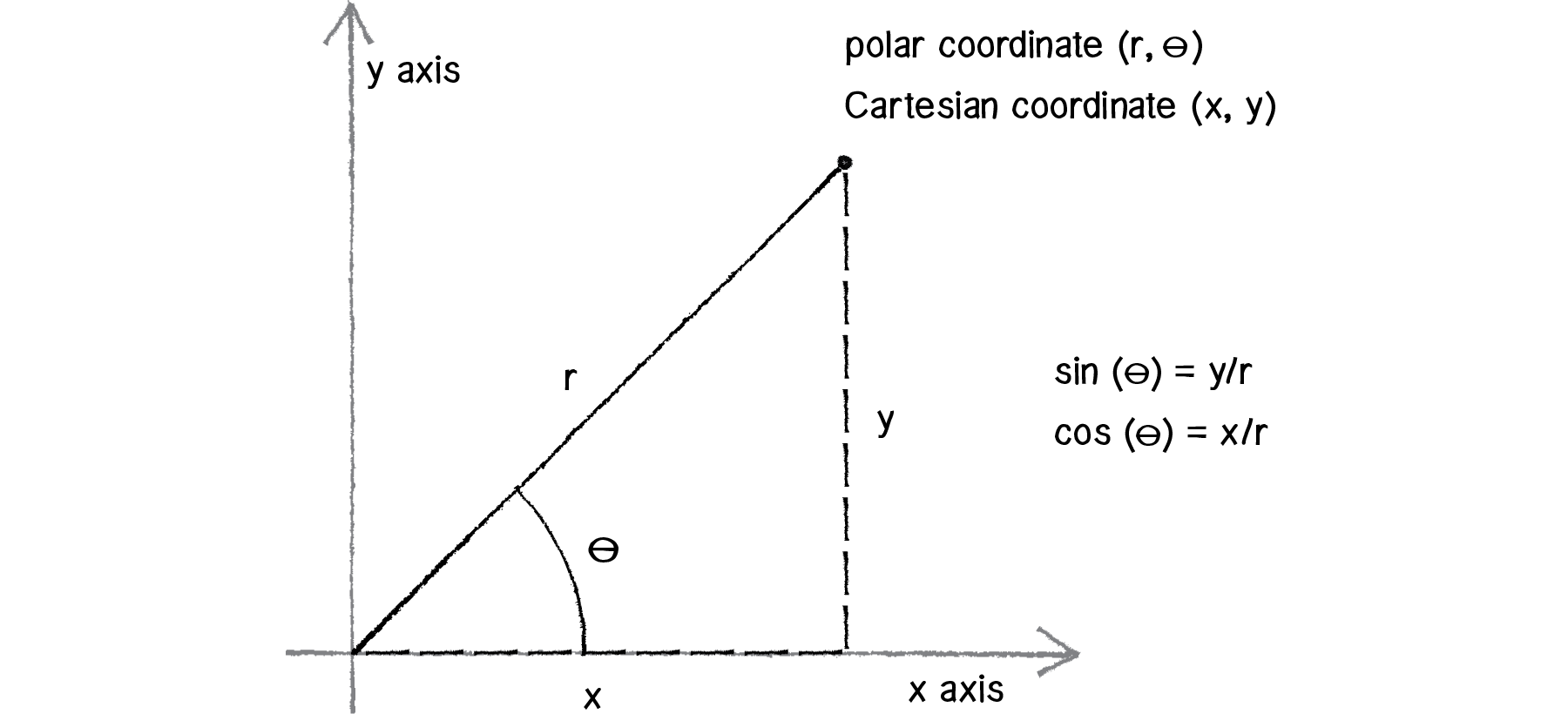
Sketch the vector field fru and express it in cartesian coordinates. The polar coordinates r the radial coordinate and theta the angular coordinate often called the polar angle are defined in terms of cartesian coordinates by x rcostheta 1 y rsintheta 2 where r is the radial distance from the origin and theta is the counterclockwise angle from the x axis. The vector urpoints along the position vector op so r rur. R r oe joe ostoe and the unit vectors are.
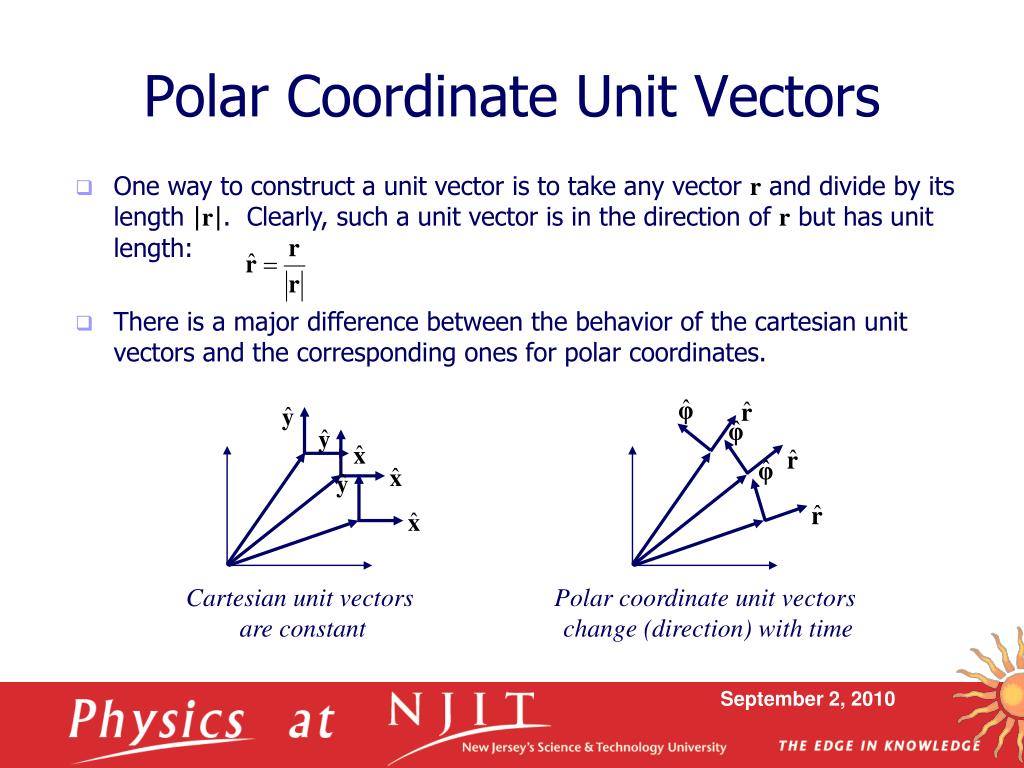
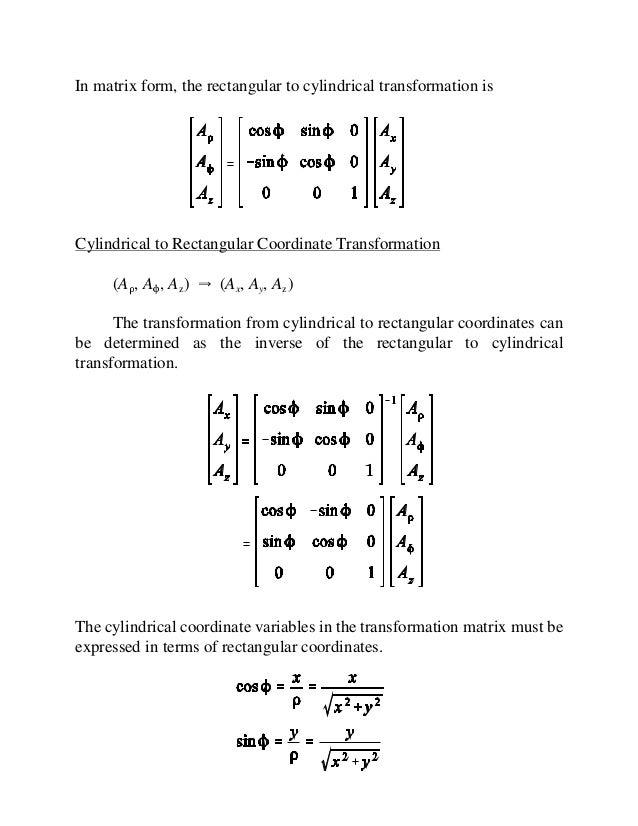
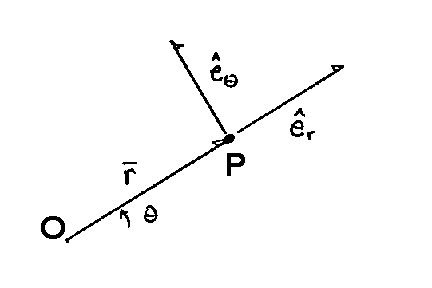
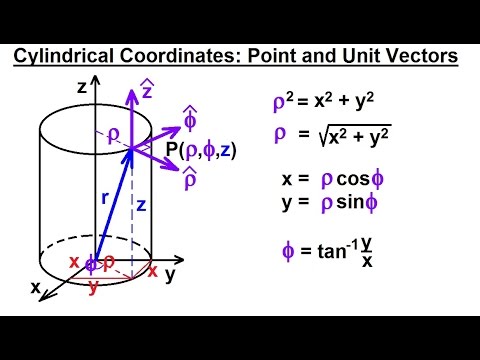
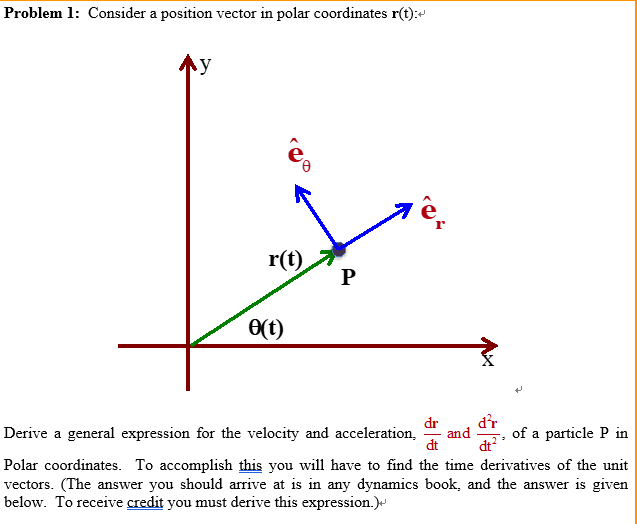
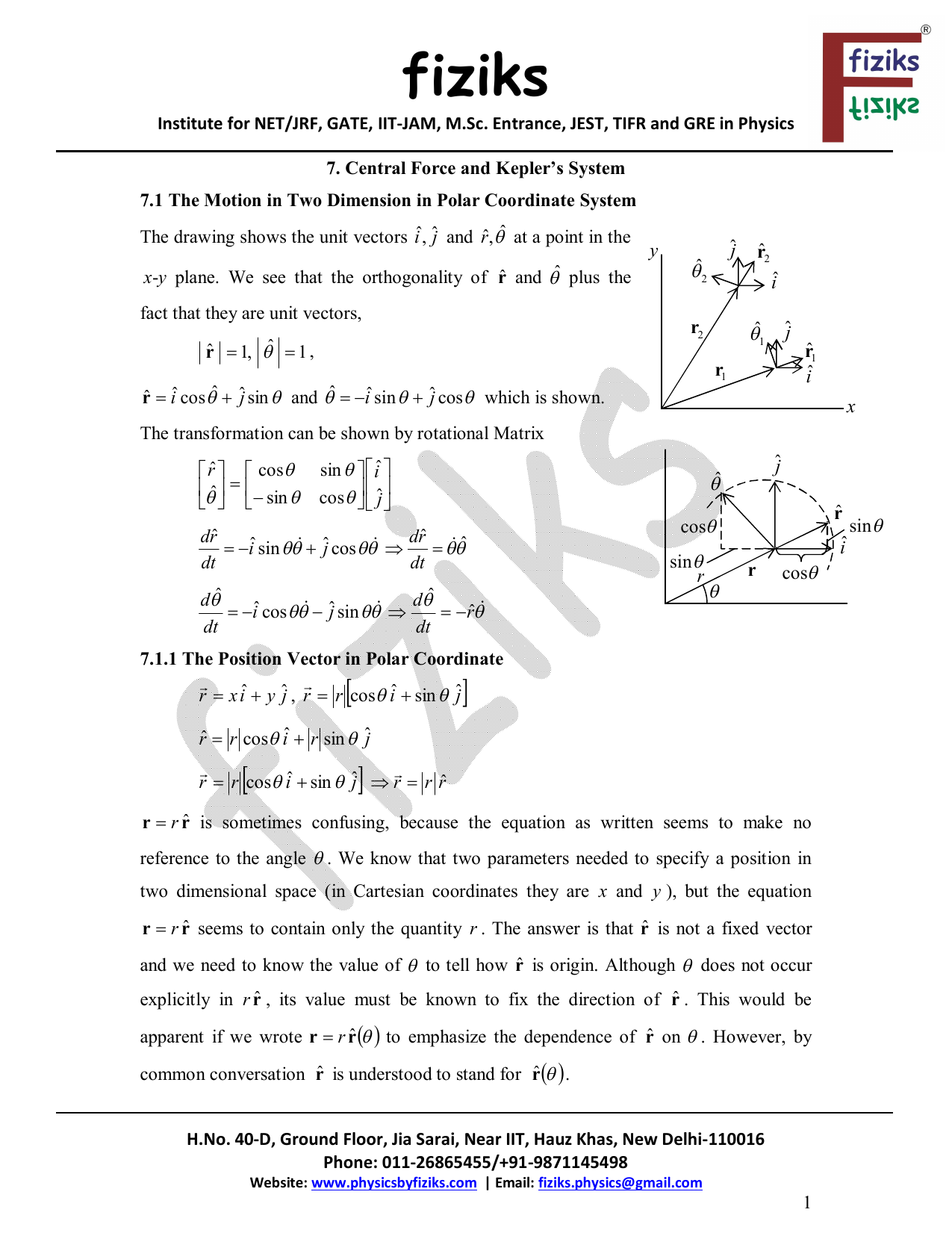
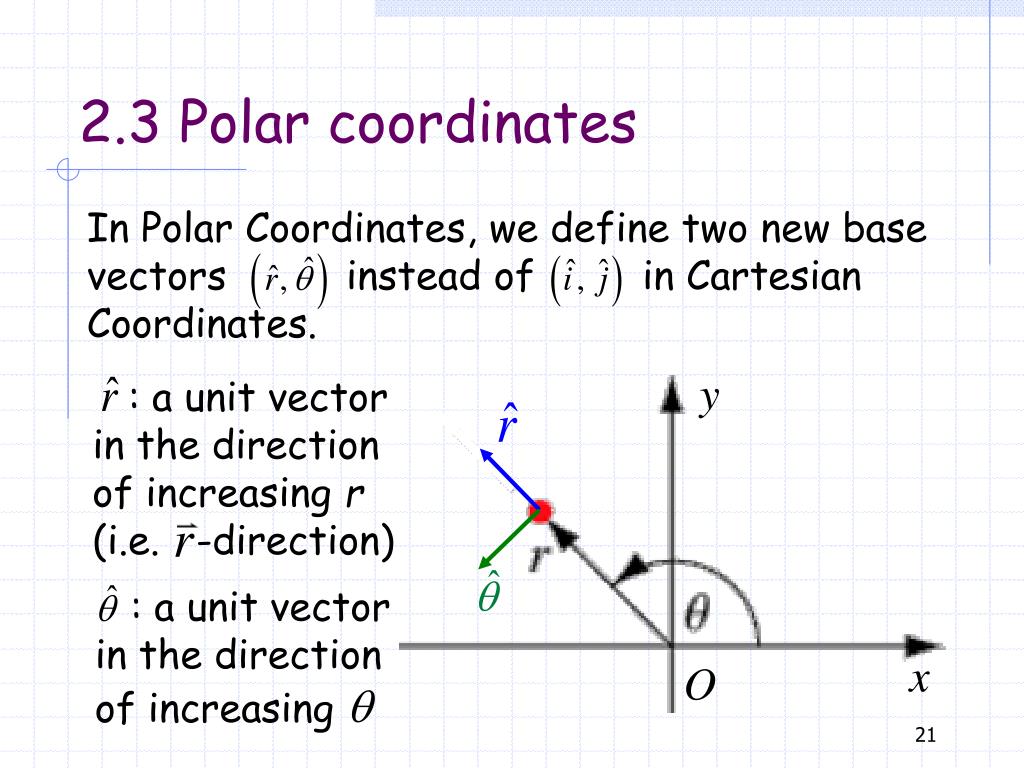
R ixy kz 1 similarly a vector in cylindrical polar coordinates is described in terms of the parameters r o and z since a vector r can be written as r rr zk. When a particle pro moves along a curve in the polar coordinate plane we express its position velocity and acceleration in terms of the moving unit vectors ur cosoi sinoj uo sinoi cosoj. Since the unit vectors are not constant and changes with time they should have finite time derivatives. In polar coordinates the location of an arbitrary point p on the plane is solely given in terms of one of the unit vector the vector hat r.
So r rero where the unit vector er is a function of the two angles. The position vector in polar coordinate is given by. In spherical coordinates the unit vectors depend on the position. For example x y and z are the parameters that dene a vector r in cartesian coordinates.
Although eis a constant vector not a function of the point rits decomposition does depend on the coordinates of the point.